For people with diabetes, lifestyle changes, such as increasing physical activity levels and improving diet, can help improve blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity.
However, recent research suggests that the timing of exercise or mealtimes also plays an important role in improving blood sugar results.
In particular, eating breakfast at the right time can be significantly beneficial in preventing post-breakfast hyperglycemia.
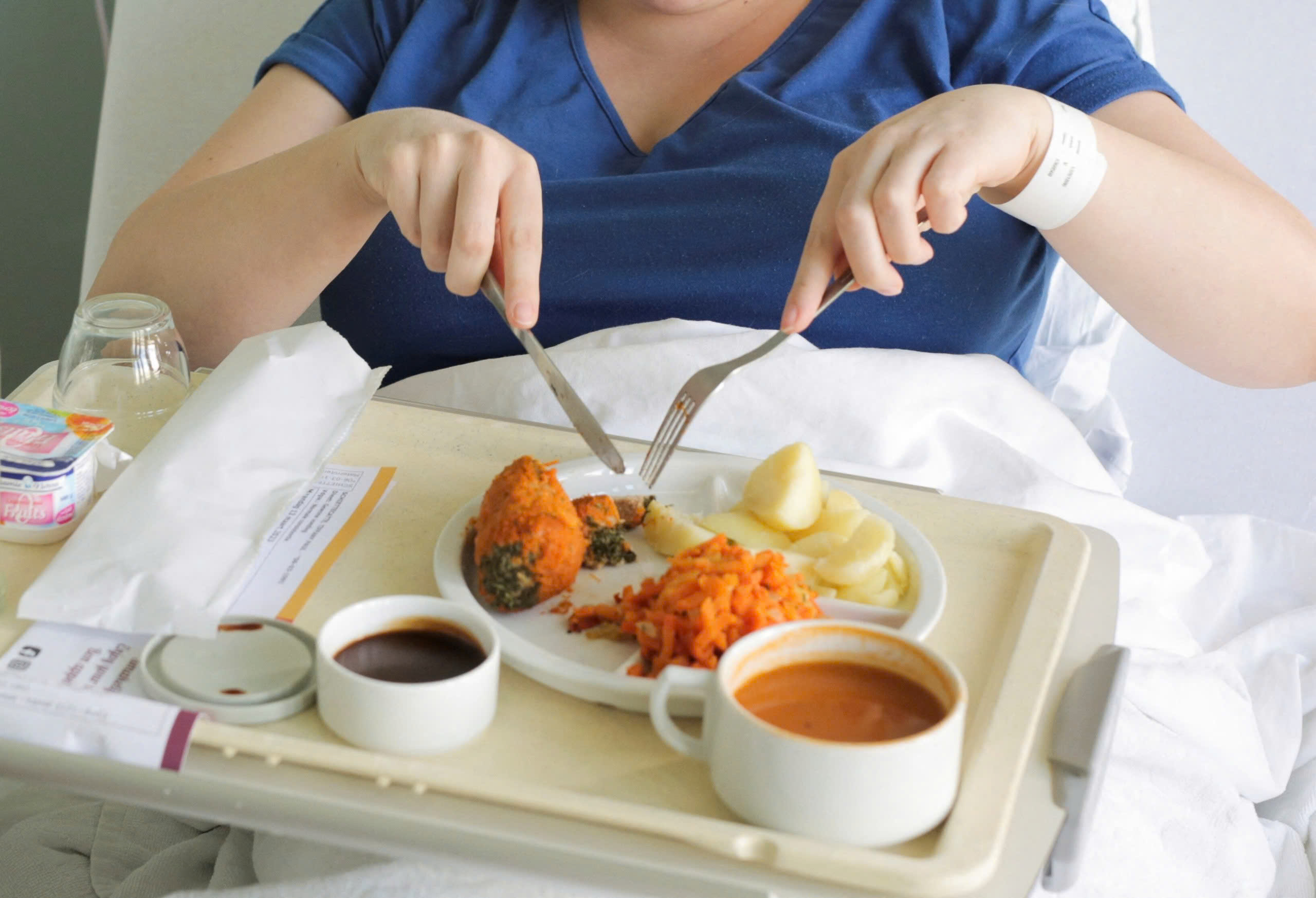

Eating breakfast late, at 9:30 a.m., can help diabetics significantly improve their blood sugar results compared to eating at 7 a.m.
Breakfast at 9:30 is beneficial for diabetics
In a study recently published in the journal Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, scientists have found the best time to eat breakfast to reduce blood sugar spikes in type 2 diabetes patients, according to the medical news site News Medical.
To investigate the combined effects of changing breakfast times and brisk walking for 20 minutes after breakfast on post-meal blood sugar, experts from the Nutrition and Exercise Research Program, Mary MacKillop Institute of Health Research, Australian Catholic University (Australia) conducted a 6-week trial on 14 diabetic patients, aged 30 - 70.
Participants were divided into three groups, eating breakfast at 7:00, 9:30, or 12:00.
They were also asked to walk briskly for 20, 30 and 60 minutes after breakfast and to record their daily food intake and sleep habits. They also wore monitors to track their blood sugar and activity.
Of the original 14 participants, 1 withdrew and 2 were disqualified for not following the rules.
Results showed that people who ate breakfast at 9:30 a.m. or at 12 p.m. had significantly lower blood sugar levels after eating compared to those who ate breakfast at 7 a.m., according to News Medical.
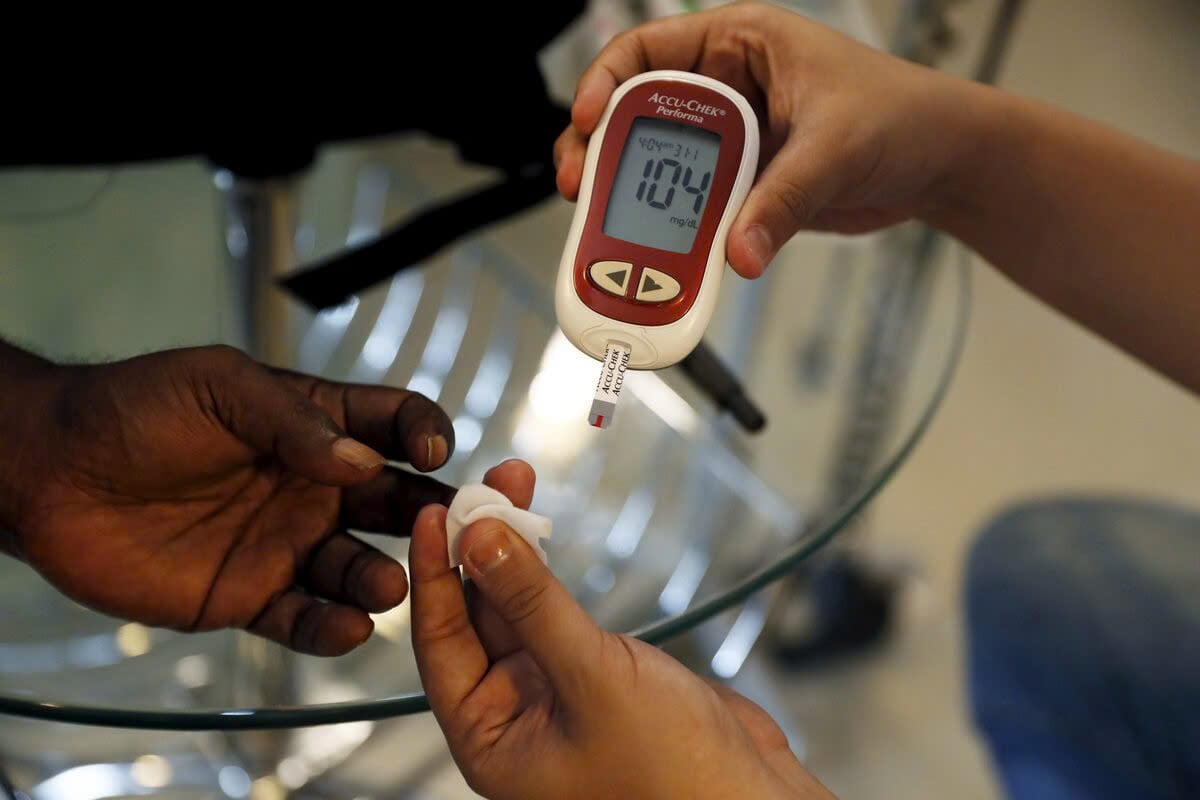
For people with diabetes, lifestyle changes, such as increasing physical activity levels and improving diet, can help improve blood sugar control.
And exercising 20 minutes after breakfast slightly improved these blood sugar levels.
The authors concluded: This is reliable evidence for the impact of breakfast timing on postprandial glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients. The results showed that breakfast at 9:30 or 12:00 can significantly improve glycemic outcomes compared with early breakfast at 7:00.
The authors say the findings suggest that changing the timing of breakfast may be a simple and practical way to help control blood sugar in people with diabetes.
The peak cortisol levels around 8 a.m. and the high blood glucose levels upon awakening contribute to the early morning glucose elevation in diabetic patients. Therefore, interventions to reduce the morning glucose elevation are important for overall daily glucose control in diabetic patients.
Researchers say: Applying the above breakfast time in the long term will help control blood sugar better, reduce the risks of poor blood sugar control, such as insulin resistance and increased cardiovascular and metabolic risk.
They also said that future studies with larger scales are needed to confirm these results to assess the long-term feasibility of adjusting breakfast timing and exercise for diabetic patients.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/phat-hien-moi-ve-thoi-diem-an-sang-tot-nhat-cho-nguoi-benh-tieu-duong-185241211220110186.htm


![[Photo] More than 17,000 candidates participate in the 2025 SPT Competency Assessment Test of Hanoi National University of Education](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/e538d9a1636c407cbb211b314e6303fd)


![[Photo] Readers line up to visit the photo exhibition and receive a special publication commemorating the 135th birthday of President Ho Chi Minh at Nhan Dan Newspaper](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/85b3197fc6bd43e6a9ee4db15101005b)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs meeting on science and technology development](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/ae80dd74c384439789b12013c738a045)
























![[Photo] Nearly 3,000 students moved by stories about soldiers](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/21da57c8241e42438b423eaa37215e0e)



































































Comment (0)