Salmonella causes more food poisoning than you think. The CDC estimates that Salmonella bacteria cause more than 1 million cases of food poisoning in the United States each year.
Who is susceptible to Salmonella infection?
Some people are at higher risk of serious Salmonella infections. These include children under 5 years of age, adults 65 years of age and older, and people with weakened immune systems due to certain medical conditions such as diabetes, liver disease, kidney disease, or cancer.
We can get Salmonella infection from many types of food.
Symptoms of Salmonella infection
Salmonella infection can be serious. Symptoms usually begin 6 hours to 6 days after infection.
Symptoms include diarrhea, fever, and stomach cramps. Most people recover within 4–7 days without antibiotics.
However, some people with severe diarrhea may need to be hospitalized or take antibiotics.
Go to the hospital immediately if you have symptoms such as: Diarrhea and fever higher than 39°C; diarrhea lasting more than 3 days without improvement; bloody stools; prolonged vomiting causing dehydration.
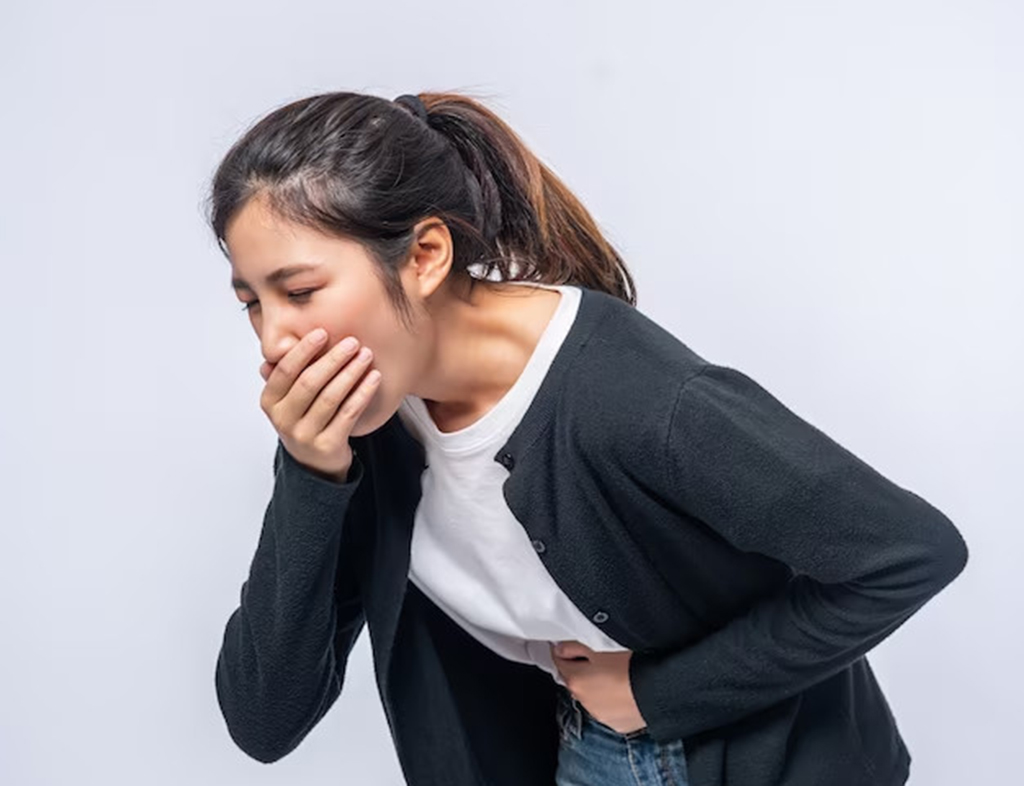

Vomiting is one of the symptoms of Salmonella infection.
Chicken is a major source of Salmonella infection.
Several recent Salmonella outbreaks have been linked to chicken.
The CDC estimates that Salmonella bacteria cause more cases of food poisoning than any other bacteria. Chicken is the main source of this poisoning.
Infection can occur from contaminated chicken if it is not cooked thoroughly. Infection can also occur if raw chicken juices leak into the refrigerator or onto kitchen counters and then contaminate raw foods such as raw vegetables and cold cuts.
Ways to help prevent Salmonella infection
Taking the following steps can help you and your family prevent Salmonella infection and food poisoning.
Wash hands with soap before and after handling food, especially after touching raw or undercooked eggs, meat, poultry, seafood, or their juices.
Thoroughly clean all equipment used in handling raw poultry, meat, or seafood with soap.
Keep raw meat, poultry, seafood, and eggs separate from other foods in shopping bags and in the refrigerator.
Never place cooked food on a plate that previously held raw or undercooked eggs, meat, poultry, seafood, or meat juices.
Cook food thoroughly.
Do not leave perishable foods such as meat, poultry, seafood, milk, cut fruits, rice and leftovers out of the refrigerator for more than 2 hours, according to the US CDC .
Source link



![[Photo] Closing ceremony of the 18th Congress of Hanoi Party Committee](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/17/1760704850107_ndo_br_1-jpg.webp)






























![[Photo] Nhan Dan Newspaper launches “Fatherland in the Heart: The Concert Film”](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/16/1760622132545_thiet-ke-chua-co-ten-36-png.webp)





































































Comment (0)