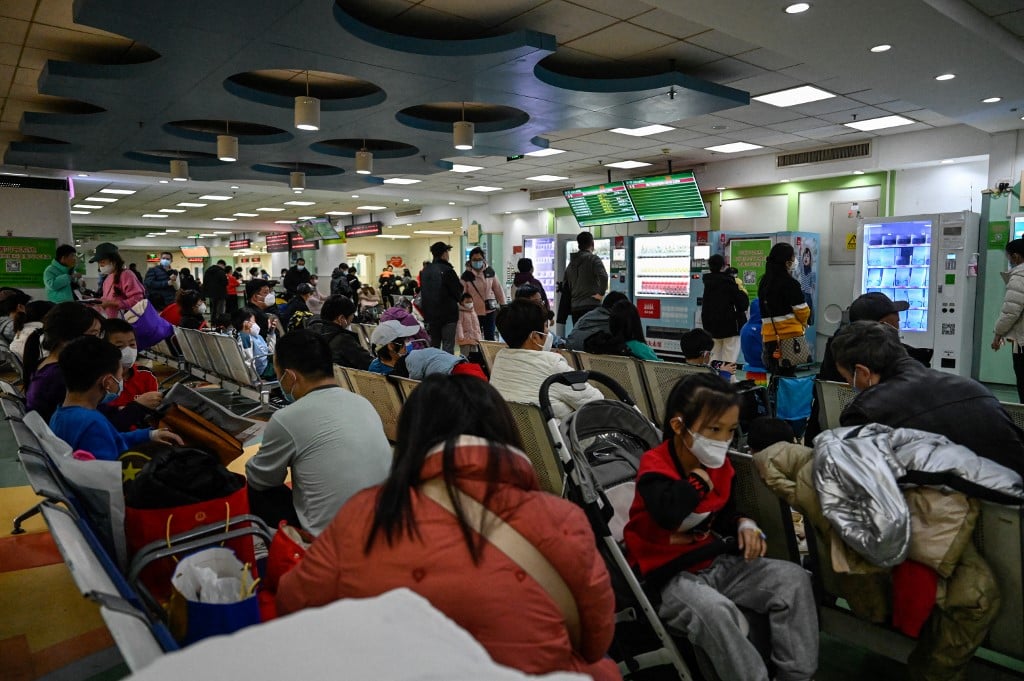

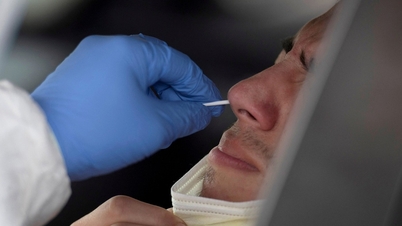
Children and parents wait to see a doctor at a children's hospital in Beijing on November 23.
AFP news agency reported on November 24 that the World Health Organization (WHO) said China confirmed that no new or unusual pathogens were detected among the rising respiratory cases among children in the northern region, after the WHO requested detailed information.
Since mid-October, WHO has been monitoring data from surveillance systems in China and has noticed an increase in respiratory illnesses among children in the northern part of the country. On November 22, WHO said it had formally requested more information from China.
WHO held a virtual meeting on 23 November with the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CCDC) and Beijing Children's Hospital, with the support of the National Health Commission and the National Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
According to the WHO statement, Chinese authorities said they have not detected any new, unusual pathogens or unusual clinical manifestations, including in Beijing and Liaoning, but only a general increase in respiratory diseases caused by many known pathogens.
“They added that the increase in respiratory illness has not resulted in the number of patients exceeding hospital capacity,” the statement said. WHO is closely monitoring the situation and is in close contact with the authorities in China, and will continue to provide updates.
WHO advises people in China to follow measures to reduce the risk of respiratory diseases, including getting vaccinated as recommended, keeping a distance from sick people, staying home when sick, getting tested and examined when necessary, and wearing masks appropriately.
The above measures are intended to reduce the risk of respiratory illness, while WHO currently does not have specific recommendations for people travelling to China.
Source link




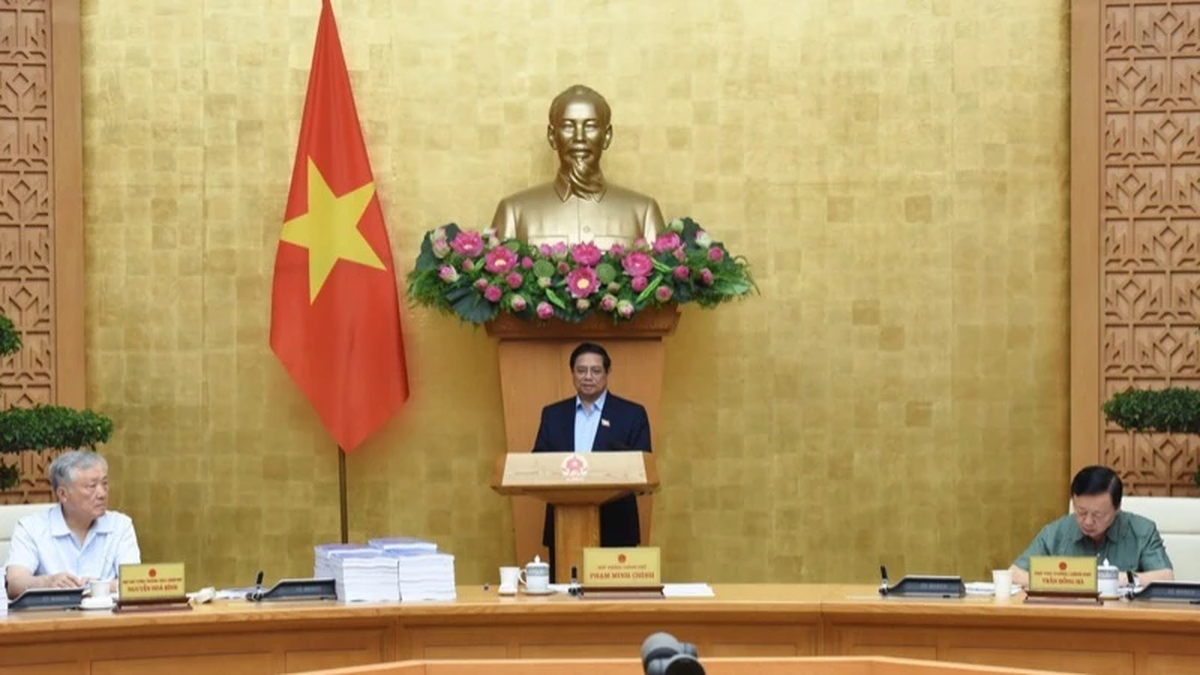
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs a special Government meeting on the arrangement of administrative units at all levels.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/9/6a22e6a997424870abfb39817bb9bb6c)
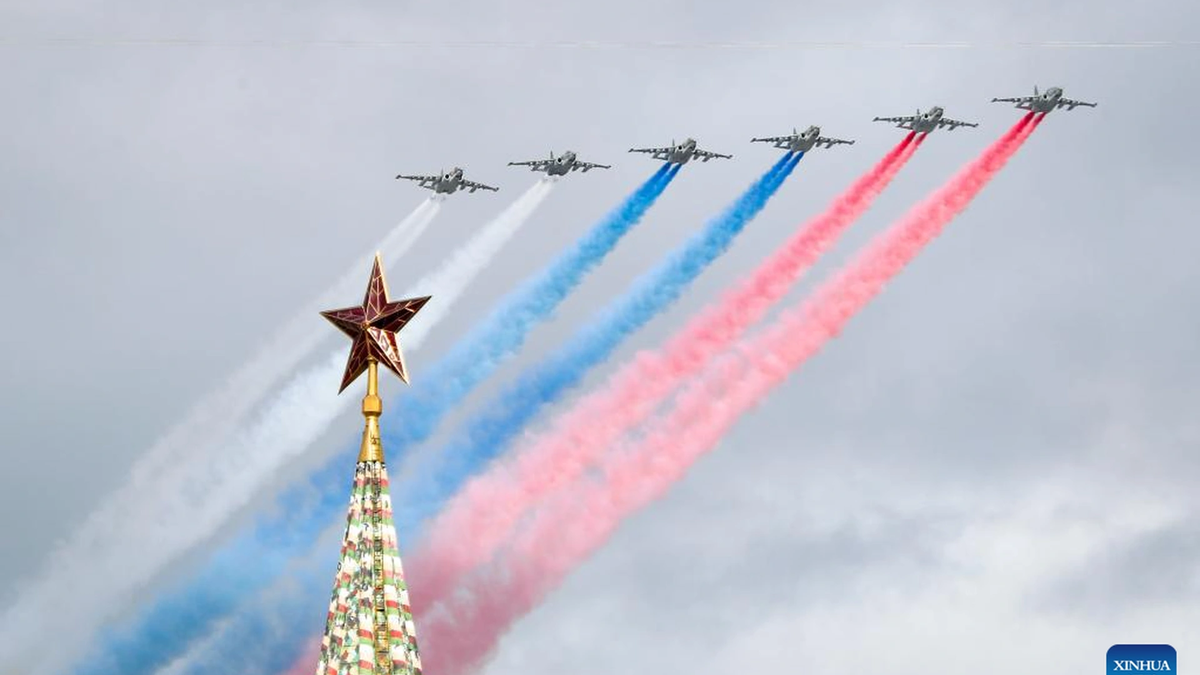
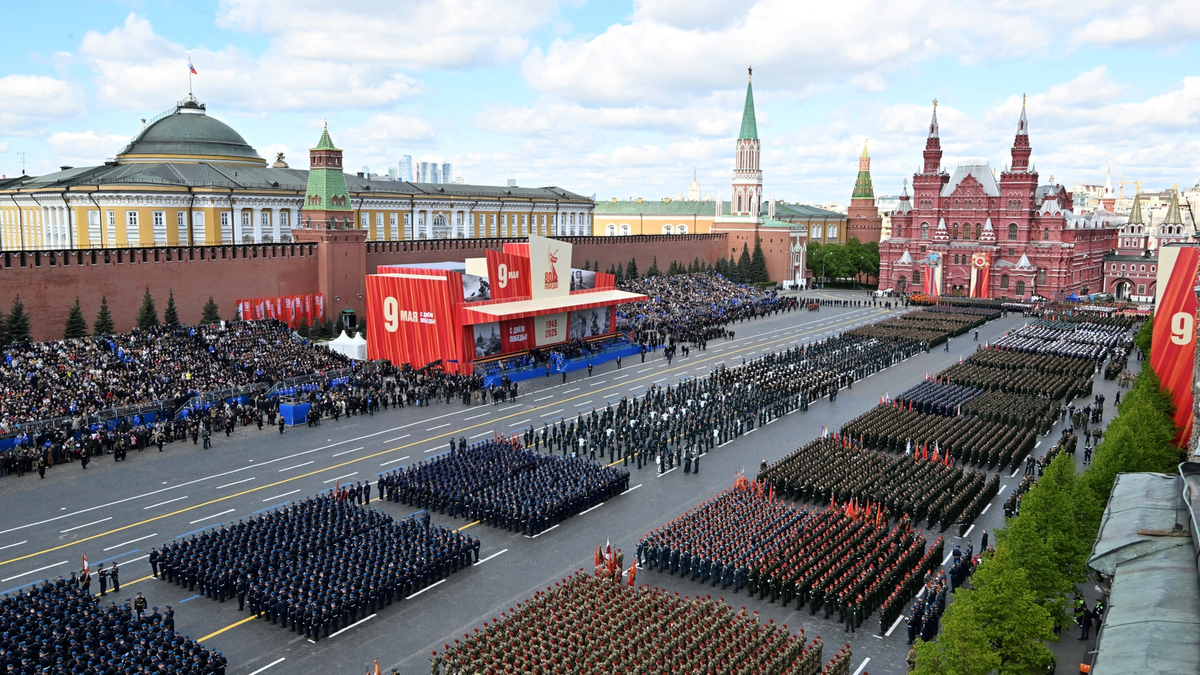
![[Photo] Russian military power on display at parade celebrating 80 years of victory over fascism](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/9/ce054c3a71b74b1da3be310973aebcfd)
![[Photo] Magical moment of double five-colored clouds on Ba Den mountain on the day of the Buddha's relic procession](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/9/7a710556965c413397f9e38ac9708d2f)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam and international leaders attend the parade celebrating the 80th anniversary of the victory over fascism in Russia](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/9/4ec77ed7629a45c79d6e8aa952f20dd3)





















































































Comment (0)