According to experts, excessive screen time, limited social interaction, and learning multiple languages are risk factors that can cause delayed language development in children.

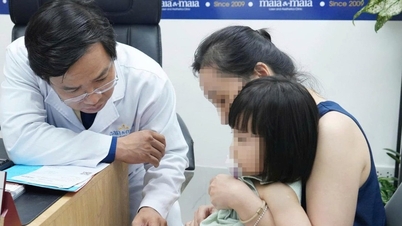
Dr. Vu Son Tung, from the Institute of Mental Health, shared information about language developmental delays in children - Photo: D. LIEU
The number of children with speech delays is increasing, and examinations are being delayed.
According to Dr. Vu Son Tung, head of the Department of Child and Adolescent Mental Health at the Institute of Mental Health, Bach Mai Hospital, in recent years, especially after COVID-19 (2020), the rate of children with speech delays seeking treatment at the hospital has increased due to various reasons.
Notably, most of these children arrive later than the golden period (from 0-3 years old).
Dr. Do Thuy Dung, from the Institute of Mental Health at Bach Mai Hospital, shared that she recently treated a 4-year-old child diagnosed with a language disorder.
According to my mother, because my father worked far away and my mother was a factory worker who went to work in the morning and came home in the evening, the children mainly lived with their grandparents.
Every day, the child is regularly shown TV and a phone by his grandparents from an early age. They let him watch TV while playing, eating, or even when he cries.
By the age of two, children can only say a few single words and not yet compound words. Now, even at four years old, they sometimes go without speaking for long periods, have a limited vocabulary, don't proactively speak when playing with neighborhood friends, rarely tell stories, and seldom show or tell their mother about their problems.
Causes of delayed speech in children
According to Dr. Vu Son Tung, a child is typically considered to have delayed speech when, by the age of two, they still cannot say about 50 single words or compound words (two-word sentences).
According to statistics, children aged 2-7 years old have speech delays, accounting for 2.3-19%. Additionally, approximately 2.1-11.4% of preschool children worldwide have speech delays, with nearly 15% of children aged 18-35 months experiencing this. Boys are 3-4 times more likely to have speech delays than girls.
Of these, 25-30% of children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) experience language developmental delays.
According to Dr. Tung, there are many causes of delayed speech in children, such as anatomical and sensory abnormalities: vocal organs (cleft lip and palate, tongue), brain regions controlling speech, oral motor skills, and hearing impairment.
Perinatal risk factors include hearing loss, prematurity, hypoxia, neonatal jaundice, and central nervous system damage.
In addition, a risk factor that makes children more prone to language development delays is a family history of speech delays. Children whose parents or siblings have language problems are 2-3 times more likely to have speech delays than children from families without such problems.
Spending more than two hours watching TV or using mobile phones in children aged 1-3 years increases the risk of speech delay. The impact of exposure to multiple languages on speech delay is 22%, while exposure to a single language is 8%.
Early intervention for children
According to Dr. Tung, early intervention, especially in children aged 0-3 years, can help improve and accelerate the achievement of language and communication skill milestones, while also reducing problems related to emotions, cognition, and social skills.
Intervention methods may include speech therapy, educational support programs, and activities that encourage children to communicate. This therapy may be provided by speech and language therapists, and other clinicians.
Children may begin showing signs of language developmental delays as early as 18 months of age, but with early intervention, their speaking and communication abilities can improve by up to 50% within the first year of intervention.
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/tre-cham-noi-nguy-co-do-xem-nhieu-dien-thoai-hoc-nhieu-thu-tieng-20250217145615513.htm







































































































Comment (0)