Salmon, mackerel, almonds, walnuts... are foods that contain fats necessary for the brain to maintain function and function well.
About 60% of the brain is made up of fat, and more than half of that fat is omega-3 fatty acids. The brain uses omega-3 fatty acids to build brain cells and nerve cells that are good for learning and memory.
According to Dr. Tran Thi Tra Phuong (Nutrihome Nutrition Clinic System), good fats include: oleic acid, omega-3, DHA, EPA, DPA. These are essential fatty acids that the body cannot synthesize itself and must come from daily foods. These fatty acids create conditions for the development and maintenance of brain cells, help prevent neurodegeneration, enhance memory, improve concentration, and think faster.
Doctor Tra Phuong suggests foods containing good fats for the brain as follows:
Fatty fish: According to the recommendations of the American Institute of Health and the American Heart Association, eating fatty fish such as mackerel and salmon 3-4 times a week provides essential fatty acids such as omega-3 and DHA.
About 100g of salmon provides about 200 kcal of energy, low in saturated fat, is a source of protein with high biological value, many essential amino acids for the body. This is also one of the abundant sources of vitamin B12, potassium, iron and vitamin D.
Salmon contains a lot of omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential fatty acids for the body, have anti-inflammatory effects, help reduce the causes of cardiovascular diseases, cancer, Alzheimer's disease, and reduce rheumatoid arthritis. Vitamin B12 in salmon can keep blood and nerve cells working well, helping to create DNA.
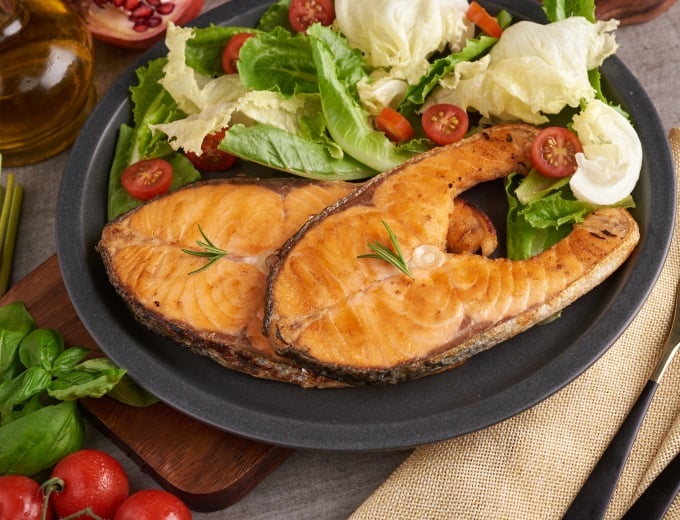

Salmon contains a lot of omega-3 fats that are good for the brain. Photo: Freepik
Mackerel is also a fatty fish with a rich flavor. About a 100g portion of mackerel provides about 190 kcal of energy and 12g of fat, 20g of protein. The fat content in 100g of mackerel is about 3g of saturated fat, 4.5g of monounsaturated fat and 2.9-3g of polyunsaturated fat. These are good fats for the body. According to US national data, a 100g serving of mackerel provides 0.77g of EPA and 1.25g of DHA, which are very good for health.
Tuna is often compared to mackerel, wild caught ocean tuna. The nutritional value of about 100g of tuna includes about 130 kcal, 0.6g of fat, rich in potassium. The fat in tuna is mainly good fat for the body, mainly omega-3 acids (DHA and EPA), which are fatty acids that have been proven to be good for health, especially heart and brain health.
Nuts: Walnuts are rich in DHA, omega-3 fatty acids (about 2.5 g of omega-3 in each walnut), polyphenols and vitamin E. Studies show that a diet containing walnuts significantly improves learning skills and enhances memory, while reducing anxiety and stress in studying and working.
Almonds contain very high levels of vitamin E and are linked to protecting against nerve cell degeneration, helping to fight memory loss, cognitive decline and language impairment in the elderly (Alzheimer's disease).
Peanuts are also high in niacin (vitamin B3 or vitamin PP), which is one of the main components that helps the development and survival of nerve cells. Studies have also demonstrated the important role of niacin in improving neurological diseases.
Hai An
Source link

































































































Comment (0)