Memory is the ability to retain information from the external environment that affects the body through the senses, recorded and stored by the body. The main place to store information is in the brain structures, this information will be reproduced, exploited and used by the body when necessary.
The essence of memory is the establishment of temporary neural connections in the brain. The physiological basis of memory is the process of forming, storing, consolidating and restoring temporary neural connections.
There are many types of memory. People can classify memory based on the formation of memory (according to this classification, memory includes: iconic memory, motor memory, emotional memory, linguistic-logical memory), or classify memory based on the duration of memory (according to this classification, memory includes short-term memory, long-term memory).
Factors affecting memory
Many factors affect memory, including external factors, the environment and those inside the body. On the other hand, the amount of information, content and form of information received are also important factors that help form memories easily and last long.
A proper diet and active healthy lifestyle will bring the best physical and mental condition.

Good nutritional and lifestyle habits help improve memory.
In our daily lives, we can forget things like keys, glasses, pens, and where we put our phones. This phenomenon can be limited if these things are always kept in order, neat, and have a designated place. People can also practice to have a good memory by planning their work, arranging and placing things neatly and tidily.
To have a good memory, we need to promote both internal and external factors, both in training to maintain a neat and tidy lifestyle, and in arranging work scientifically and with a plan.
Good nutrition for the brain
A reasonable diet will provide our body with enough energy, micronutrients, and highly active substances that play a very important role in memory, such as: omega-3; omega-6; phospholipids; and amino acids.
Essential fats (omega-3 and omega-6): These are essential fats, which are the building blocks of nerve cells. The brain also needs saturated fats and cholesterol, but because the body can synthesize them, there is no shortage. Omega-3 and omega-6 are easily deficient, so they must be taken in from the outside through the diet. These essential fats are found in fish and oily seeds.
Phospholipids: These are your memory's best friend. They coat your nerves and promote smooth transmission of signals in your brain. Although your body can make phospholipids on its own, they're still good to have in your diet. Phospholipids are abundant in egg yolks and organ meats.
Amino acids: These are the building blocks of neurotransmitters (substances that carry signals from one nerve cell to another) and are therefore essential. These amino acids are found in protein-rich foods such as meat, fish, eggs, milk, soy and other beans.
In addition, many micronutrients also directly or indirectly contribute to enhancing and maintaining memory, for example, iron is an important micronutrient involved in the process of blood formation. We will not be able to absorb information well if our body is always tired and sleepy due to nutritional anemia.
Understanding the factors related to the formation and maintenance of memory, we will have positive changes, especially in nutritional habits and lifestyle, so as to always maintain the best health and clear mind. That is the basic condition to help you have a good memory.
Source


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs a special Government meeting on the arrangement of administrative units at all levels.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/9/6a22e6a997424870abfb39817bb9bb6c)
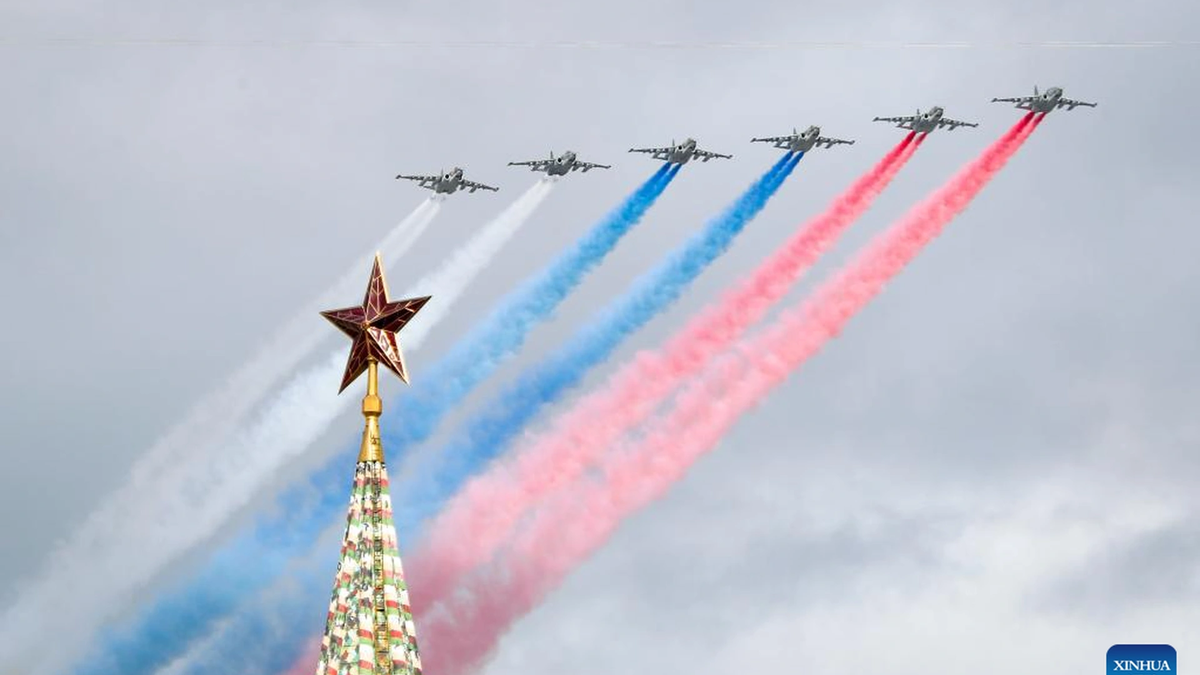

![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam and international leaders attend the parade celebrating the 80th anniversary of the victory over fascism in Russia](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/9/4ec77ed7629a45c79d6e8aa952f20dd3)
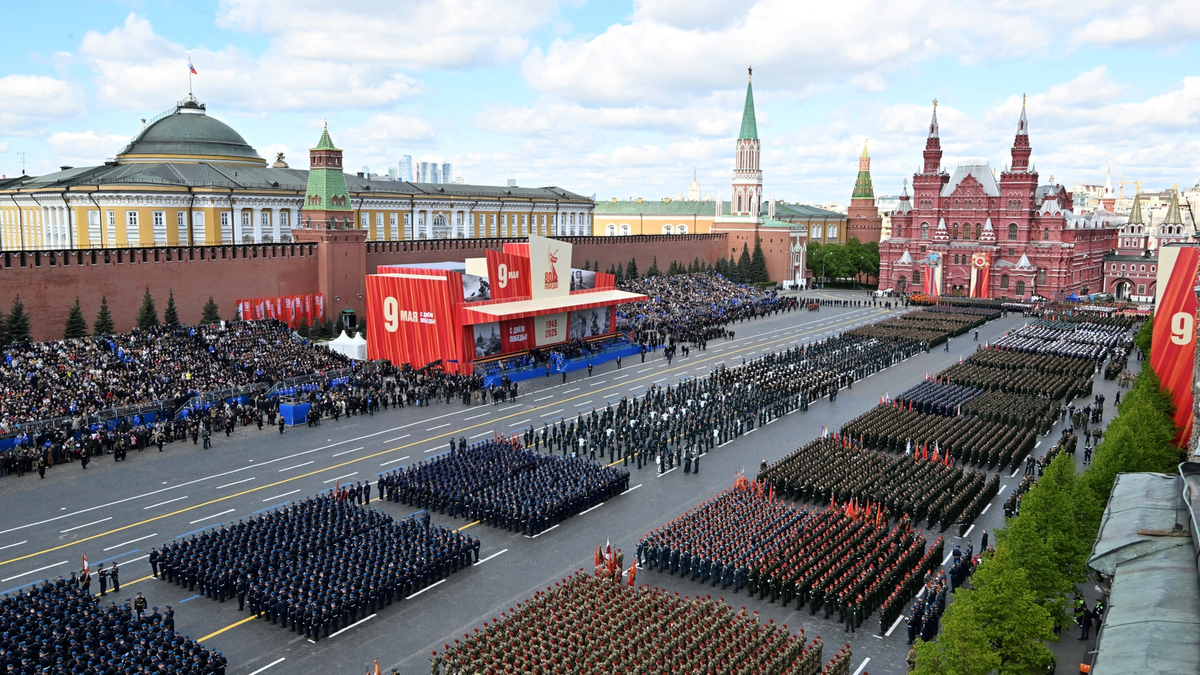
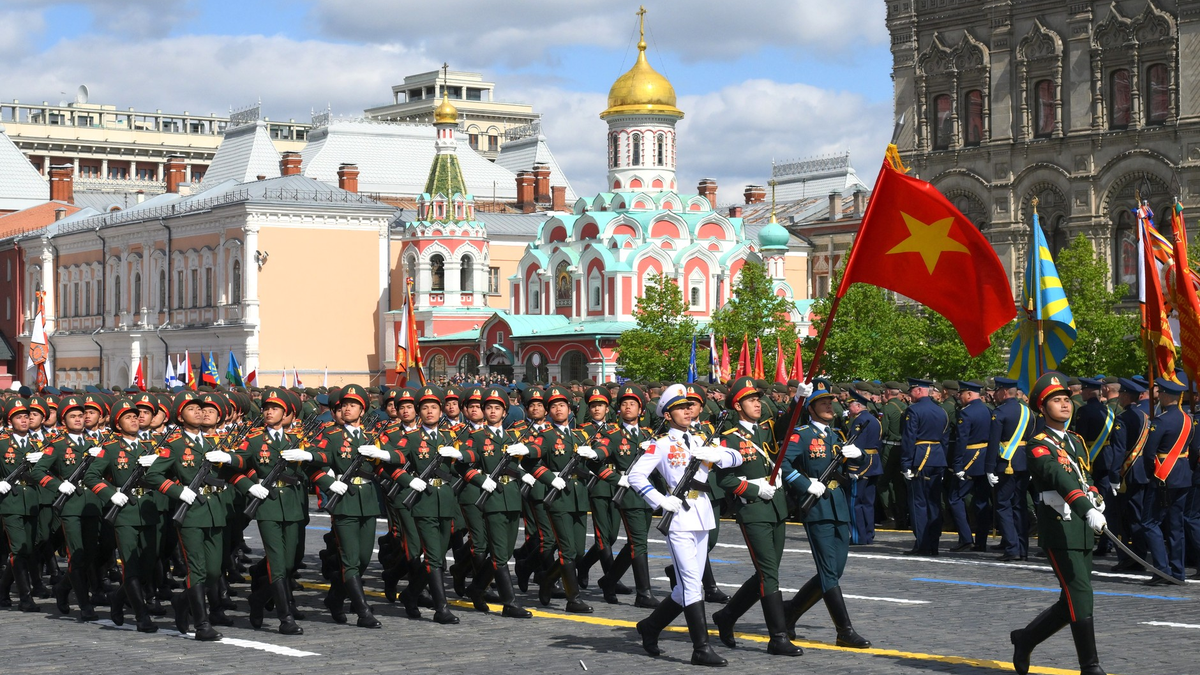


![[Photo] Russian military power on display at parade celebrating 80 years of victory over fascism](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/9/ce054c3a71b74b1da3be310973aebcfd)
























![[Photo] Magical moment of double five-colored clouds on Ba Den mountain on the day of the Buddha's relic procession](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/9/7a710556965c413397f9e38ac9708d2f)



























































Comment (0)