On January 9th, information from Da Nang Hospital indicated that the hospital had just performed endoscopic surgery to remove a portion of the lower lobe of the left lung for a patient with a large and rare case of lung-within-a-lung anomaly.
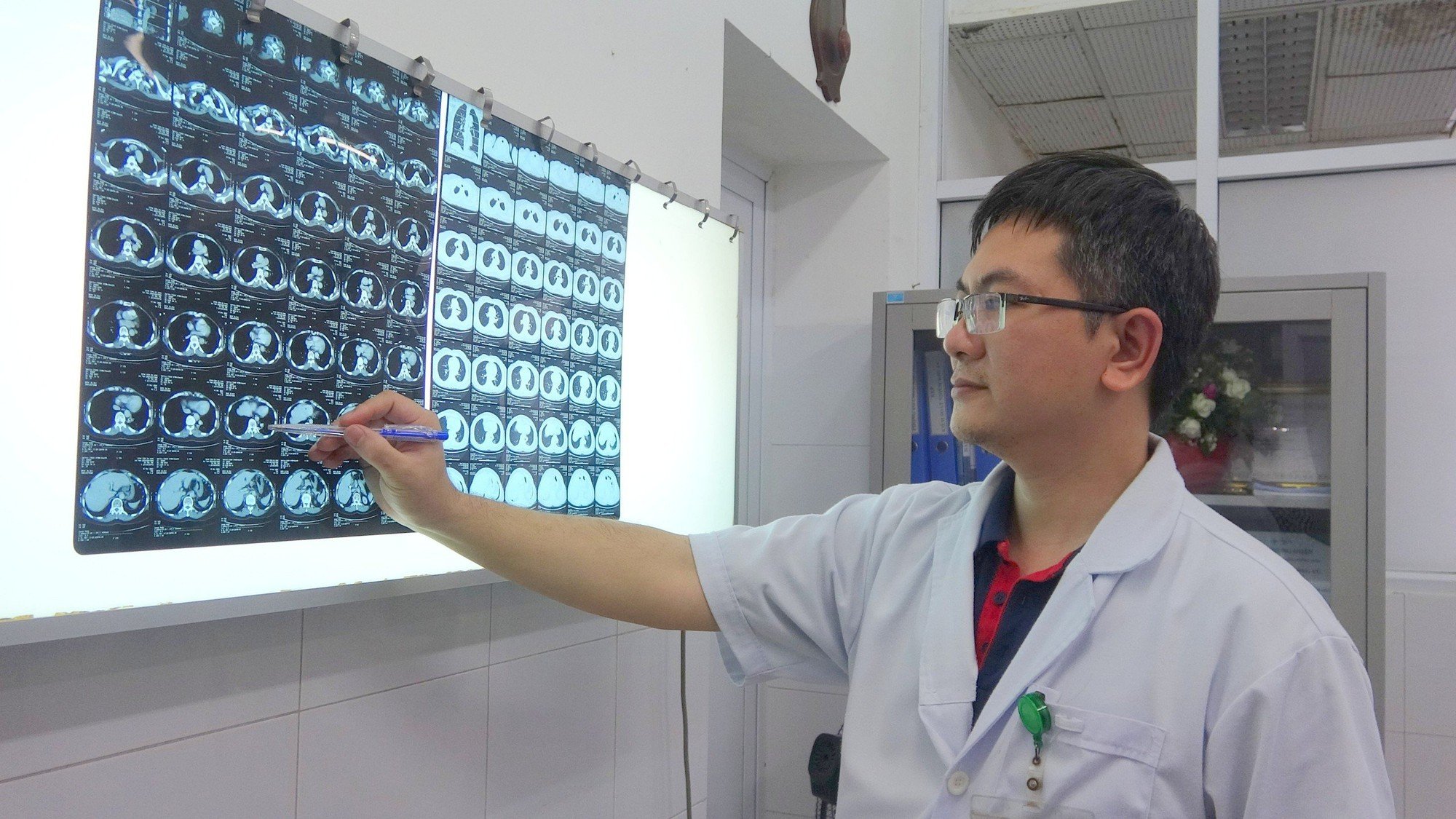
Previously, patient VTT (58 years old, residing in Hoa Vang District, Da Nang City) went for a check-up and incidentally discovered a lesion in the lower lobe of the left lung. Through examination and chest CT scan, doctors discovered that this lesion was located in the lower lobe of the left lung, nourished by a branch of the artery originating from the thoracic aorta.
The diameter of this feeding artery branch is half the diameter of the thoracic aorta. The patient was diagnosed with pulmonary ischemia in the lower lobe of the left lung and was scheduled for thoracoscopic resection of the isolated lung segment.
Doctors from the Thoracic Surgery Department of Da Nang Hospital performed the surgery, which lasted three hours. Five days after the operation, the patient was stable and discharged from the hospital.
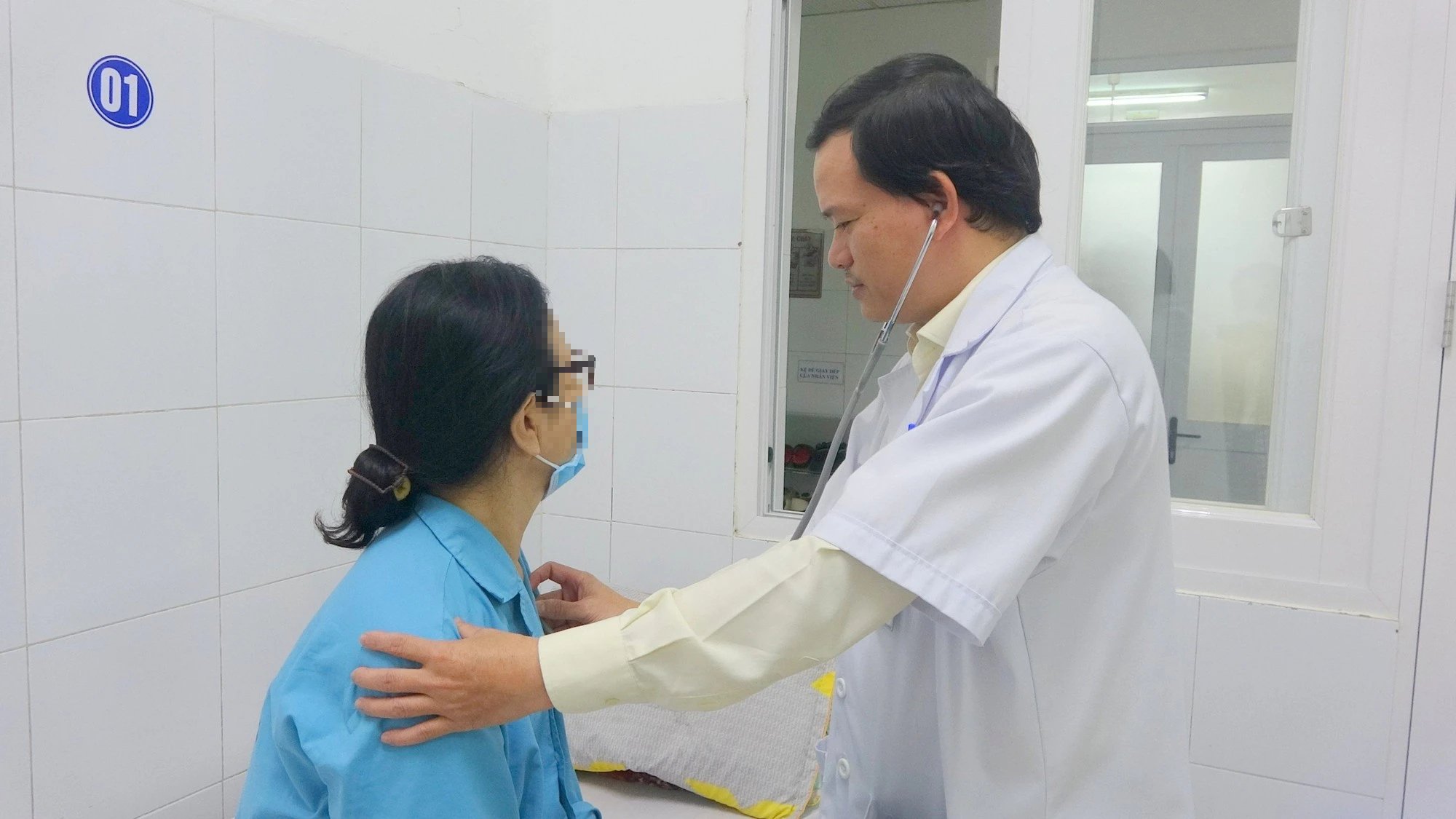

The patient with VTT was discharged from the hospital 5 days after surgery.
Dr. Than Trong Vu, Head of the Thoracic Surgery Department at Da Nang Hospital, said this was a rare case, a difficult and complex surgery because the artery supplying the lung in this patient was large in diameter, originating from the thoracic aorta, and showed signs of calcification, making it prone to rupture and bleeding. Therefore, the doctors had to carefully remove only the damaged part of the lung without removing the entire lung lobe.
According to Dr. Vu, isolated lung is a congenital abnormality of the lung. It is a rare disease; the incidence of congenital airway-lung malformations is approximately 1 in 8,300 to 1 in 35,000 live births (meaning that for every 8,300 to 35,000 live births, one child will have a congenital airway malformation). Among congenital airway-lung malformations, isolated lung accounts for 0.15 to 6.4%.
At Da Nang Hospital, only one case of isolated lung has been encountered in the past 10 years. Diagnosis of isolated lung is usually made in young children. In adults, the detection of asymptomatic isolated lung is very rare, often discovered incidentally during screening for other conditions.
The doctors assessed the patient's condition.
According to Dr. Vu, the treatment for isolated lung disease primarily involves surgery to remove the non-functional portion of the lung early. If the disease progresses with symptoms such as pneumonia or lung abscess, treatment becomes more difficult, and it may even be necessary to remove the entire lung lobe containing the isolated lung, affecting the patient's respiratory function later on.
"Therefore, patients who frequently experience chest pain or recurrent pneumonia, and whose X-rays show lesions in the lower chest, should be suspected of having isolated lung lesions. From there, more in-depth tests such as chest CT scans with intravenous contrast should be performed to detect and treat isolated lung lesions, avoiding complications that may require lobectomy," Dr. Vu advised.
Source link


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives the Governor of Tochigi Province (Japan)](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F16%2F1765892133176_dsc-8082-6425-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives Lao Minister of Education and Sports Thongsalith Mangnormek](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F16%2F1765876834721_dsc-7519-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)
![[Image] Leaked images ahead of the 2025 Community Action Awards gala.](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F16%2F1765882828720_ndo_br_thiet-ke-chua-co-ten-45-png.webp&w=3840&q=75)


![[Live] 2025 Community Action Awards Gala](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F16%2F1765899631650_ndo_tr_z7334013144784-9f9fe10a6d63584c85aff40f2957c250-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)





























































![[Video] Independence and self-reliance linked with international integration through 40 years of reform](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/16/1765899635777_1-1-8054-png.webp)


































Comment (0)