A team of experts has discovered a mysterious interstellar tunnel that connects the solar system with distant stars in the universe, according to a report published in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.
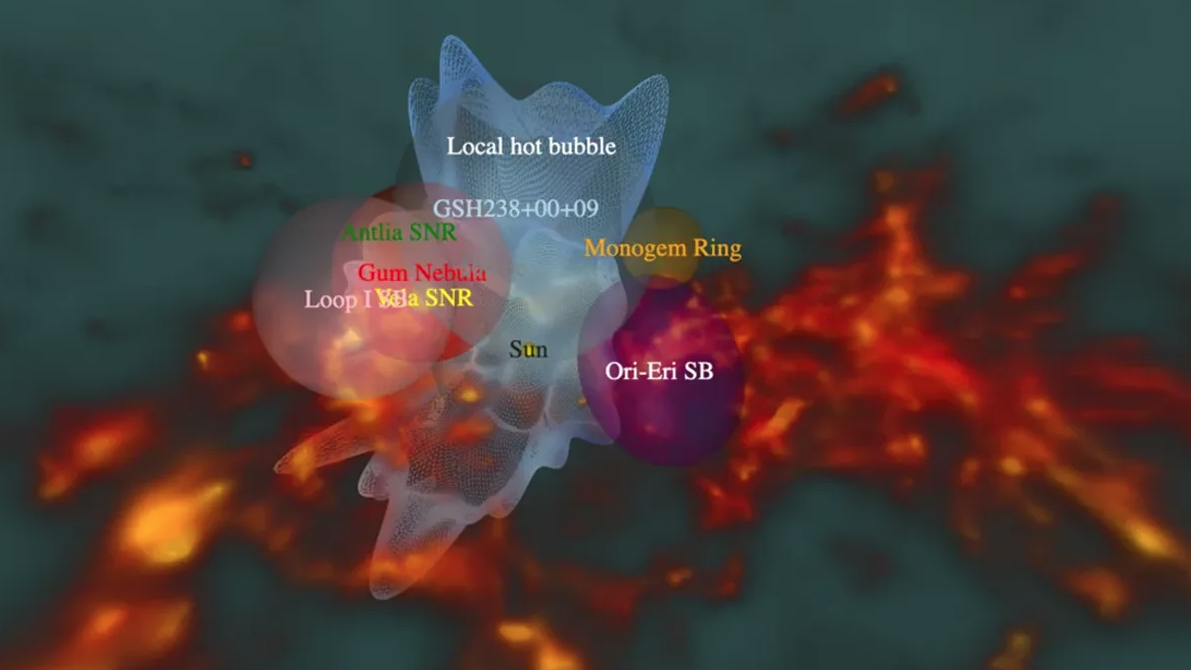
Simulation image of LHB and tunnel connecting to the outside
Photo: Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics
In a new discovery that could reshape humanity's understanding of interstellar space, a team of astronomers has found plasma "tunnels" that connect the local interstellar cloud to other star systems.
The newly discovered tunnel belongs to a giant structure of hot gas with a radius spanning hundreds of light-years and surrounding the solar system called the "Local Hot Bubble" (LHB).
Not stopping there, this tunnel can connect to a nearby and even larger bubble.
Data from the eROSITA telescope
The discovery was made thanks to a huge amount of data from the eROSITA telescope, the first X-ray observatory located outside the Earth's atmosphere.
The researchers successfully built a 3D model of the entire LHB, which not only confirmed some of the predicted features but also revealed some completely new ones.
"What we didn't know was the existence of an interstellar tunnel leading to the constellation Centaurus," said report co-author Michael Freyberg, an astronomer at the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics (Germany). The constellation Centaurus is about 11 million light-years away from Earth.
The existence of LHBs was first suggested 50 years ago. Astronomers believe the bubble may have formed around 14 million years ago, when a series of supernovae exploded and blew away all the interstellar matter. The result was a vast void 1,000 light-years across that encircled our Solar System.
With the help of modern telescopes, the team of German experts confirmed that the LHB is real, and the tunnel is probably part of an interstellar medium network that spans the Milky Way.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/phat-hien-duong-ham-bi-an-ket-noi-he-mat-troi-voi-cac-the-gioi-khac-185241218204700481.htm





![[Photo] "Ship graveyard" on Xuan Dai Bay](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/08/1762577162805_ndo_br_tb5-jpg.webp)
































![[Video] Hue Monuments reopen to welcome visitors](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/05/1762301089171_dung01-05-43-09still013-jpg.webp)






































































Comment (0)