ANTD.VN - After being extended for 6 months, Circular 02 of the State Bank on debt repayment restructuring and maintaining debt groups will expire on December 31, 2024. Accordingly, banks will have to record credit costs for restructured debts.
However, according to some comments, the impact on banks' asset quality when Circular 02 expires will be controllable in 2025.
According to experts from Vietnam Investment Credit Rating Joint Stock Company (VIS Rating), the problem debt situation is forecast to be not serious, thanks to the fact that the rate of bad debt formation has slowed down as customers' cash flow improves throughout 2024.
“We expect borrowers’ ability to repay their debts to continue to improve amid strong growth in Vietnam’s business and macroeconomic conditions thanks to the Government’s continuous efforts to boost economic activity,” the analysts said.
According to VIS Rating's report, the banking sector's total problem debt (including on-balance sheet bad debt, restructured debt and VAMC bonds) remained stable at 6.9% of the total outstanding credit of the entire system as of June 2024. Compared to the 2022-2023 period, this ratio has stabilized after a sharp increase of 2.7 percentage points in the previous period.
Along with that, the total restructured principal debt of the whole industry decreased to 0.9% of the total credit of the whole industry, from 1.2% at the end of 2023.
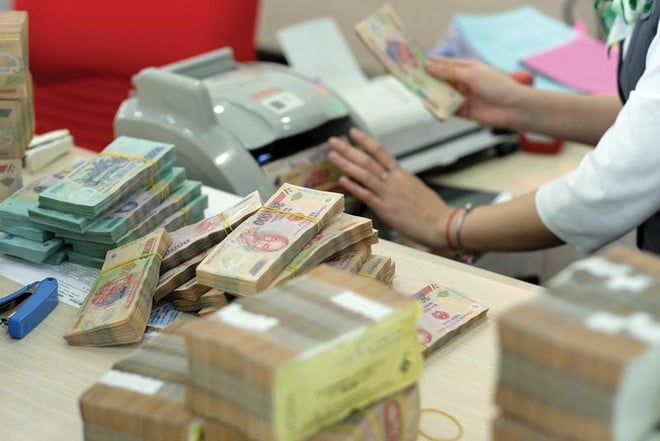 |
Bad bank debt tends to slow down recently |
VIS Rating experts commented that in the first 3 quarters of 2024, the rate of overdue debt formation at banks has slowed down, reflecting a significant improvement in customer cash flows. “Most banks have expressed confidence that customer cash flows will continue to recover thanks to better domestic business conditions. We also see that the size of restructured debts has decreased significantly at a number of state-owned and private banks,” VIS Rating said.
When Circular 02 expires at the end of 2024, banks will have to record all credit costs for restructured debts. However, according to the analysis of the expert group, the impact on the business results of banks will be controlled for large banks, especially those with limited restructured debt scale.
However, some banks with higher restructured debt ratios may face greater asset risks, mainly related to large clients and loans in the real estate sector. These banks are still facing some difficulties, especially in the context of the real estate market facing legal issues and low demand for some new projects.
In addition, these banks also face higher credit costs amid increased competition among banks to support credit growth. Some small banks have plans to reduce lending risks to address asset quality issues, which may continue to put pressure on net interest margins in the coming period.
Sharing the same view, the group of analysts from BIDV Securities Company (BSC) also said that this will not have a significant impact on the balance sheets of banks, and there will not be a sudden increase in the bad debt ratio or provisioning costs.
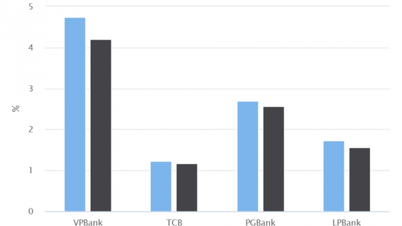
According to BSC, the outstanding debt restructured under Circular 02 accounts for a low proportion, at the end of the third quarter of 2024 it was about 1.6% of the total outstanding debt of the entire system, of which only a few banks recorded this ratio higher than the general level such as VPBank (2.5%), MSB (1.2%), TPBank (0.8%), the rest are all less than 0.5%.
Similarly, according to ACBS Securities Company's forecast, although bad debt in the whole industry has increased slightly for two consecutive quarters, it seems to have peaked and may improve in 2025.
Accordingly, the ratio of overdue debt (including restructured debt) tends to decrease gradually and is at 0.23% of outstanding debt in the third quarter, lower than the historical average of about 0.5%/quarter. In addition, group 2 debt decreased by 0.08% in the third quarter of 2024 and maintained a downward trend for two consecutive quarters thanks to the recovery of the retail customer group. Restructured debt according to Circular 02/2023 also tends to decrease and accounts for only about 0.8%.
According to TPBank Securities (TPS) analysts, in 2025, banks' bad debt ratio could fall to 1.8% supported by tighter risk management measures and improvements in asset quality.
However, credit costs are expected to increase slightly as buffers are no longer thick. In particular, the banking system will continue to face challenges in handling bad debts, especially loans related to real estate.
Source: https://www.anninhthudo.vn/no-xau-ngan-hang-co-tang-vot-sau-khi-thong-tu-02-het-hieu-luc-post600543.antd







![[Photo] Buddha's Birthday 2025: Honoring the message of love, wisdom, and tolerance](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/12/8cd2a70beb264374b41fc5d36add6c3d)




















![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam arrives in Minsk, begins state visit to Belarus](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/11/76602f587468437f8b5b7104495f444d)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam meets and expresses gratitude to Vietnam's Belarusian friends](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/11/c515ee2054c54a87aa8a7cb520f2fa6e)

































































Comment (0)