Units are ready to prepare rooms and temporary quarantine areas for suspected and infected cases at border gates (if necessary); at the same time, training is provided to improve the capacity of medical quarantine officers on monitoring and controlling Marburg disease, paying attention to infection prevention.
Faced with the complicated situation of the Marburg virus epidemic in Africa, the Department of Preventive Medicine ( Ministry of Health ) has just issued an urgent dispatch on proactively monitoring, detecting and controlling the Marburg epidemic entering our country.
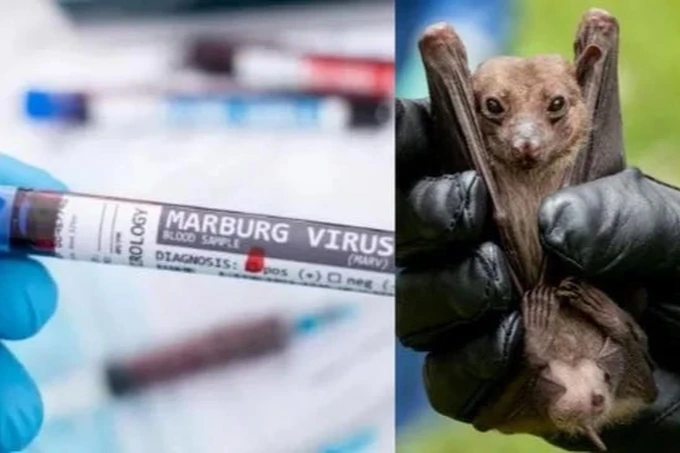

Accordingly, the Department of Preventive Medicine requested the Institute of Hygiene and Epidemiology/Pasteur; International Health Quarantine Centers, Centers for Disease Control of provinces and cities with medical quarantine activities to update information on countries and territories that are recording Marburg disease cases to strengthen and proactively closely monitor subjects subject to medical quarantine from these areas entering, transiting, and importing through border gates in our country; fully implement personal protective measures for officers, employees and people in contact with suspected cases of the disease, not to infect medical staff or spread to the community.
Units are ready to prepare rooms and temporary quarantine areas for suspected and infected cases at border gates (if necessary); at the same time, training is provided to improve the capacity of medical quarantine officers on monitoring and controlling Marburg disease, paying attention to infection prevention.
The Department of Preventive Medicine also requested functional units and localities to organize communication at border gates for passengers and people about prevention measures, especially the need to immediately notify medical facilities when they detect symptoms and epidemiological factors related to Marburg disease within 21 days from the date of entry into Vietnam; review and update contingency plans to respond to Marburg epidemic situations at each border gate with the participation and coordination of functional agencies at the border gate and local health agencies.
The Institutes of Hygiene and Epidemiology/Pasteur provide guidance, training, and support to localities on surveillance and prevention measures, sampling, and safe transportation of specimens; receive specimens for Marburg disease diagnosis from localities; continue to strengthen the capacity for testing and diagnosis of Marburg disease, as well as review and strengthen the rapid response team at the unit, ready to respond when suspected or infected cases are recorded in localities.
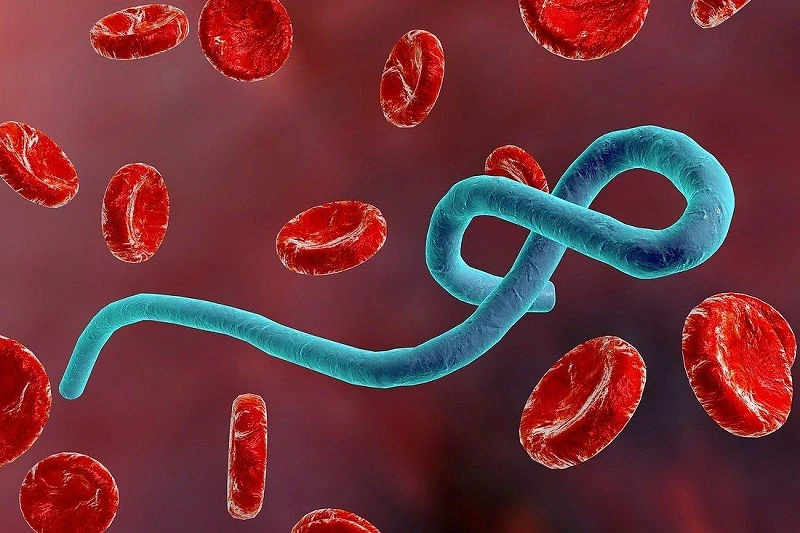
Through the infectious disease surveillance system, since the end of September 2024, in Rwanda (Africa), the first case of Marburg disease was recorded in this country. By October 10, 58 cases were recorded, including 13 deaths in 7 of the 30 districts of this country, about 70% of the cases were medical staff.
Marburg disease is a dangerous infectious disease caused by the Marburg virus. This virus is transmitted from animals to humans, causing severe bleeding in many parts of the body. The disease is highly contagious and has a mortality rate of more than 80%.
Currently, there is no vaccine or specific treatment for the disease caused by the Marburg virus. The disease is classified as group A in Vietnam's Law on Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases.
MINH KHANG
Source: https://www.sggp.org.vn/nhieu-nhan-vien-y-te-nuoc-ngoai-nhiem-virus-marburg-bo-y-te-chi-dao-khan-post763472.html




![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs the second meeting of the Steering Committee on private economic development.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/01/1762006716873_dsc-9145-jpg.webp)











































































































Comment (0)