Good sleep increases the production of female sex hormones, helps create follicles, ovulation such as FSH, LH, estrogen, which control the physiology and reproductive function of women.
Dr. Hoang Quyet Tien, Medical Information Center, Tam Anh General Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, said that in the body, the synthesis, secretion and metabolism of hormones are often synchronized with biological rhythms and regulated by sleep. Sleep disorders can lead to disruption of the hypothalamic axis (pituitary gland - gonads), affecting the synchronous release of reproductive hormones, negatively affecting the physiology and reproduction of women.
Sleep affects the hormone FSH, which stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles and the production of estrogen. FSH levels in women of reproductive age who get enough sleep can be 20% higher than those who sleep less.
Getting enough sleep also helps women stabilize LH and estradiol hormones (male and female reproductive hormones). LH regulates ovulation and releases progesterone after ovulation. Estradiol helps the growth and development of ovarian follicles, ovulation, and maintenance of female characteristics.
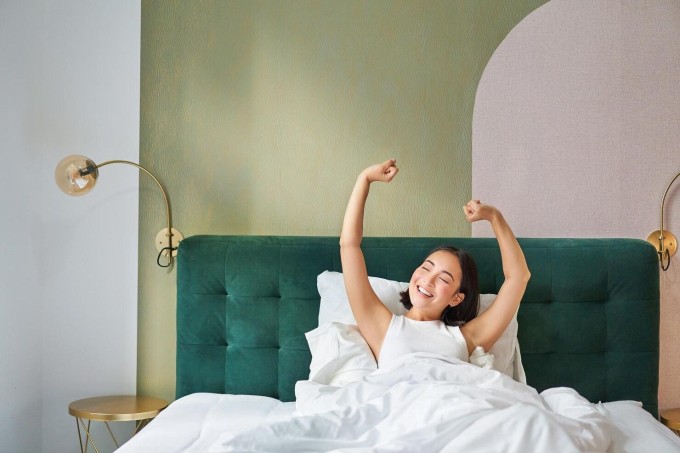

Good sleep is beneficial for women's health. Photo: Freepik
Quality sleep also plays an important role in stabilizing glucocorticoid hormones and increasing fertility in women, according to Dr. Tien. Glucocorticoids indirectly affect ovarian function by altering gonadotropin (metabolic, growth hormone) levels and inhibiting kisspeptin (a protein that can inhibit gonads) neurons. Glucocorticoids also regulate many signaling and biological processes important for fertility.
Melatonin hormone is mainly produced in the pineal gland, has antioxidant properties, regulates the female sex hormone progesterone, stabilizes the quality and quantity of egg cells. Good sleep is beneficial for endogenous melatonin secretion.
When women lack sleep or do not sleep well, the level of TSH hormone (thyroid stimulating hormone) increases, leading to the risk of not ovulating, irregular menstruation, amenorrhea and recurrent miscarriage. Insomnia also changes the secretion of prolactin (PRL) hormone at night, contributing to infertility.
Dr. Tien advises women to go to bed and wake up at a fixed time every day, avoid staying up late, stress, and not use technology devices close to bedtime. Prioritize blood-enriching, sedative foods such as chrysanthemum tea, lotus seeds, and poultry. Do not eat too much after 7 p.m., avoid drinking too much water close to bedtime, and do not drink strong tea or coffee after 3 p.m.
Insomniacs can nourish themselves with foods that are beneficial to sleep according to oriental medicine such as chicken and lotus seed porridge, chicken egg and millet porridge, lotus seed and longan tea. Maintain daily exercise, prioritizing gentle exercises that help you fall asleep easily such as walking, breathing exercises, meditation, back stretching, legs up the wall, crane pose, head and face massage.
Women can use additional sleep-aiding essences such as anthocyanin and pterostilbene extracted from North American blueberries and essences found in ginkgo biloba to sleep well. Lepidium meyenii essence (South American herbal extract) and P. leucotomos (South Central American herbal extract) can enhance the activity of the brain-pituitary-ovary axis, stabilize female hormones, help sleep well and improve physiology.
Nguyen Phuong
| Readers ask questions about neurological diseases here for doctors to answer |
Source link



![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh meets with representatives of outstanding teachers](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/15/1763215934276_dsc-0578-jpg.webp)


![[Photo] Panorama of the 2025 Community Action Awards Final Round](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/15/1763206932975_chi-7868-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives Vice President of Luxshare-ICT Group (China)](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/15/1763211137119_a1-bnd-7809-8939-jpg.webp)





































































































Comment (0)