Sapodilla ripens twice a year from February to March and August to September. In addition to being a delicious and attractive fruit, sapodilla also has many medicinal effects.
According to nutritionists, sapodilla is rich in calcium. This fruit helps promote bone health. In addition to calcium, sapodilla is also a source of minerals such as magnesium, potassium, zinc, copper, phosphorus and selenium that help strengthen bones, regulate blood pressure and circulation.
Sapodilla contains many antioxidants, also rich in vitamins A, B, C, which help strengthen the body's immunity. Sapodilla provides a lot of fiber and iron, which is useful for people fighting anemia.
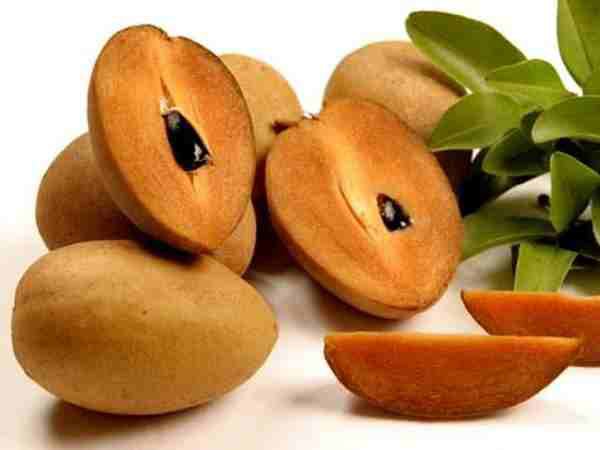

Illustration photo
Health benefits of sapodilla
Good for the intestines
In folk medicine, there has been a remedy for diarrhea using green sapodilla since ancient times. Green sapodilla contains a large amount of tannin (which creates an astringent taste) that can quickly stop diarrhea. In addition, the abundant source of fiber in ripe sapodilla helps laxative, improve and prevent constipation. Eating sapodilla helps us have a clean stomach and a healthy digestive system.
Good for the nervous system
Scientific studies have shown that eating ripe sapodilla helps calm the nerves, reduce stress and fatigue. People with anxiety, insomnia, and depression who regularly eat ripe sapodilla can help improve their spirits. An unexpected benefit that few of us know about, right?
Helps regulate blood pressure
The composition of sapodilla fruit contains Potassium, which has the effect of reducing blood pressure in patients with high blood pressure. For normal healthy people, this substance can help stabilize blood pressure, reducing the risk of high blood pressure. However, you should also note that this food cannot replace the blood pressure medications that the patient is using.
Good for bones and joints
Based on the above ingredient table, we can see that just by eating 100g of ripe sapodilla, you can provide your body with 21mg of calcium. Calcium is an important mineral that makes up the bones and teeth. Eating ripe sapodilla is an easy way for you to supplement natural calcium for your body. This helps children develop optimal height and adults can prevent osteoporosis.

Illustration photo
Good for eyesight
Ripe sapodilla is rich in vitamin A. This vitamin helps improve our eyesight. In addition, vitamin C also has antioxidant effects, protecting retinal cells. You may be surprised to know that vitamin C in the eyes is much higher than the concentration of vitamin C in other body fluids.
Vitamin E also protects fatty acids in the retina from oxidation. This is important for people of all ages, especially the elderly with impaired vision.
Prevent chronic diseases
Antioxidants in ripe sapodilla help the body prevent many chronic diseases, including cancer. According to scientists, this fruit can help us reduce the risk of oral cancer, lung cancer, and colon cancer effectively.
5 groups of people should not eat sapodilla
People with digestive problems
Because sapodilla is rich in fiber, it will cause digestive problems if eaten in large quantities. Especially for people with weak stomachs, the increased amount of fiber will form a membrane that blocks the digestion of food in the stomach, thereby causing uncomfortable conditions such as bloating, indigestion, constipation...
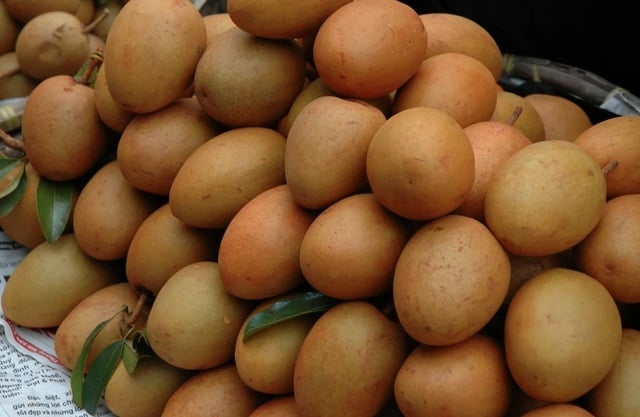

Illustration photo
People with allergies
For people with allergies, eating sapodilla can trigger an allergic reaction in the body. Sapodilla contains tannin - an astringent, which can cause an itchy, uncomfortable feeling in the mouth, itchy throat and rash immediately after eating.
People with stomach pain
In rare cases, eating too much sapodilla can lead to stomach pain. People with stomach problems, if they often eat sapodilla when hungry, will affect the stomach, even cause ulcers.
People who are taking medication
Sapodilla can reduce the effectiveness of medications. The tannins in sapodilla have strong anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and antibacterial properties, but they can also reduce the effectiveness of some medications. You can eat sapodilla at least 2 hours before taking medication to ensure it does not affect the effectiveness of the medication.
People with diabetes
Sapodilla is also not good for people with diabetes, because the sugar content in the fruit is very high. Uncontrolled use of sapodilla can cause high blood sugar.
How to identify sapodilla "soaked" in chemicals
Nowadays, for profit, many traders are willing to use toxic chemicals to ripen sapodilla. According to experts, iron powder and chemicals used to ripen sapodilla are very toxic. People who are regularly exposed to iron powder can suffer from asthma, gastritis, dizziness, kidney failure, etc. and are susceptible to cancer.
To avoid buying chemically soaked persimmons, buyers need to observe carefully:
About the sapodilla peel : Chemically soaked sapodilla peel is usually smooth, dark yellow and almost flawless. Meanwhile, unsoaked sapodilla peel is not smooth, many have green veins through the thin peel, lighter yellow-brown color.
About taste : Ripe sapodilla without chemical soaking has a mild aroma, fine sand, sweet and cool taste. Meanwhile, sapodilla soaked in chemicals to ripen by force, has a strong sweet taste and does not have the characteristic taste of sapodilla.
Source


![[Photo] Party Committees of Central Party agencies summarize the implementation of Resolution No. 18-NQ/TW and the direction of the Party Congress](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/27/1761545645968_ndo_br_1-jpg.webp)

![[Photo] The 5th Patriotic Emulation Congress of the Central Inspection Commission](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/27/1761566862838_ndo_br_1-1858-jpg.webp)






























![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man receives Chairman of the House of Representatives of Uzbekistan Nuriddin Ismoilov](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/27/1761542647910_bnd-2610-jpg.webp)









































































Comment (0)