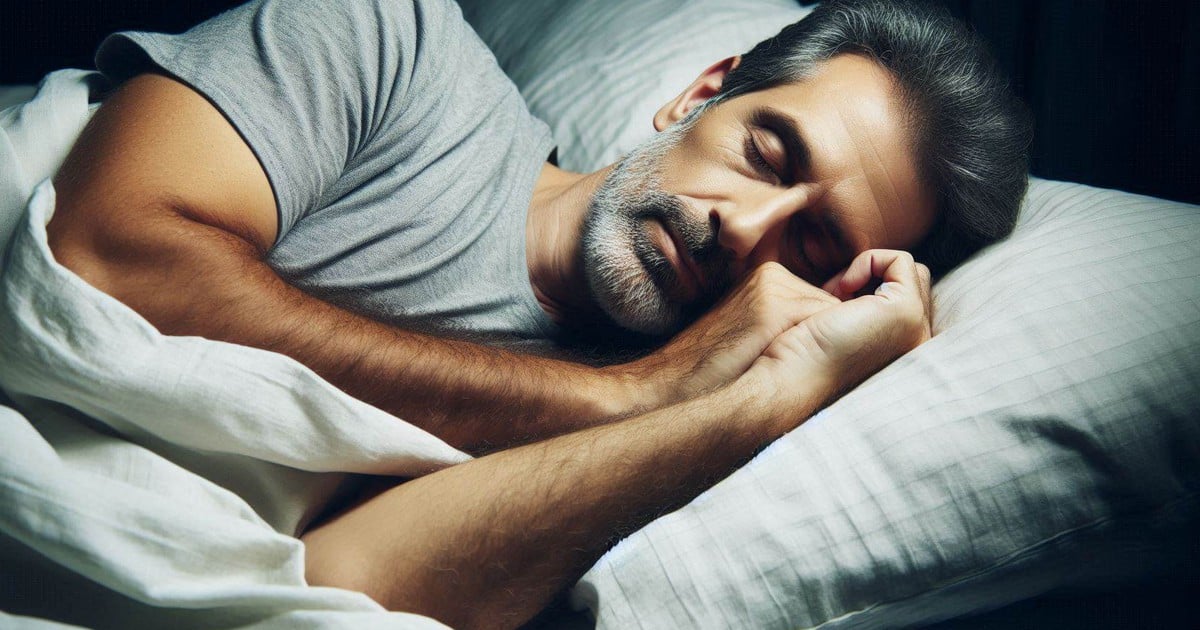
From side sleeping, stomach sleeping to back sleeping, everyone has a favorite sleeping position.
Previous studies have linked the back sleeping position to a number of potential health risks, including high blood pressure and obstructive sleep apnea, and to people with nocturnal reflux or pregnancy. Now, a new study has found another potential downside to this sleeping position.

Many studies show that sleeping on your back causes some potential harmful effects on health.
The new research builds on a 2019 study that found that sleeping more than 2 hours per night in a supine position increases the risk of neurodegenerative disease, according to Medical News Today.
The new study, by a team of scientists from the University of California San Francisco, Mayo Clinic School of Medicine (USA) and Saint Mary's General Hospital in Toronto (Canada), included people with mild cognitive impairment, progressive supranuclear palsy - a late-onset neurodegenerative disease, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's dementia and a control group.
Participants wore devices that calculated the number of hours they slept in a supine position each night, and assessed nine sleep biomarkers to distinguish the risk of neurodegenerative disorders.
Sleeping on your back for more than 2 hours is linked to neurodegenerative conditions
Results found that people who slept more than 2 hours in a supine position had four neurodegenerative conditions compared with the control group.
The researchers believe this provides further evidence of a strong link between sleeping on your back and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and mild cognitive impairment.

Sleeping more than 2 hours per night in a supine position increases the risk of neurodegenerative disease
Why might sleeping on your back increase your risk?
The researchers explain that neurotoxin clearance is less efficient when sleeping on your back than when sleeping on your side due to differences in the way venous blood returns to the heart from the brain. In addition, sleeping on your back causes more severe sleep apnea, leading to more frequent sleep disruptions that also contribute to neurotoxin accumulation. The new study suggests that inefficient neurotoxin clearance due to years of sleeping on your back contributes to neurodegeneration.
Some emerging research suggests that sleeping in a side-lying position may help the brain clear waste products, which could theoretically reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases, the authors added.
In summary, although sleep position is important for brain health, it is more important to prioritize good sleep hygiene and overall lifestyle factors to reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases, according to Medical News Today.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/khoa-hoc-chi-ra-tu-the-ngu-co-the-gay-hai-nguoi-lon-tuoi-nen-tranh-185240914201733219.htm



![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs meeting of Steering Committee for key projects and railway projects](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/26/b9534596258a40a29ebd8edcdbd666ab)
![[Photo] Readers' joy when receiving the supplement commemorating the 50th anniversary of the liberation of the South and national reunification of Nhan Dan Newspaper](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/26/283e56713da94988bf608393c0165723)

![[Photo] Young people line up to receive the special supplement commemorating the 50th anniversary of the Liberation of the South of Nhan Dan Newspaper](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/26/9e7e624ae81643eba5f3cdc232cd07a5)
![[Photo] Ho Chi Minh City people's affection for the parade](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/26/7fcb6bcae98e46fba1ca063dc570e7e5)






















































































Comment (0)