After nearly two years of aggressive policy tightening, many of the world's biggest central banks have paused interest rate hikes as they consider their next move.
On November 2, the Bank of England (BoE) announced that it would keep interest rates unchanged at a 15-year high. A day earlier, the US Federal Reserve (Fed) also decided not to raise interest rates after its policy meeting.
Financial markets have now turned their attention to when central banks will cut interest rates. Growth in many economies has slowed and inflation has cooled.
According to Reuters statistics, in the interest rate hike cycle starting from September 2021, 9 developed countries have raised interest rates by a total of nearly 4,000 basis points (40%). Japan is the only name that is out of this trend, when it still maintains an interest rate of -0.1%.
Below are interest rate developments in the 10 economies with the most traded currencies in the world, according to LSEG Financial Group (UK).
America
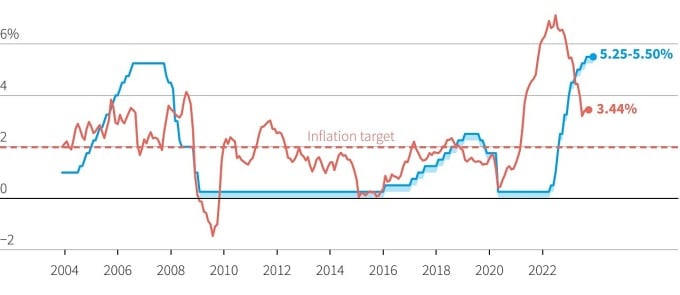
US interest rate (green) and inflation (red) developments since 2004. Chart: Reuters
The US Federal Reserve (Fed) announced on November 1 that it would keep interest rates at 5.25-5.5%. This is the second time they have kept them unchanged, after 11 consecutive increases since the beginning of 2022.
Fed officials said more time was needed to assess whether financial markets were tight enough to control inflation. The U.S. economy has continued to grow impressively, with 4.9% growth in the third quarter.
New Zealand
The Reserve Bank of New Zealand was one of the first to join the wave of interest rate hikes in 2021. Currently, the reference rate here has reached a 15-year high of 5.5% since May.
However, the tightening campaign in this country is expected to come to an end, as the New Zealand economy shows many signs of slowing. Markets currently think that the possibility of a rate hike at the meeting later this month is only 10%.
Older brother
The Bank of England announced on November 2 that it would keep interest rates unchanged at a 15-year high. However, the agency stressed that inflation risks remain.
The UK economy is forecast to grow at zero in 2024. The market now sees a high probability that the BoE will cut interest rates from August 2024.
Canada
After its October 25 policy meeting, the Bank of Canada announced that it would keep its benchmark interest rate unchanged at 5%. Markets are now expecting the rate to remain at that level for some time. Governor Tiff Macklem has said that the bank is prepared to raise rates further if high inflation persists.
Eurozone
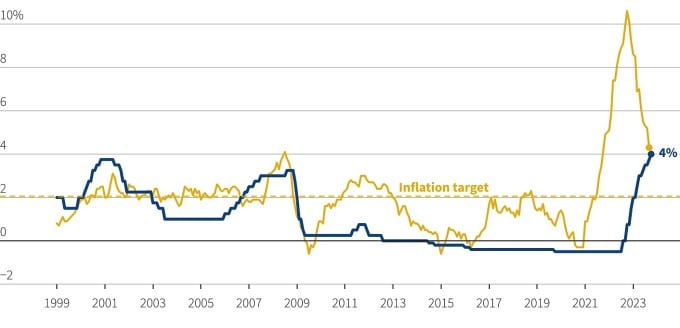
Eurozone interest rate (green) and inflation (yellow) developments since 1999. Chart: Reuters
Last week, the European Central Bank (ECB) announced that it would keep its benchmark interest rate unchanged at 4%. It said the latest data showed that inflation was slowing, gradually returning to its 2% target.
With inflation cooling and signs of an economic slowdown becoming more evident, investors are now betting the ECB is set to cut interest rates. The ECB is expected to cut interest rates by another 25 basis points early next year.
Norway
Norway's central bank also kept its key interest rate unchanged at 4.25 percent yesterday and said it could still raise rates at its December meeting. Inflation in Norway cooled faster than expected in September. However, the central bank said it needed more evidence that price pressures were easing.
Sweden
Sweden raised its benchmark interest rate to 4% in September, but now faces a tough choice.
A Reuters poll of economists showed the Swedish economy is forecast to shrink by 0.7% in 2023. However, the country's core inflation (excluding energy prices) remains high, at 6.9% in September.
Australia
The possibility of the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) raising interest rates is increasing as data on November 1 showed house prices here reaching near record levels. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) also recommended that the country tighten fiscal and monetary policies to curb inflation.
The market is now pricing in a nearly 70% chance of the RBA raising rates to 4.35% at its meeting this month.
Switzerland
The Swiss franc hit an eight-year high against the euro on news of the Gaza conflict. The currency is a popular haven during times of uncertainty. The Swiss National Bank (SNB) is now widely expected to keep its key interest rate at 1.75% at its December policy meeting.
The strong franc has helped the SNB keep inflation in check, at just 1.7% in October. However, it has also weighed on the country's exports amid a slowing economy.
Japan
The Bank of Japan (BOJ) kept its key interest rate unchanged at -0.1% on October 31. They only loosened control over the yield cap on 10-year government bonds. This move disappointed investors and the yen continued to depreciate against the USD and the euro.
The BOJ also raised its inflation forecast for Japan, which has been above its 2% target for more than a year.
Ha Thu (according to Reuters)
Source link


![[Photo] More than 17,000 candidates participate in the 2025 SPT Competency Assessment Test of Hanoi National University of Education](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/e538d9a1636c407cbb211b314e6303fd)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs meeting on science and technology development](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/ae80dd74c384439789b12013c738a045)



![[Photo] Readers line up to visit the photo exhibition and receive a special publication commemorating the 135th birthday of President Ho Chi Minh at Nhan Dan Newspaper](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/85b3197fc6bd43e6a9ee4db15101005b)


























![[Photo] Nearly 3,000 students moved by stories about soldiers](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/21da57c8241e42438b423eaa37215e0e)






































































Comment (0)