Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are two common blood filtration methods for patients when kidney function is no longer effective.
Dr. Dinh Cam Tu, Head of the Artificial Kidney Unit, Department of Nephrology - Blood Filtration, Center for Urology - Nephrology - Andrology, Tam Anh General Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, said that blood filtration is a method of using machines to support the patient's kidneys to filter waste and excess fluid out of the body when the kidneys can no longer perform this function. There are currently two methods of blood filtration for kidney patients.
Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis is indicated for people with end-stage renal failure (stage 5 chronic renal failure), with almost complete loss of kidney filtration function, glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) below 15ml/min/1.73m2 of skin; acute renal failure (usually due to poisoning) progressing rapidly and threatening life; or excess water, hyperkalemia, increased blood acidity that is not effectively treated with medication.
During hemodialysis, two small needles are placed into a vein in the patient's arm, attached to a system of tubes and connected to a dialysis machine. A blood pump system carries blood through the dialysis machine to remove waste (urea, creatinine), excess substances (potassium, fluid), toxins, and retain blood cells, proteins and essential substances. After filtering, the blood is returned to the body through the remaining needle tube.
Long-term traditional hemodialysis can cause some complications such as itching, fatigue, skin darkening, cardiovascular complications, anemia, and low blood pressure. Doctor Tu said that the current online HDF hemodialysis technique is an "upgraded version" of traditional hemodialysis. Thanks to the use of ultra-pure water and high-efficiency filter membranes, this technique overcomes the above disadvantages.
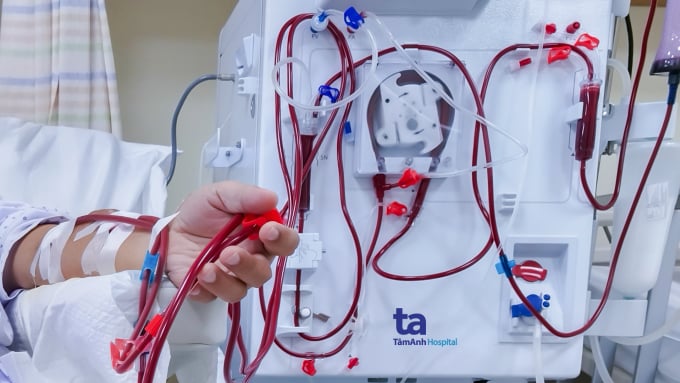
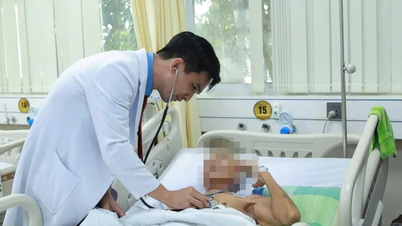
Patients undergoing hemodialysis at Tam Anh General Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City. Photo: Anh Thu
Peritoneal dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis (peritoneal dialysis) is a method that uses the patient's own abdominal membrane to replace the kidney function that has been weakened or completely lost. Before treatment, the patient has a soft tube placed in the abdomen that is responsible for directing the dialysis fluid into the abdomen and waste and excess substances out of the body.
In the abdominal cavity, the peritoneum separates the fluid-filled cavity from the vascular cavity. During treatment, dialysate flows through a tube into the abdominal cavity. The dialysate absorbs waste and excess fluid from the blood, passes through the peritoneum, and is then eliminated from the body. The abdominal cavity can hold two liters of peritoneal dialysis fluid without causing discomfort to the patient.
According to Dr. Tu, there are currently three peritoneal dialysis methods including:
Acute peritoneal dialysis : The doctor places a temporary catheter into the patient's abdominal cavity. Each time, two liters of dialysate are introduced into the patient's peritoneal cavity. After two hours, the waste fluid is discarded and replaced with new dialysate. This process is continued until the patient's electrolyte disturbances are gone, the internal environment is balanced, and kidney function is restored.
This method is indicated for patients with acute renal failure or severe progression of chronic renal failure, blood pH below 7.2, blood potassium above 6.5 mmol/l, blood urea above 30 mmol/l, circulatory volume overload threatening acute pulmonary edema...
Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis : The surgeon places a catheter in the abdominal cavity throughout the procedure. During peritoneal dialysis, the dialysate remains in the patient's abdominal cavity and is changed four times a day, every four to eight hours. Dialysate changes can be done manually at home.
Automated periodic peritoneal dialysis : Peritoneal dialysis is performed by a machine in different cycles, usually at night, while the patient is sleeping at home or in the hospital.
Doctor Tu said the advantages of peritoneal dialysis are that it is suitable for all patients, does not depend on machines, is effective, preserves kidney function, patients do not have to eat or drink too much, and can be done at home.
Thang Vu
| Readers ask questions about kidney disease here for doctors to answer |
Source link






























































































Comment (0)