According to The Hacker News , among the Android vulnerabilities patched by Google, three are being exploited in targeted attacks. One vulnerability, assigned the code CVE-2023-26083, is a memory leak that affects the Arm Mali GPU driver for Bifrost, Avalon, and Valhall chips.
The vulnerability was exploited in an attack that installed spyware on Samsung devices in December 2022. It was considered serious enough for the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA - US) to issue a patch order to federal agencies in April 2023.
Another critical vulnerability, CVE-2021-29256, is a high severity vulnerability that affects specific versions of the Bifrost and Midgard Arm Mali GPU kernel drivers. The bug allows an unprivileged user to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data and escalate privileges to the highest level.
The third exploited vulnerability is CVE-2023-2136, a high-severity vulnerability in Skia, Google's cross-platform open-source 2D graphics library. It was initially identified as a zero-day vulnerability in the Chrome browser that allowed remote attackers to escape the sandbox and remotely deploy code on Android devices.
Google's July Android security patch also addresses a critical vulnerability, CVE-2023-21250, affecting an Android system component that could allow remote code execution without user interaction or additional privileges.
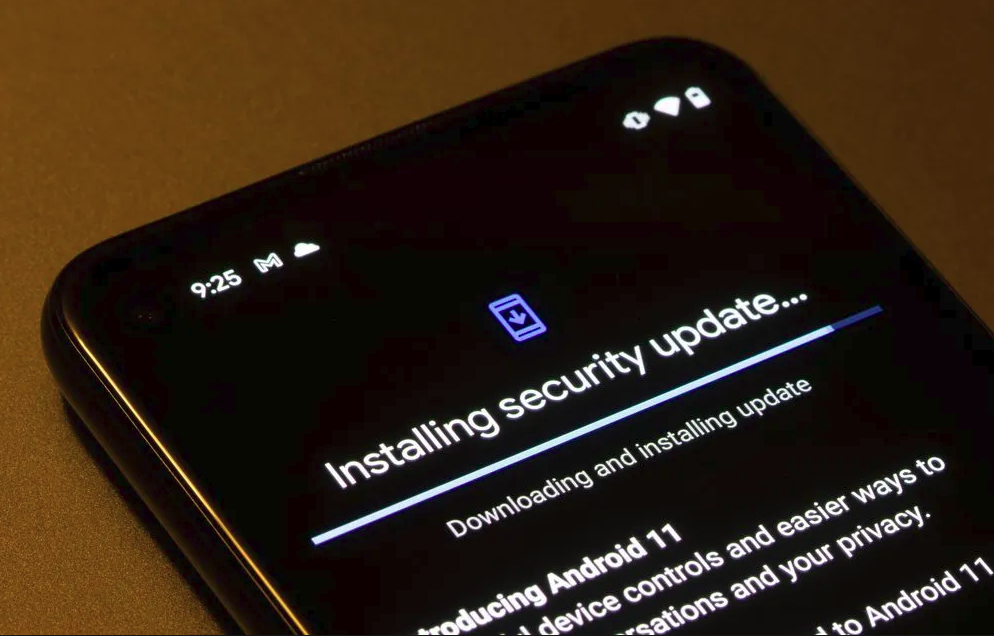
The discovered bugs are worrying because they affect even older Android devices.
These security updates are being rolled out at two levels. The first patch released on July 1 focuses on core Android components, addressing 22 security flaws in the framework and system components. The second patch released on July 5 addresses kernel and closed source components, addressing 20 vulnerabilities in kernel components, Arm chips, and imaging technology in MediaTek and Qualcomm processors.
The impact of the vulnerabilities may extend beyond supported Android versions (11, 12, and 13), however, potentially affecting older versions of the operating system that no longer receive official support.
Google also released security patches to address 14 vulnerabilities in components for Pixel devices. Two of these critical flaws allow elevation of privilege and denial of service attacks.
Source link


![[Photo] Cultural, sports and media bloc at the 50th Anniversary of Southern Liberation and National Reunification Day](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/30/8a22f876e8d24890be2ae3d88c9b201c)
![[Photo] "King Cobra" Su-30MK2 completed its glorious mission on April 30](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/30/5724b5c99b7a40db81aa7c418523defe)
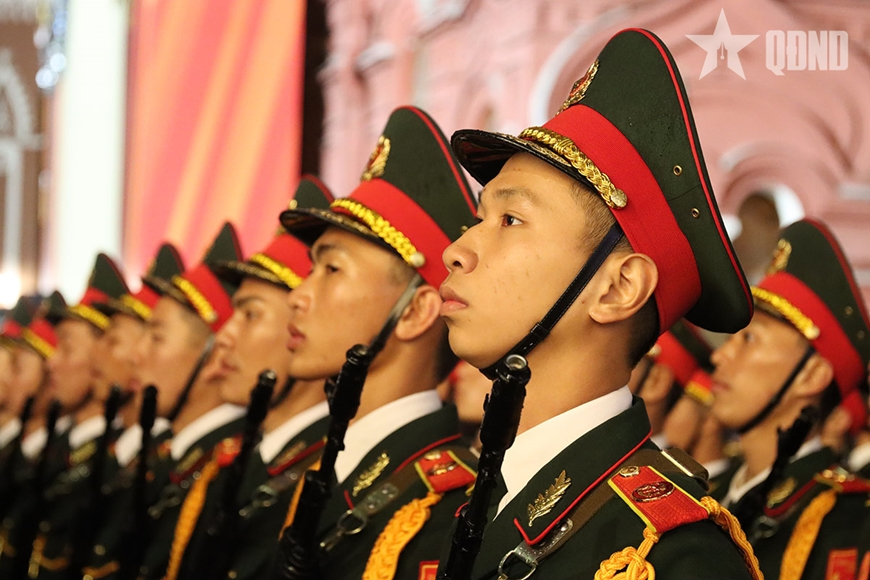

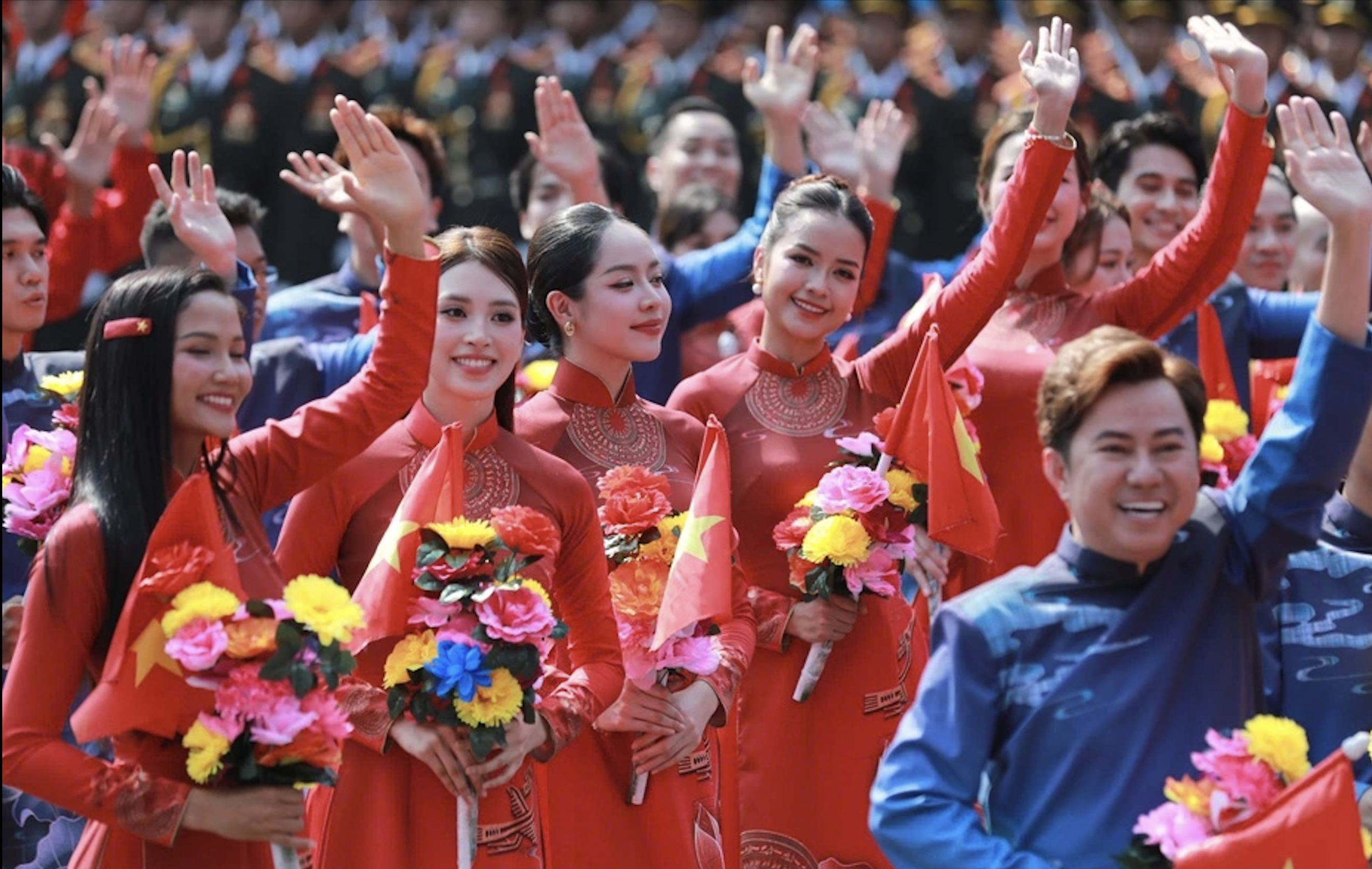
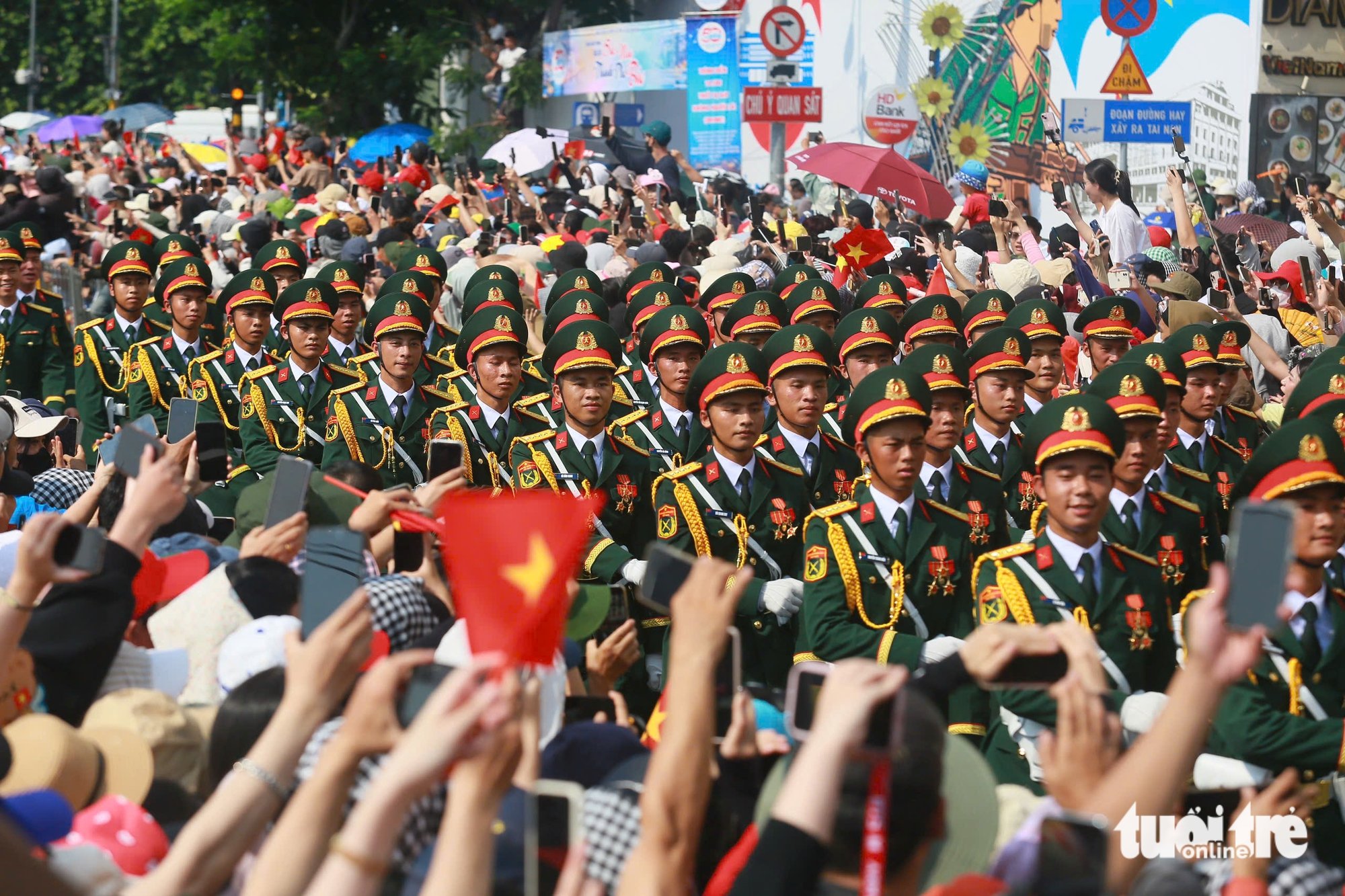
![[Photo] The parade took to the streets, walking among the arms of tens of thousands of people.](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/30/180ec64521094c87bdb5a983ff1a30a4)




























































































Comment (0)