Recently, doctors at Children's Hospital 2 said they had performed an endoscopic clip to stop bleeding for a patient with severe gastrointestinal bleeding due to duodenal ulcer.
The patient is a boy HGH (13 years old, living in Ho Chi Minh City), hospitalized with vomiting blood and passing a lot of black stools.
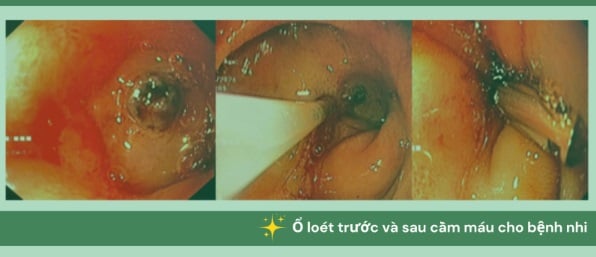
Endoscopy doctors stop bleeding for a child with gastrointestinal bleeding due to duodenal ulcer.
After examination, the doctors performed blood transfusion, fluid infusion and emergency endoscopy. It is known that on the endoscopy camera image recorded, the patient's duodenum (the beginning of the small intestine located between the stomach and the jejunum) had a very large ulcer. At the site of the injury, blood spurted out.
The medical team performed a clamping and injection to stop the bleeding, treated the ulcer, and took a sample for testing. The results showed that the child was infected with Helicobacter pylori (HP) bacteria.
After the intervention, the child no longer had bleeding and his health gradually recovered.
Causes of HP bacteria infection in children
According to Dr. Nguyen Thi Thu Thuy - Deputy Head of Gastroenterology Department, gastrointestinal bleeding due to gastric and duodenal ulcers is increasing in children.
The most common cause of peptic ulcers in children is Helicobacter pylori infection. Many of these patients require endoscopic intervention to stop bleeding.
The exact cause of H. pylori infection in children is unknown, but doctors believe it may be passed from person to person through close contact, such as kissing, or through the digestive tract. Most children are susceptible to H. pylori infection. However, only some children will develop an infection.
Signs of children infected with HP bacteria
Depending on each person's constitution, they may experience different symptoms, but in general, people with HP infection often have the following typical signs:
- Dull abdominal pain about 2-3 hours after eating. When hungry, the pain can come and go for a few days or weeks.
- Weight loss, loss of appetite.
- Bloating, flatulence, heartburn, nausea and vomiting.
- Black or bloody stools.
How to prevent HP infection in children
HP is a highly contagious bacteria. Fecal-oral and oral-oral transmission are the two main ways HP bacteria is transmitted from person to person. Therefore, parents need to develop good habits for their children such as:
- Teach children to get into the habit of washing their hands before eating and after using the toilet.
- Instruct and advise children not to share spoons, forks, personal hygiene items and to change toothbrushes at least every three months.
- Families with members with HP should be tested and treated to avoid exposure to other members.
- Maintain a reasonable diet to prevent iron deficiency anemia. Increase the amount of cruciferous vegetables such as cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli... to supplement vitamins and essential minerals to enhance digestive immunity.
 5 causes of stomach pain and signs to recognize
5 causes of stomach pain and signs to recognizeSource: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/be-13-tuoi-oi-ra-mau-vi-nhiem-khuan-hp-khuyen-cao-cha-me-can-lam-dieu-nay-de-phong-benh-cho-tre-172241011232503631.htm


![[Photo] Readers line up to visit the photo exhibition and receive a special publication commemorating the 135th birthday of President Ho Chi Minh at Nhan Dan Newspaper](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/85b3197fc6bd43e6a9ee4db15101005b)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs meeting on science and technology development](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/ae80dd74c384439789b12013c738a045)



![[Photo] More than 17,000 candidates participate in the 2025 SPT Competency Assessment Test of Hanoi National University of Education](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/e538d9a1636c407cbb211b314e6303fd)

























![[Photo] Nearly 3,000 students moved by stories about soldiers](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/21da57c8241e42438b423eaa37215e0e)

































































Comment (0)