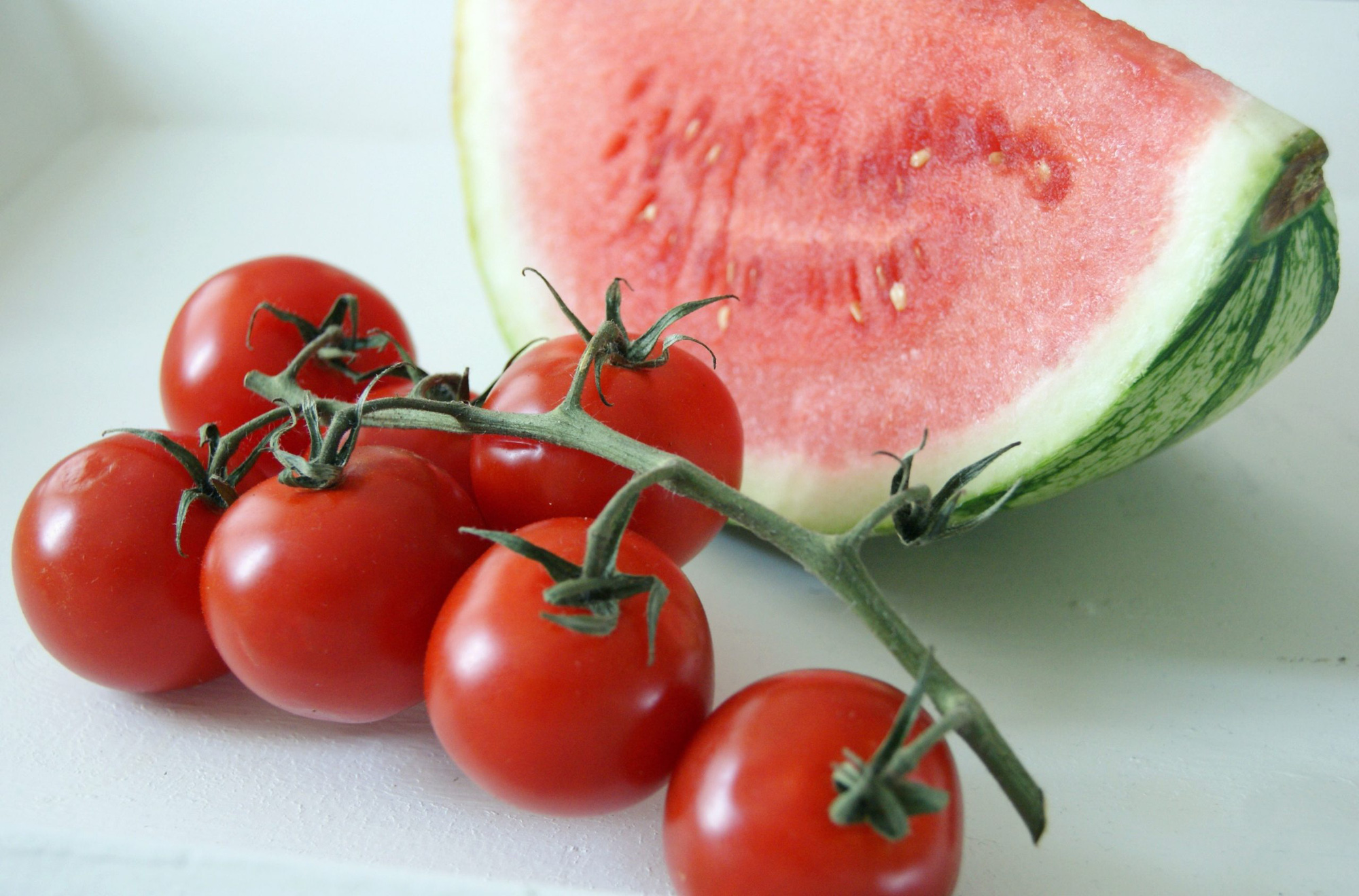

Flavonoids are abundant in berries such as strawberries, mulberries, raspberries, tomatoes, watermelon... - Photo: norvanreports.com/SONY DSC
The study, led by Queen's University Belfast (UK), analyzed dietary data from more than 120,000 people aged 40-70 in UK Biobank, a database that holds medical and lifestyle records of 500,000 people in the UK.
Research shows that consuming six additional servings of flavonoid-rich foods and drinks a day, especially berries, tea, and red wine, can reduce the risk of dementia by 28%. This finding is particularly relevant for people at high genetic risk and those with depression.
Flavonoids, which are found mainly in plant foods, have a range of health benefits, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties, the researchers said. They have also been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, as well as improved cognitive function.
Common berries are strawberries, mulberries, raspberries, blueberries, currants, grapes, watermelon, bananas, peppers, tomatoes, cantaloupe, cucumbers, pumpkins...
According to the Guardian newspaper on September 18, it is predicted that by 2050, the number of people suffering from dementia worldwide will nearly triple to 153 million people, creating a huge burden on the global health and social care system.
Age and genetics remain the biggest risk factors, but experts say nearly half of cases can be prevented or delayed, and there is growing evidence that diet may play a role in disease risk.
"Currently, there is no effective treatment for this disease, so preventive interventions to improve health and quality of life, as well as reduce economic and social costs, should continue to be a public health priority," said Amy Jennings, an author of the study.
The study was published in the journal JAMA Network Open .
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/an-nhieu-ca-chua-dua-hau-giup-giam-nguy-co-suy-giam-tri-nho-20240918151031968.htm


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives Swedish Minister of International Development Cooperation and Foreign Trade](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/12/ae50d0bb57584fd1bbe1cd77d9ad6d97)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh works with the Standing Committee of Thai Binh Provincial Party Committee](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/12/f514ab990c544e05a446f77bba59c7d1)














![[Video] New treatment regimen helps pregnant women with cancer give birth safely](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/13/e2d843bd206e435bb530f4f75e1903bb)
















































































Comment (0)