Not monitoring blood sugar, drinking little water, eating the wrong amount of carbs... are mistakes that diabetics on a low-carb diet can easily make.
Low carb diets are used by many diabetics to control and improve their condition. This diet limits carbohydrates (sugar and starch), and includes foods rich in protein to help stabilize blood sugar, lose weight, and improve cholesterol levels. People with type 2 diabetes who follow this diet also reduce triglycerides and high blood pressure. Below are common mistakes that diabetics make when eating low carb.
Eating the wrong amount of carbs
Each person needs a different amount of carbs, depending on their physical condition. Patients should consider factors such as health status, blood sugar control, medication use, eating preferences... to balance the amount of carbs. People can consult a nutritionist or treating doctor for specific instructions on the appropriate amount of carbs.
No blood sugar monitoring
A low-carb diet can help control blood sugar levels, but it is not the first-line solution for long-term blood sugar stability. Diabetics should regularly monitor their blood sugar to adjust their carb intake to avoid increasing or decreasing blood sugar levels. Monitoring blood sugar also helps adjust meal portions, carb intake, and medication dosage. Patients should monitor their blood sugar regularly, such as before and after meals, after exercise, etc., to avoid sudden increases or decreases.
Ignore carb quality
Some people tend to focus on counting total carbs without paying attention to the quality of carbs. This affects the amount of nutrients they take in. Patients should balance carbs according to their nutritional needs, focusing on whole, unprocessed foods and increasing healthy fats.
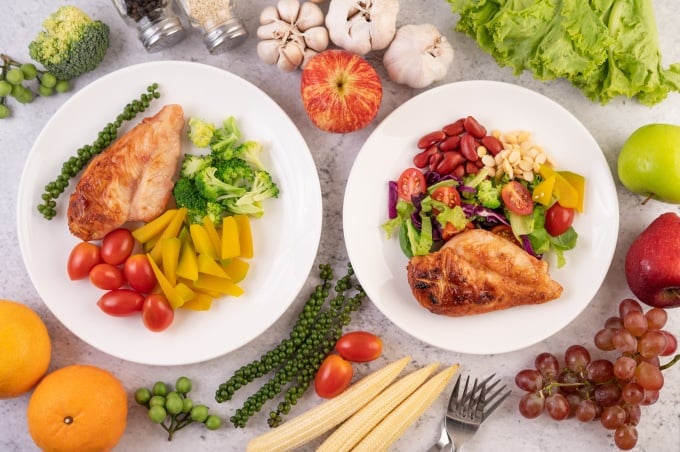

The low carb diet prioritizes fat, protein and fiber. Photo: Freepik
Cut a lot of carbs at once
You should not reduce carbs too much in one meal but need to distribute the amount consumed evenly throughout the day. This is beneficial for the goal of stabilizing blood sugar, maintaining energy levels for activities. People with type 2 diabetes should have 30-45g of carbs per meal (including snacks).
Skip the fiber
Fiber is very important for people with diabetes. It helps reduce blood pressure, improve insulin, stabilize blood sugar, and keep you full longer. Many people who follow this diet tend to balance fat and protein, which prevents the body from getting enough fiber. The diet should be low to moderate in carbs but high in fiber from green leafy vegetables, berries, beans, nuts, etc.
According to the US Department of Agriculture , the recommended daily fiber intake for men and women under 50 years old is 25g, 38g respectively, and over 50 years old is 21g and 30g.
Drink too little water
Low-carb diets can increase the risk of dehydration, causing electrolyte imbalances. When carbs are reduced, water stores are reduced, causing the body to produce less insulin. The kidneys excrete both water and sodium (salt) from the body. Adults with diabetes should drink 2-2.5 liters of water per day.
Mai Cat (According to Everyday Health )
Source link




![[Photo] Standing member of the Secretariat Tran Cam Tu chaired a meeting with Party committees, offices, Party committees, agencies and Central organizations.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/1/b8922706fa384bbdadd4513b68879951)































































































Comment (0)