Smoking is always associated with lung disease. Statistics show that more than 90% of smokers will suffer dangerous complications, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or cancer, according to the health website Verywell Health (USA).
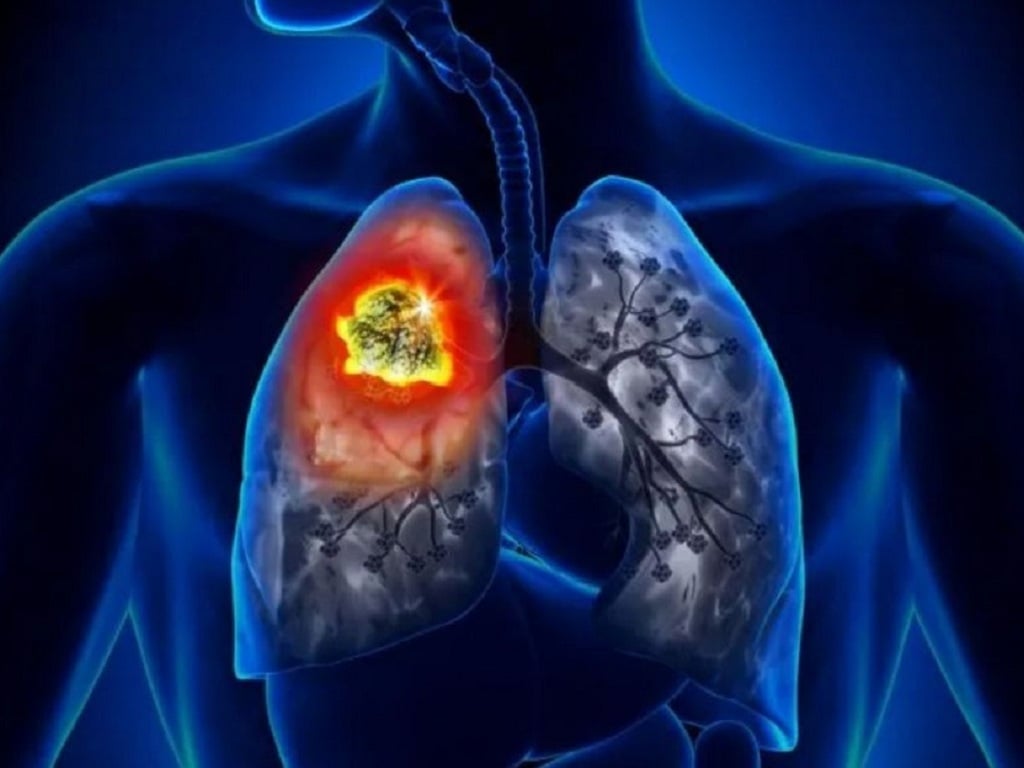
Exposure to toxic chemicals can damage DNA in cells and cause lung cancer.
With lung cancer, not only cigarettes but the following factors also increase the risk of the disease:
Occupational hazards
Many people get lung cancer even if they don't smoke. In that case, their disease may be caused by exposure to toxic gases in the workplace. These gases can include arsenic, uranium, asbestos, or diesel exhaust.
Research shows that in many people with lung cancer unrelated to smoking, their DNA shows signs of damage from environmental chemicals. It is this DNA damage that causes cancer to thrive.
Radon exposure
Radon is a naturally occurring gas found in rocks, soil, and water. It can enter buildings through cracks or holes. Long-term exposure to radon can cause lung cancer.
In the United States, the US Environmental Protection Agency estimates that radon gas is responsible for about 21,000 lung cancer deaths each year.
Air pollution
Some research evidence suggests that outdoor air pollution causes about 10% of all lung cancer cases in non-smokers. This is because air pollutants damage the DNA in cells and cause cancer.
Effects of radiation
Exposure to high-energy radiation is a risk factor for lung cancer. This radiation can be from medical X-rays or other types of radiation from the environment.
People who have had cancer and radiation therapy to the chest are at higher risk of developing lung cancer. The risk of developing lung cancer after radiation exposure depends on age and the amount of exposure, according to Verywell Health.
Source link






![[Photo] Nearly 3,000 students moved by stories about soldiers](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/21da57c8241e42438b423eaa37215e0e)










































































![[Infographic] Numbers about the 2025 High School Graduation Exam in Dong Thap Province](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/c6e481df97c94ff28d740cc2f26ebbdc)



















Comment (0)