The high sugar content and stimulants in carbonated soft drinks put a strain on the liver and can lead to elevated liver enzymes.
Liver enzymes are enzymes that catalyze metabolic reactions; AST, ALT, ALP, and GGT enzymes are present in high concentrations in the liver. Excessive liver cell damage releases these enzymes into the bloodstream, causing elevated liver enzymes.
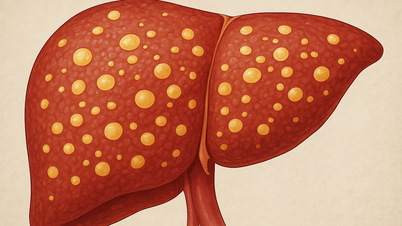
Elevated liver enzymes are often a warning sign of acute hepatitis, hepatic coma, chronic hepatitis, pancreatitis, etc. If not controlled promptly, high enzyme levels can easily lead to severe and dangerous disease progression.
Dr. Vu Truong Khanh, Head of the Gastroenterology Department at Tam Anh General Hospital in Hanoi , said that drinking a lot of sugary soft drinks can easily increase liver enzymes. Soft drinks contain a lot of sugar, about 10.6g of sugar per 100ml; 100ml of energy drink contains about 8.7g of sugar. Drinking a 330ml can of soft drink is equivalent to consuming 29-35g of sugar. Meanwhile, the American Heart Association (AHA) recommends that adult women should not consume more than 25g of sugar per day, and men should not consume more than 36g of sugar.
People with liver disease who frequently consume this type of beverage put a strain on their liver, forcing it to work harder, easily increasing liver enzymes, and over time potentially leading to cancer.
The liver easily absorbs the high sugar content in this type of beverage, then converts it into fat, leading to fat accumulation in the liver, resulting in fatty liver disease and elevated liver enzymes. The accompanying health consequences include an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity.
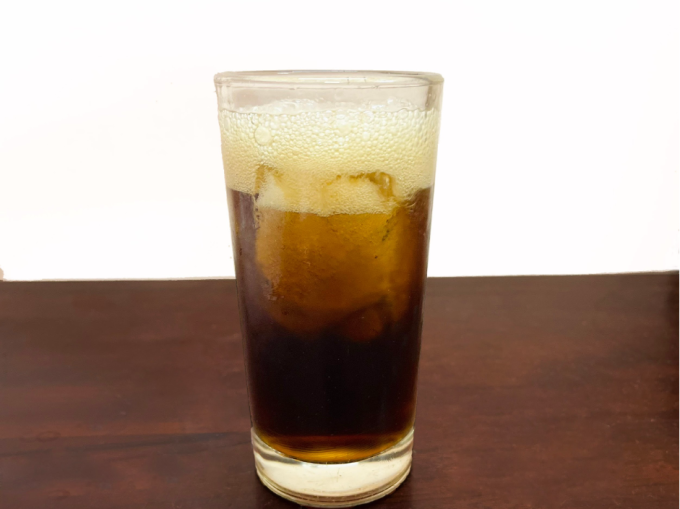

Drinking too much soda is bad for your liver. Photo: Ly Nguyen
Elevated liver enzymes can also occur due to several diseases such as hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E viral infections, fatty liver disease, overweight, and diabetes. Unhealthy lifestyles; unbalanced diets; consumption of many processed, canned, and high-fat foods; and alcohol abuse are also contributing factors.
Symptoms of elevated liver enzymes include loss of appetite, dark urine, pain or heaviness in the right lower abdomen, nausea, jaundice, abdominal pain, enlarged spleen, ascites, and mild fever. Signs are less pronounced in mild or moderate cases of elevated liver enzymes.
A liver enzyme test is the only way to determine if liver enzymes are elevated. If the levels are excessively high, patients need to take medication as prescribed by their doctor, combined with a healthy diet and lifestyle.
To prevent the disease, Dr. Khanh advises limiting alcohol, beer, and carbonated soft drinks. Each week, you should drink a maximum of 350 ml, or about one bottle of soda, but ideally, you shouldn't drink at all to protect your liver. Quitting smoking reduces the burden of toxins on the liver. Regular exercise helps boost metabolism, burn excess energy, limit fat accumulation in the liver, and stimulate the body's natural detoxification process through sweat.
Eating plenty of fruits and vegetables provides vitamins, fiber, and carotenoid pigments. Vegetables such as kale, collard greens, cabbage, cauliflower, onions, avocados, lemons, and grapefruits help neutralize toxins, promote liver regeneration and healing, and thus lower liver enzymes.
Losing weight if you are overweight can also help lower liver enzymes. Maintaining a balanced work and rest schedule, staying relaxed, and having regular health checkups are also ways to control liver enzymes and maintain overall health.
Ly Nguyen
| Readers can ask questions about digestive diseases here for doctors to answer. |
Source link


![[Photo] Closing Ceremony of the 10th Session of the 15th National Assembly](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F11%2F1765448959967_image-1437-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)



![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh holds a phone call with the CEO of Russia's Rosatom Corporation.](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F11%2F1765464552365_dsc-5295-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)















































![[OFFICIAL] MISA GROUP ANNOUNCES ITS PIONEERING BRAND POSITIONING IN BUILDING AGENTIC AI FOR BUSINESSES, HOUSEHOLDS, AND THE GOVERNMENT](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/11/1765444754256_agentic-ai_postfb-scaled.png)



















































Comment (0)