The Need for AI in the Food Industry
In addition to providing opportunities to solve complex industry challenges, AI is also changing the overall business landscape. Companies are responding to consumer trends and bringing products to market faster than ever before, and consumers are starting to expect this. To keep up with trends and succeed in their go-to-market strategies, product innovation needs to be faster-paced than ever.
Traditionally, food companies’ new product development cycle from inception to shelf has been plagued by limited information and fragmented data. This complexity arises from different aspects of the process cycle, including marketing, research and development (R&D), and sales. These challenges result in slow decision making and long innovation cycles.
It is therefore no surprise that around 80% of food product launches fail, largely due to lack of consumer acceptance. AI is helping to effectively address these challenges by reducing the need for extensive testing and promoting cross-departmental collaboration using powerful data networks. It can streamline the entire process by optimizing product formulations, process parameters, and analyzing market trends.
“The whole digital agenda is relevant and exciting because if done well, it really accelerates things,” says Miriam Überall, former R&D director at Kraft Heinz and Unilever. “Avoid a lot of the trial and error that a traditional R&D organization does, and be more predictive.”
The Role of AI in Driving the Food Industry Innovation Cycle
Enhance consumer insights and idea generation . AI is reshaping the new product development process by leveraging a multidimensional data-driven approach.
First, AI interprets real-time trends from external sources, gathering information about consumer opinions and sentiments. This includes social media analysis, keyword tracking, using chatbots for surveys, and image analysis.
Second, AI also extends to Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, which collect consumer data on product choices and cooking preferences. Furthermore, it conducts analytics, leveraging historical sales data and market trends to accurately forecast consumer needs and preferences, optimize new product launch times, and adapt to market changes.
The startup Tastewise is a prime example of using AI to inspire new product development. The company has developed software that collects massive amounts of data from a variety of sources (social media, reviews, menus, recipes, etc.) to understand emerging food trends and consumer tastes.
This software is a valuable tool for food companies as it helps create products that are desired and preferred by consumers.
Discovering new food ingredients . In the new product development cycle, AI can also accelerate the discovery of new food ingredients, improve the screening and characterization of ingredients. Startups around the world are researching and developing an efficient algorithm to support the food discovery process. Ginkgo Bioworks and Arzeda, for example, are using a combination of computational design and AI to create new proteins and enzymes. Meanwhile, Amai Proteins uses AI to design new proteins that are optimized to produce different characteristics and flavors.
Research, development and optimization . AI plays a central role in predicting and enhancing attributes for diverse food products. It suggests ingredient ratios to match flavor profiles and offers healthier alternatives while maintaining flavor.
Additionally, AI assists in assessing food product texture, ensuring product characteristics meet expectations. On the nutritional front, AI optimizes recipes to achieve specific goals, whether it’s reducing sugar content or increasing protein levels, while also predicting nutritional content to meet labeling requirements.
Recently, food companies have applied AI in their R&D cycles, reducing product development and processing time from months to days. Unilever used AI to create low-salt products, speeding up the flavor analysis process from months to days. Kraft Heinz tested AI algorithms to optimize costs, sugar, and salt, achieving remarkable results. Quantitative descriptive analysis achieved 94% accuracy in reproducing the original tomato product.
Optimizing productivity and costs . After developing food products at laboratory scale, food companies face the challenge of arranging machinery and lines for large-scale production while maintaining the same competitiveness and quality as at laboratory scale. AI provides a solution by analyzing data to determine the optimal conditions for scaling up production.
Pioneering startups like Animal Alternative Technologies and Umami Bioworks are leading the way in this space, developing scalable intellectual property and technology through data science optimization. Another notable startup in this space is Eternal, which uses AI and robotics to automate testing, analysis, and optimization of biomass fermentation. These advances are also benefiting large manufacturers looking for a viable and sustainable path to large-scale alternative protein production.
Challenges to AI Application in the Food Industry
The application of AI in the food industry offers many benefits, including cost efficiency, speed, customization, predictive capabilities, and data-driven insights. However, the process also faces a number of challenges.
Limited historical data : An emerging field like food technology lacks historical data to feed algorithms, making it more difficult to generate meaningful results. If available, it is often found in various unstructured and disparate data formats. Therefore, there is a need for development to make relevant input data in a more recognizable form.
High implementation costs : Setting up and maintaining an AI system can be expensive, especially for small businesses. On the other hand, large companies’ current systems may not be future-proof and therefore require significant investment to continue to grow.
Legal and ethical complexities : The increasing complexity of AI systems, especially in predictive applications, raises the challenge of accountability from a legal and ethical perspective to address potential AI errors and consequences. Additionally, assessing the impact of AI on traditional food culture is critical to understanding its overall impact.
Data security issues : Protecting proprietary data, such as secret recipes, while promoting data sharing to optimize AI applications is a complex challenge that requires effective governance mechanisms. Additionally, protecting against digital attacks is critical.
Changing regulations : Food laws change frequently, requiring AI systems to keep up with these adjustments. Additionally, regulations often require interpretation, which current AI may not be well-suited to.
Multidisciplinary collaboration and skill sharing : Combining AI and food expertise requires effective communication between experts from different fields (food scientists, engineers, and data scientists). This requires accelerated skill sharing and cross-functional building to make integrated, data-driven decisions.
Consumer Acceptance : Alleviating consumer concerns and fears about AI-produced food requires rigorous, in-depth research. It is a long, rigorous, and expensive research process.
Environmental Impact : In addition to efficiency, the environmental impact of AI needs to be considered and weighed against the benefits of reducing environmental impact. Addressing these challenges is critical to helping the food industry capitalize on the potential of AI, while proactively addressing its limitations and societal implications.
Prospects of AI application in the food industry
Since the late 2010s, the world has seen a surge in startups specializing in AI-based food product development. The crux of the matter lies in providing AI-based solutions for tasks such as market analysis, consumer insights forecasting, as well as predictive modeling for product and process parameters.
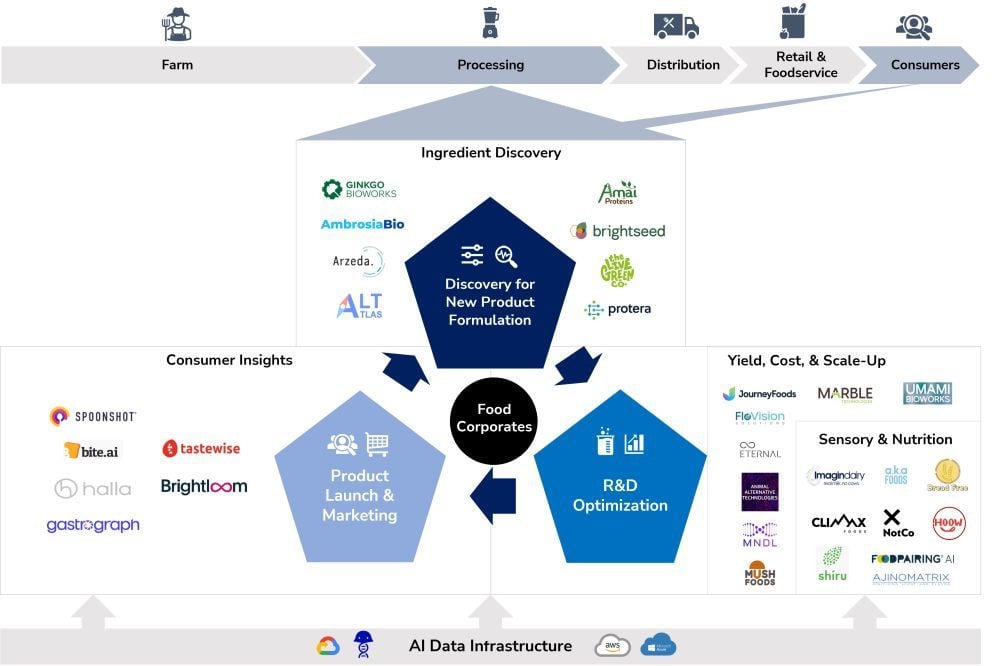
Startups are increasingly merging with food companies to drive innovation – a trend that is expected to gain more momentum in the near future. Challenges in data quality, processing power, and ethics are emerging, however, AI applications have already penetrated deeply into the food industry. Therefore, once a harmonized application mechanism is determined, AI is expected to revolutionize the food industry.
The powerful synergy between AI and food technology is an inevitable link to address growing food demand and sustainability requirements. From new product design inspiration based on consumer demand data, to suggested new process parameters that can improve productivity and reduce costs, AI will contribute to optimizing every step in the new product development cycle of the food industry in the coming time.
(According to peakbridge.vc, ieeexplore.ieee.org)
Source



![[Photo] T&T 1 and Ho Chi Minh City 1 People's Police Teams won the men's and women's team championships](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/22/39db06ae67cb4001b7a556e8d9a56d07)































































































![[Podcast] Week introducing more than 500 OCOP products in Hanoi](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/22/d144aac2416744718388dbae3260e7fd)

Comment (0)