According to Space , the supermoon on the Mid-Autumn Festival night (August 15th lunar calendar) will be at its fullest when it moves to the point opposite the Sun in the sky at an angle of 180 degrees. This moment will happen at about 4:57 p.m. on September 29 - just a little before sunset on the Mid-Autumn Festival night.
When observing the fullest supermoon at sunset, astronomy lovers will have a very beautiful view due to the "moon illusion" effect, which occurs when looking at this celestial body while it is still hanging low, through a thick layer of atmosphere. This illusion will make the supermoon have a magical pink-orange color and look even bigger.
This is also the last supermoon to appear in 2023, also known as the "Harvest Moon." This supermoon will not be as bright as the rare "super blue moon" in August, but will still appear brighter and larger than a normal full moon.
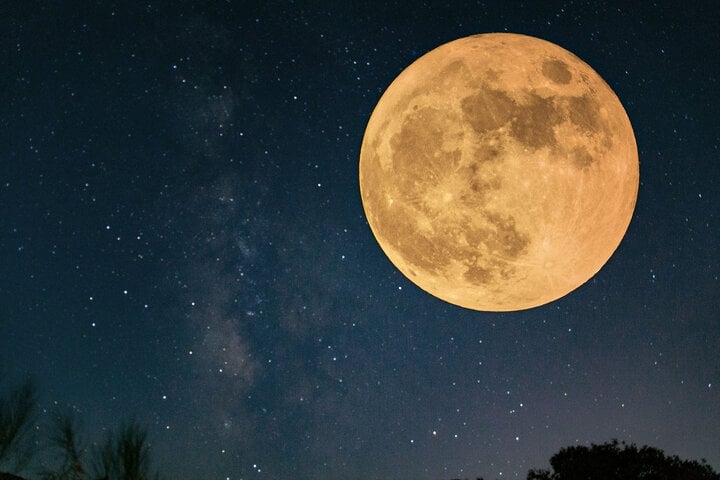

This year's Mid-Autumn Festival coincides with the appearance of the last supermoon of 2023. (Photo: The Epoch Times)
At perigee, the Moon is only 361,552 km from Earth, 21,000 km closer than the average of 382,900 km.
The September supermoon is accompanied by Jupiter and Saturn, which will be clearly visible during these days. Jupiter will be located right next to the supermoon's left side, in the constellation Aries.
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) defines a supermoon as a full moon that can be up to 14% larger and 30% brighter than the dimmest moon of the year. The reason is that when a supermoon occurs, the moon is at its closest point to Earth in its orbit, called perigee.
"The difference between this full moon and the August supermoon is only 4,370 km. So it will be very close to 14% and 30% of the largest full moon of the year," said Noah Petro, project scientist for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter at NASA.
As for the name "harvest moon," it comes from the time when farmers in the Northern Hemisphere are ready to harvest their crops. While it's not as close or bright as August's supermoon, it can take on a deep yellow, orange, or red hue, especially as it rises above the horizon.
According to Mr. Petro, the Moon only changes color when it rises or sets on the horizon, or during a lunar eclipse. The reason is similar to the phenomenon of red sunrise and sunset.
"The Earth's atmosphere scatters light, except for red or orange," Petro explains. Atmospheric elements such as clouds, smoke, and dust can also change the color and brightness of the Moon.
Moonrise is the best time to see the full size of a supermoon. When the moon is close to the horizon, foreground objects like trees and rocks can give a clearer sense of size. As a result, the moon appears at its largest at this time, according to NASA.
Tra Khanh (Source: Space)
Source



![[Photo] Dan Mountain Ginseng, a precious gift from nature to Kinh Bac land](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F11%2F30%2F1764493588163_ndo_br_anh-longform-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)




































































































Comment (0)