Processed foods
Processed foods are often high in preservatives, salt, sugar and saturated fats, which are difficult to digest and can negatively impact the digestive system. These ingredients can increase the risk of inflammation of the stomach and intestinal lining, leading to problems such as constipation or bloating.
Additionally, diets high in processed foods have been linked to obesity and other metabolic problems like diabetes and heart disease.
Fried food
Fried foods are high in fat, especially saturated and trans fats. This slows down digestion, causing bloating, indigestion, and heartburn.
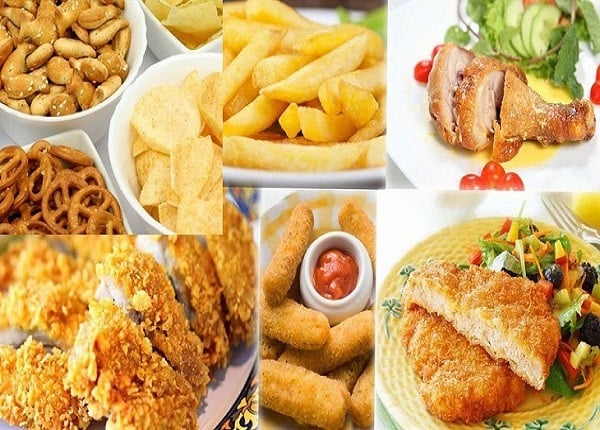

Consuming too much fried foods can increase the risk of gastritis.
Excessive consumption of fried foods can increase the risk of gastritis, stomach ulcers and cardiovascular disease.
Spicy food
Spicy foods can irritate the lining of the stomach and esophagus, leading to heartburn and indigestion. In addition, capsaicin – the main compound that gives chili peppers their spicy taste – can also increase stomach acid secretion when consumed in large amounts, which can make the burning pain symptoms in people with gastritis / ulcers worse.
Drink a lot of alcohol or caffeine
Both alcohol and caffeinated drinks can increase stomach acid secretion, irritating the lining, leading to problems such as heartburn, gastritis and stomach ulcers.
In addition, consuming too much caffeine can also reduce esophageal spasm function, causing esophageal reflux and heartburn. Meanwhile, drinking too much alcohol or drinking for a long time can also damage the liver, causing fatty liver and possibly leading to cirrhosis.
Raw, undercooked or undercooked food
Raw or undercooked foods, such as sashimi, soft-boiled eggs or rare beef, carry the risk of contamination with worms, bacteria and parasites. These agents can cause food poisoning, gastrointestinal infections and acute diarrhea.
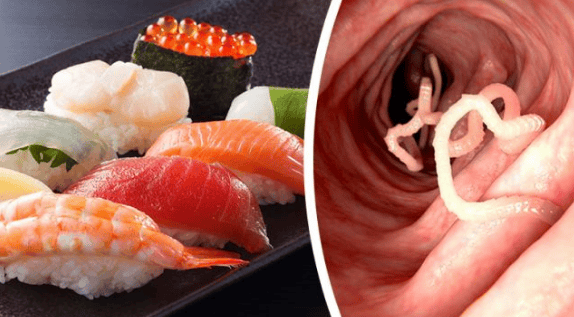
Raw or undercooked foods, such as sashimi, soft-boiled eggs or rare beef, pose a risk of contamination with worms, bacteria and parasites.
Carbonated soft drink
Carbonated soft drinks contain sugar, artificial sweeteners and carbonation, which if overused will have negative effects on digestive health. Specifically:
Carbonation and acid in soft drinks: Can irritate the stomach lining, leading to heartburn, acid reflux, and other problems like bloating.
Sugar and artificial sweeteners: Can disrupt the bacterial balance in the gut, increasing the growth of harmful bacteria, while inhibiting beneficial bacteria.
Additionally, excessive consumption of soft drinks is linked to metabolic diseases such as fatty liver, diabetes and obesity, which affect the digestive system and overall health.
Source: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/tranh-xa-cac-thuc-pham-sau-neu-khong-muon-bi-loet-da-day-va-benh-tim-mach-172250418023541423.htm





![[Photo] Magical moment of double five-colored clouds on Ba Den mountain on the day of the Buddha's relic procession](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/9/7a710556965c413397f9e38ac9708d2f)




















![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam begins official visit to Russia and attends the 80th Anniversary of Victory over Fascism](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/8/5d2566d7f67d4a1e9b88bc677831ec9d)


































































Comment (0)