Ho Chi Minh City – Ms. Phuong Anh, 36 years old, is busy with work and often holds her urine, causing her bladder to double its normal size and resulting in a loss of the urge to urinate.
The woman, a department head at a software company, worked continuously from morning till night, drank little water, and held her urine. Over time, she lost the urge to urinate, only feeling a dull ache in her stomach, but even then, she had difficulty urinating and a weak urine stream. Recently, she experienced blood in her urine, self-medicated, and drank over a liter of water, but still had no need to urinate.
On October 18th, Dr. Le Phuc Lien, Head of the Female Urology Unit, Center for Urology - Nephrology - Andrology, Tam Anh General Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, suspected the patient had excessive bladder distension due to prolonged urine retention, leading to loss of sensation and a risk of bladder muscle paralysis. The patient also had a urinary tract infection, resulting in hematuria (blood in the urine).
Urodynamic measurements (bladder pressure measurement) showed that the patient's bladder capacity was twice that of a normal person, capable of holding 700-1,000 ml of fluid. Doctor Phuc Lien believes the patient was fortunate that the bladder muscle had not been damaged.
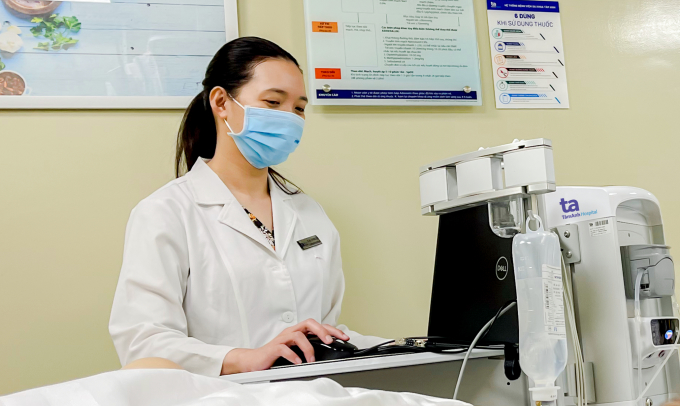

Doctor Phuc Lien monitors the patient's urodynamic measurement results. Photo: Anh Thu.
Dr. Lien prescribed medication for medical treatment, instructed the patient to practice urinating every 2-3 hours, not holding it in for more than three hours, and to practice bladder muscle exercises daily. If the patient adheres well to the instructions, the bladder muscles and the sensation of needing to urinate will recover, the risk of urinary tract infections will decrease, and the hematuria will disappear.
At Tam Anh Hospital in Ho Chi Minh City, approximately 50% of young people seeking urological examinations report symptoms such as loss of sensation during urination, urinary incontinence, urinary tract infections, and hematuria (blood in urine). Their common causes include drinking insufficient water, holding urine for extended periods due to busy work schedules, forgetfulness, or a lack of attention to their health. This condition is also frequently seen in older adults with urinary tract diseases or weakened bodies due to age.
According to doctors, holding urine for too long causes the bladder to expand to hold all the waste fluid. Over time, the body loses its natural reflex to urinate regularly and loses the sensation of needing to urinate. The muscles that open or close the urethra to prevent urine from flowing out gradually lose control, causing urine to leak out (urinary incontinence, frequent urination), especially when laughing loudly, sneezing, or coughing.
If the bladder muscle is overstretched for too long, it can become paralyzed. At this point, no medication can stimulate the bladder muscle to function again. The patient will lose control of their urination.
Prolonged retention of urine in the bladder can also cause urinary stones and urinary tract infections. The risk of these conditions is higher if the patient does not drink enough water. Women, especially pregnant women, are more susceptible to urinary tract infections due to their shorter urethra compared to men.
Recurrent urinary tract infections can lead to complications such as interstitial cystitis, causing decreased urine output, frequent urination, and persistent bladder and pelvic pain. Interstitial cystitis is incurable; only temporary pain relief is possible.
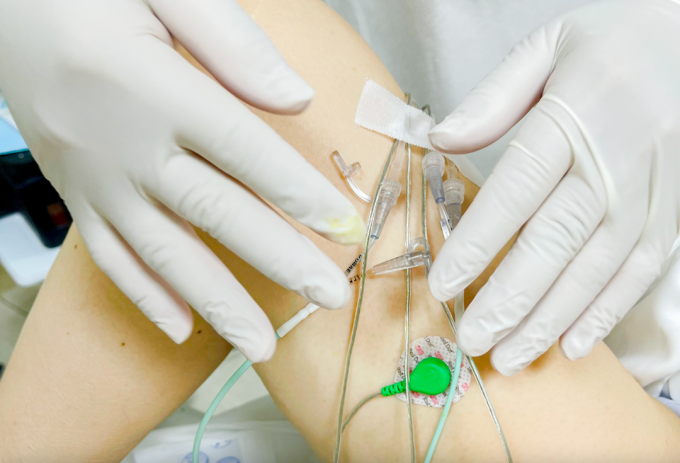
Nurses perform urodynamic testing to assess bladder function. Photo: Anh Thư
Dr. Lien stated that holding urine for too long not only harms the bladder but also causes urine to flow back up to the kidneys, leading to infection or kidney damage, and in the worst cases, kidney failure. This is the final complication of urinary tract diseases. Failed kidneys cannot filter toxins and waste products from the blood, causing a decline in overall health. Currently, there is no cure for kidney failure; treatment can only slow its progression. End-stage kidney failure requires dialysis or a kidney transplant to sustain life.
Doctors recommend that people urinate every 2-3 hours, avoid overfilling the bladder, and refrain from holding in urine. Urinating fewer than 8 times a day, with a steady, easy stream of urine and a feeling of empty bladder, is normal. Adults urinate 1-2 liters of water per day, depending on fluid intake and the amount of water lost through sweat and breath.
People experiencing symptoms such as blood in the urine, difficulty urinating, urinary incontinence, or loss of the urge to urinate should see a urologist immediately for diagnosis and early treatment.
Anh Thu
| Readers can post their urinary tract questions here for doctors to answer. |
Source link











































































































Comment (0)