 |
| Young journalists in the professional exchange program with Associate Professor, Dr. Do Thi Thu Hang - Head of the Professional Department of the Vietnam Journalists Association . (Photo: Dan Viet) |
It can be said that the destination of digital transformation of journalism is digital journalism. To develop and manage digital journalism - a media journalism associated with digital subjects, digital content, digital platforms, digital tools, it is necessary and useful to approach the theory of information society to analyze and find out the problems for the development of digital journalism.
Reaching the public in a new way
Reality shows that the information society in Vietnam is in the process of formation and development. All developed economic countries clearly understand the need for state orientation in the information market and have issued legal documents to regulate the activities of state power agencies, agencies responsible for building and implementing national information policies.
In the information society, digital press and mass media play an important role on the Internet. Print newspapers, if they want to be accessible to the public, must find ways to digitize to appear in the "public space" and digital ecosystem. The press is based on the flow of press information with four traditional forms and traditional means of propaganda, agitation, and advertising. Now there are many information flows with overlapping content and information forms.
In terms of models, the information society forms three major streams including: first, interpersonal communication forms and media; second, press and mass media; third, social media. These three components are closely related and have a dialectical relationship, reciprocal and interactive with each other.
Digital journalism, when published on social media platforms, will interact with the information society in five dimensions, including: first , developing the digital economy, with the origin of the digital media economy; second , promoting technology and diffusing science and technology; third, creating career changes in society; fourth , creating diverse and rich information flows, with three basic information flows corresponding to groups of press and media products on social media platforms as mentioned above, along with interpersonal communication and social media, with fierce competition to occupy the leading position to attract the public and lead public opinion; fifth , signs of expansion, of which the most important are signs of expanding democracy, media culture, media safety and security, responsibility to the community, society, etc.
Prerequisites
Each press agency needs to identify the digital newsroom model as the destination of digital transformation. Considering digital journalism in a dialectical, inseparable relationship is a prerequisite for building a digital newsroom model, converging Digital Content + Digital Technology + Digital Public + Digital Economy .
Corresponding to this is the model of convergence of four areas of the digital newsroom, including: digital product area (planning digital content strategy); digital business operation area (including: determining key business positions, human resources and material resources within the newsroom responsible for organizing production and distribution of digital press products and value-added services; key partners of the press agency); digital public area (public segmentation, digital customers, customer relations, marketing, implementing digital public/customer development strategy); digital economic area - administration, business of digital press products and value-added services.
This is also a prerequisite for the issues raised with the elements of digital journalism, including: digital journalism subjects (journalists, machines/robots, digital public), digital content, digital platforms, digital tools, and digital ecosystems.
Recently, research on the experience of using social networks and new media tools in public opinion polls, organizing communication programs and campaigns and crisis management in countries provides many suitable references for governments of developing countries in general and Asian media in particular, including Vietnam.
Key factors
Practice shows that, in addition to building a digital journalism model and digital transformation in press agencies, it is necessary to focus on key factors: human resources and material resources. In particular, human resources for digital journalism are currently very lacking and weak compared to reality.
The requirements for digital journalism subjects are very high: they need to have the qualities and capacity to perform seven functional blocks of the digital newsroom model including: first, the management and direction function layer; second, the technical infrastructure layer; third, the shared services layer; fourth, the application and database layer; fifth, the portal service layer; sixth, the distribution channel; seventh, the user/public layer.
Therefore, there needs to be a specific strategy and solution for digital journalism subjects with the ability to use and control technology in all processes, content creation processes, and editorial office management.
Vietnam, like many other countries, is making great efforts to achieve this goal. Information technology resources are core but not enough. There needs to be human resources capable of using and applying traditional digital technology platforms and new technology platforms such as: audio, automated journalism, chatbots, live-stream video and content creation platforms compatible with vertical, horizontal and multimedia digital storytelling techniques. In other words, communication technology capacity must always be integrated with content creation capacity compatible with technology platforms and multi-channel, multi-platform coordination, including both traditional platforms and new social platforms.
In determining the training content and human resource development, it is necessary to include three core groups: digital technology + digital content + digital fine arts. However, with a bachelor's training program, it is difficult to "force" too much training content, both basic and specialized knowledge and skills, updating new achievements and technology trends (which change daily, hourly). The process of updating content to be compatible with the rapid innovation of platforms and trends in applying communication technology faces many barriers, along with the barriers to building curricula and learning materials on digital technology or digital content today.
For short-term training courses (less than three months), the pressure on training content is many times greater because the input of members of the training courses is not equal, and only focused in a short period of time, making it even more difficult to develop content and teaching materials.
Training in communication technology requires multidisciplinary knowledge and innovation capacity of the training subject, requiring organization according to the 4.0 education model, including the operation of connection and interaction of modeling, practical learning (experience), learning according to needs, applying artificial intelligence, organizing the deep learning process of learners, practical assessment and diversifying training forms, especially distance learning (online).
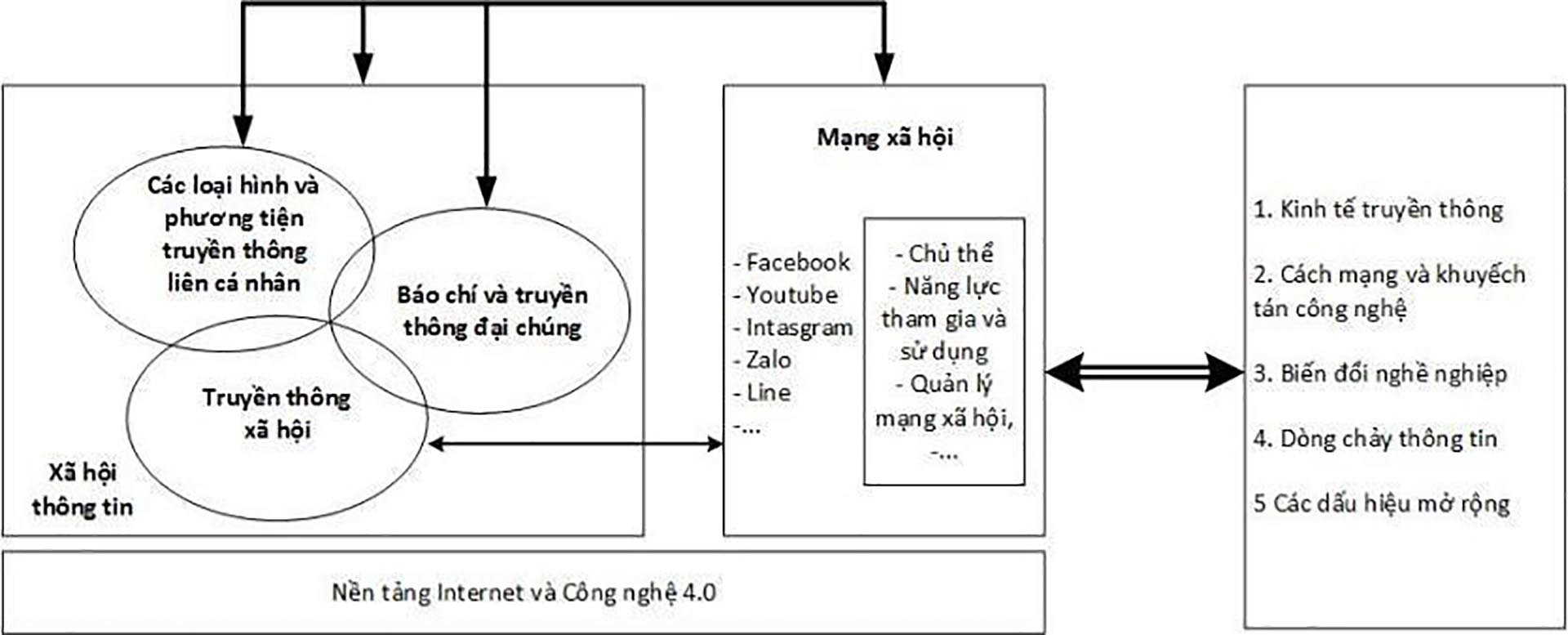 |
| Model of social network interaction analysis from the perspective of information society. |
Efforts to train human resources for policy communication
The training fields of information technology and media journalism have a wide open market due to the great attraction from press agencies, media enterprises in the media industry, culture and entertainment industry. Due to the compatible job positions, the number of graduates choosing to work in the field of policy communication is less. The ability to apply technology in policy communication does not meet the high requirements as in the field of journalism or business.
The target group for training policy communication human resources is usually the human resources working in the propaganda or communication departments of Party agencies, central ministries, or local authorities at all levels. These groups have uneven qualifications, most of them are no longer young, so accessing the technology field, especially learning through practice, is much more difficult than university students with good background knowledge and the ability to adapt quickly in the digital environment.
Despite great efforts in investing in facilities, techniques and technology in training communication technology, most training institutions in Vietnam still face limitations due to the compulsory nature of training in communication technology practice. Field trips and internships for students are a huge challenge because in reality, there are not many communication institutions that have sufficient conditions in terms of human resources for guidance, policy communication technology models, and advanced policy communication technology platforms, so organizing vocational skills training is a significant difficulty.
Source


![[Photo] Hue: Inside the kitchen that donates thousands of meals a day to people in flooded areas](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/29/1761738508516_bepcomhue-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chaired a meeting to evaluate the operation of the two-level local government model.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/29/1761751710674_dsc-7999-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Human love in the flood in Hue](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/29/1761740905727_4125427122470875256-2-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chaired a meeting to discuss solutions to overcome the consequences of floods in the central provinces.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/29/1761716305524_dsc-7735-jpg.webp)










































































![[Live] Concert Ha Long 2025: "Heritage Spirit - Brightening the Future"](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/29/1761743605124_g-anh-sang-am-thanh-hoanh-trang-cua-chuong-trinh-mang-den-trai-nghiem-dang-nho-cho-du-khach-22450328-17617424836781829598445-93-0-733-1024-crop-1761742492749383512980.jpeg)





























Comment (0)