According to Daily Mail, the US Space Force (USSF) is still keeping secret information about the missions that this $200 million spacecraft performs.
The X-37B has completed seven successful missions, but much of its activities remain shrouded in secrecy. Officials have only said the craft is engaged in a series of experiments involving “spatial awareness technology,” without revealing specific details.
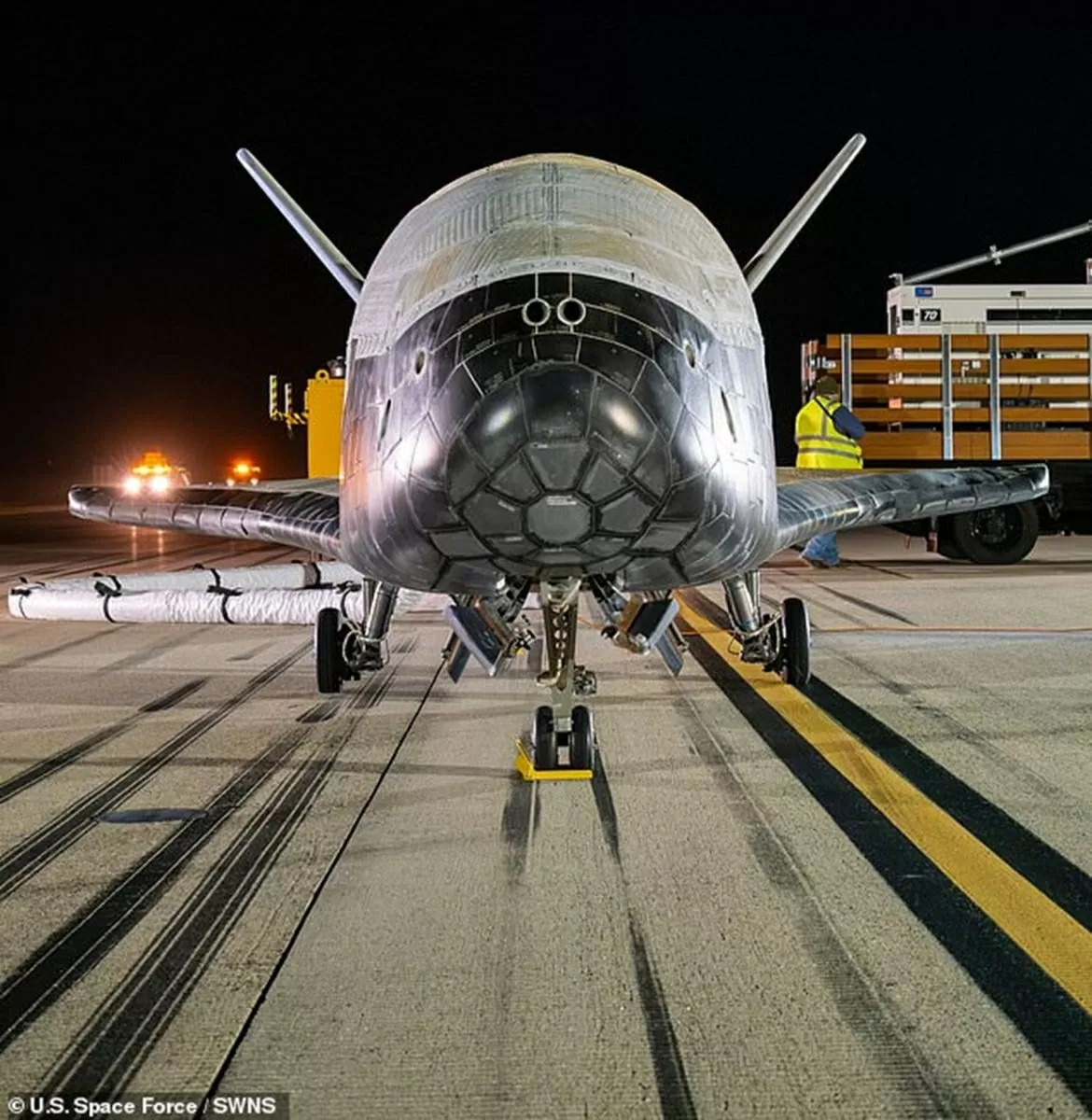 |
| The US Space Force's X-37B spacecraft. (Source: USSF) |
The overall role of the USSF, however, is clear. In a recent speech, General Bradley Chance Saltzman, the USSF's chief of operations, emphasized the importance of controlling space.
"Control of the space domain is a unique mission of the fighting forces, a responsibility that only the military can undertake. Space is the new battlefield and our goal is to achieve absolute superiority," Mr. Saltzman declared.
He also said the USSF is ready to use both "dynamic" ( military operations) and "non-dynamic" (electronic warfare, signal jamming) measures to weaken or neutralize adversary capabilities when necessary.
What did the X-37B test during its 434 days?
The X-37B is an unmanned aircraft launched from the Kennedy Space Center (Florida) in late December 2023. Although its main mission remains a mystery, observers say the spacecraft could be used to track other satellites in orbit.
What is certain is that in October 2024, the X-37B performed a new set of recorded flight maneuvers. The spacecraft tested a technique called “aerobraking,” which involves using the Earth’s atmosphere to slow down.
Specifically, the X-37B lowered into orbit, sending part of the spacecraft into the atmosphere. As air molecules rub against the surface of the spacecraft, drag is created to help it slow down. This is an important tactic to adjust the orbit or reduce speed enough for Earth's gravity to pull the spacecraft back.
Additionally, the technique allows for the removal of a service module attached to the rear of the X-37B before landing, although the contents of the module have not been revealed.
"The X-37B's seventh mission opened new possibilities, demonstrating that the spacecraft can conduct flexible experiments in a variety of orbital regimes," Saltzman said in a USSF statement.
X-37B – a tool for the US to gain space superiority?
The X-37B, built by Boeing, has a similar design to NASA's former space shuttle. It is launched into orbit by a rocket and returns to Earth like a conventional aircraft.
Holly Murphy, Boeing’s program manager, said in a November 2024 video that the X-37B missions continue to advance American space technology. “We are testing new technologies, reducing risk and shaping the future of space systems,” he said.
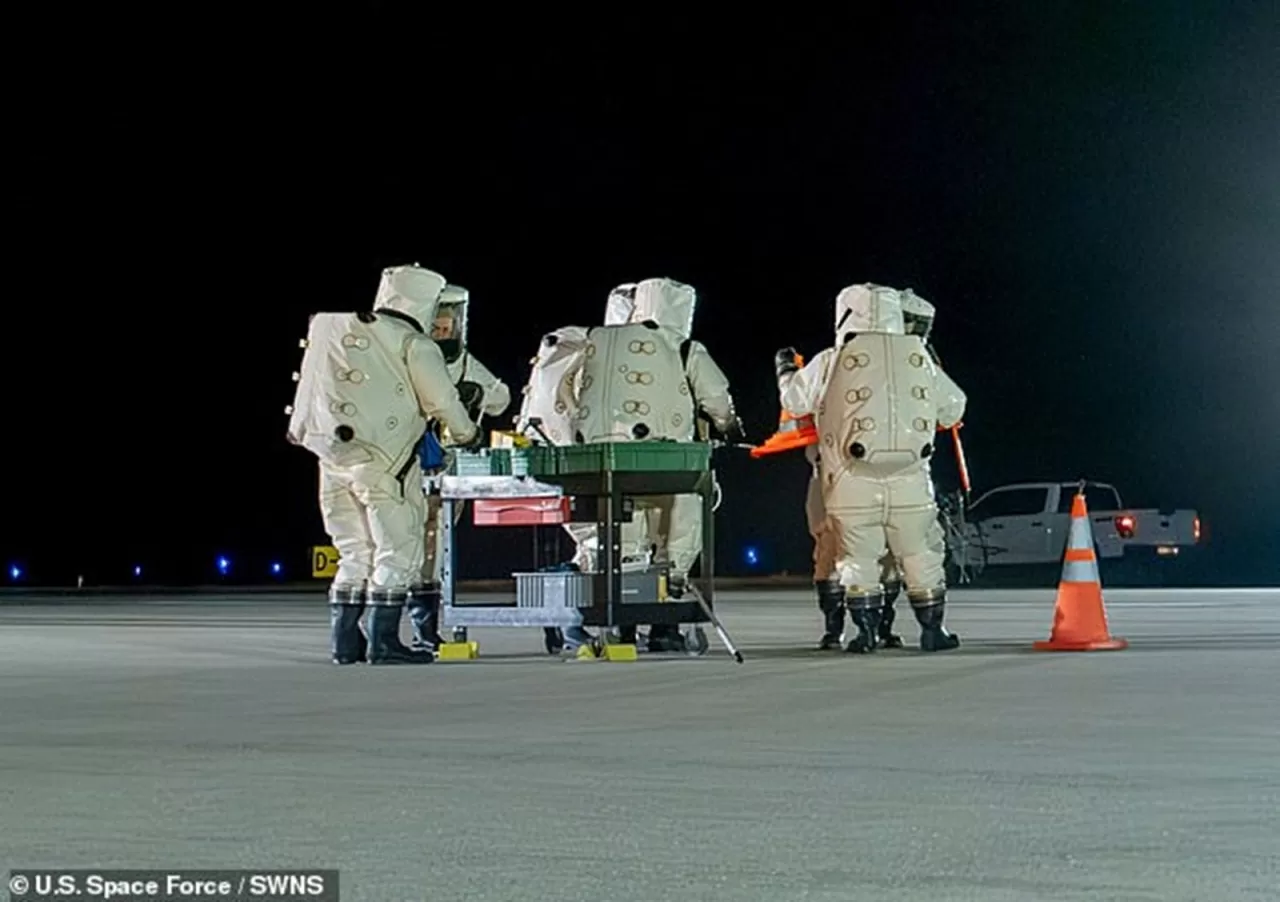 |
| Ground crews at Vandenberg Space Base were on hand to witness the X-37B's landing. (Source: USSF) |
After a 434-day journey, the spacecraft landed at Vandenberg Space Base in California early on the morning of March 8.
In a speech at the Association of Air and Space Forces Warfighting Conference in Aurora, Colorado on March 4, General Saltzman emphasized the importance of gaining superiority in the space domain, especially in the context of strategic competition with other powers.
"If we truly want to be space warriors, we need to accept responsibility for controlling space. We must perfect all elements: manpower, training, equipment and sustainment. If any element is lacking, we will lose our strategic advantage," he declared.
The X-37B may be just one part of a broader US strategy to cement its lead in the space race. And while the spacecraft’s exact mission remains unclear, it’s clearly a key piece in the Pentagon’s space ambitions.
Source


![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam received the delegation attending the international conference on Vietnam studies](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/26/1761456527874_a1-bnd-5260-7947-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Nhan Dan Newspaper displays and solicits comments on the Draft Documents of the 14th National Party Congress](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/26/1761470328996_ndo_br_bao-long-171-8916-jpg.webp)

![[Photo] Enjoy the Liuyang Fireworks Festival in Hunan, China](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/26/1761463428882_ndo_br_02-1-my-1-jpg.webp)






















![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh attends the opening of the 47th ASEAN Summit](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/26/1761452925332_c2a-jpg.webp)














































































Comment (0)