A stroke can cause the patient to lose the ability to walk, talk, or function independently in just a few minutes. Proper rehabilitation can help a lot.
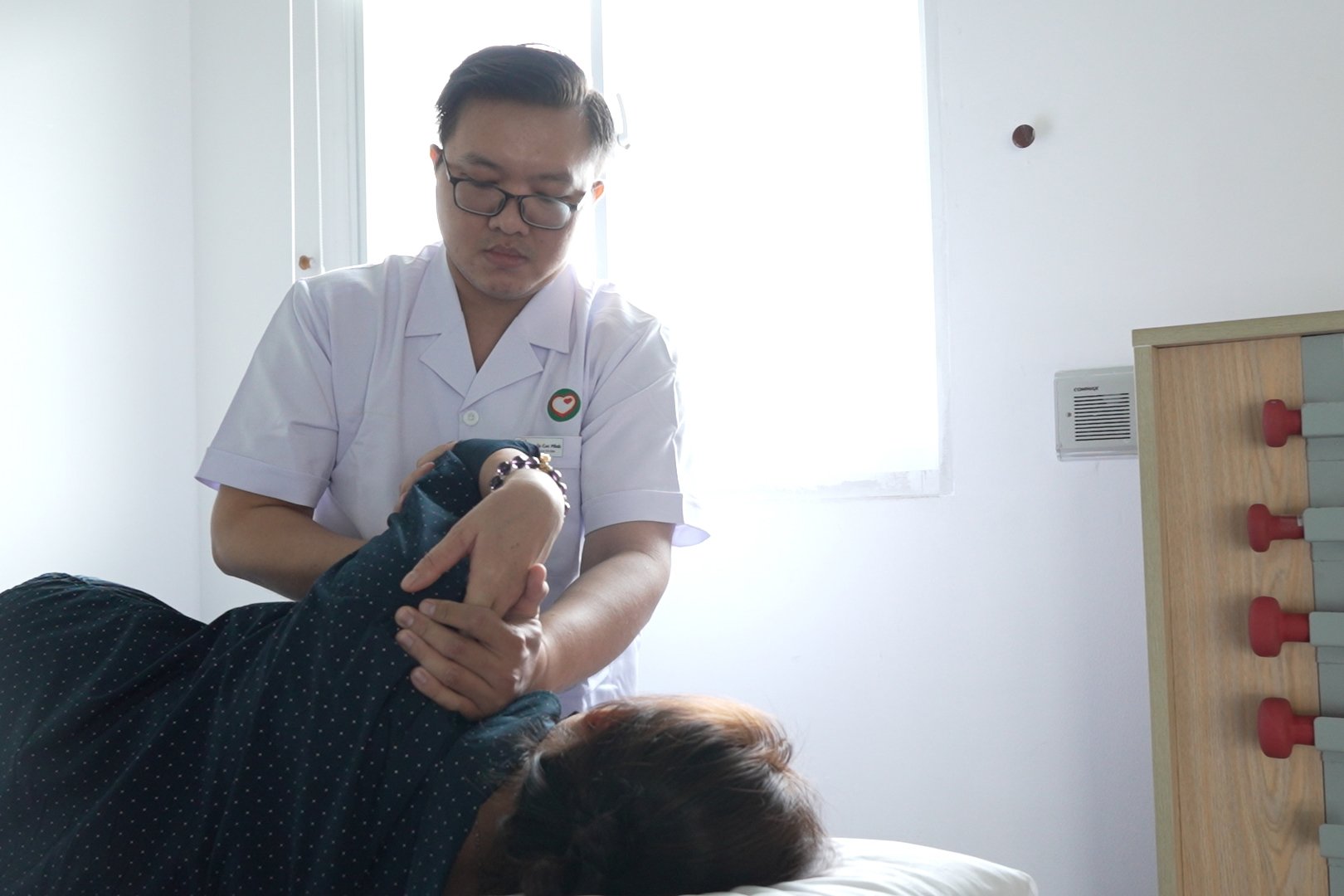
Rehabilitation helps patients relearn skills lost after a stroke - Photo: T.D.
Starting early, being persistent and choosing the right method are the keys to helping patients overcome stroke sequelae and regain independence.
What is stroke rehabilitation?
Stroke rehabilitation is a program of different therapies designed to help patients relearn skills lost after a stroke.
Rehabilitation methods depend on the part of the brain affected by the stroke. Rehabilitation helps improve mobility, speech, and daily living skills, helping patients regain independence and improve quality of life.
Stroke causes many complications and the level of recovery of each patient is also different. Studies have noted that patients who participate in intensive stroke rehabilitation programs have better outcomes than those who do not participate in the program. Therefore, stroke rehabilitation is recommended for all stroke patients.
There are five main types of disabilities caused by stroke:
Paralysis, problems controlling movement: walking, balance, swallowing…
Sensory disturbances (ability to perceive multiple senses of touch, temperature, position, etc.)
Difficulty using or understanding language
Problems with thinking and memory
Emotional disorders
There are many approaches to helping people recover from a stroke. In general, rehabilitation focuses on specific, repetitive actions. The rehabilitation plan depends on the body parts or abilities affected by the stroke.
Physical activities include:
Motor skills exercises: exercises that help improve muscle strength and coordination, including the muscles used for balance, walking, and even swallowing.
Mobility training: patients learn how to use mobility aids such as walkers, canes, wheelchairs, ankle braces, etc.
Restriction-induced therapy: An unaffected limb is restrained while the patient practices moving the affected limb to help improve function of that limb.
Range of motion therapy: Certain exercises and treatments help relieve muscle tension, and help patients regain range of motion.
Cognitive and emotional activities include:
Cognitive symptom therapy: Occupational therapy and speech therapy help patients overcome cognitive deficits including memory, processing, problem solving, judgment, and safety awareness.
Communication therapy: Speech therapy helps regain the ability to speak, listen, write, and understand.
Psychological assessment and treatment: The patient's ability to regulate emotions may be tested, with counseling or support group participation.
When should stroke rehabilitation start?
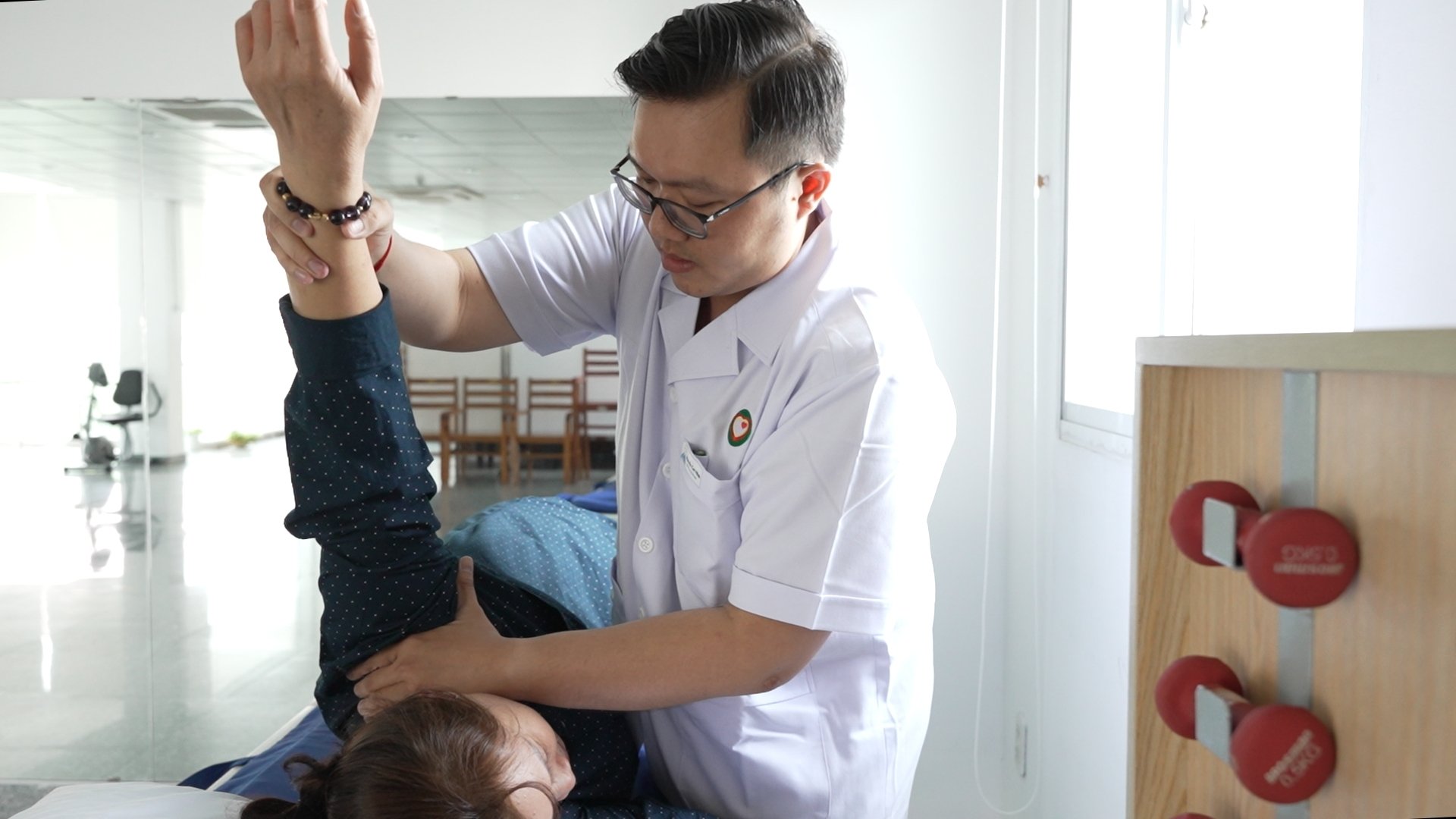
The sooner stroke patients start rehabilitation, the better - Photo: T.D.
The sooner a patient begins rehabilitation after a stroke, the better the chance of regaining lost abilities and skills.
Stroke rehabilitation usually begins as early as 24 to 48 hours after a stroke and while the patient is still in the hospital.
Stroke rehabilitation time depends on the severity of the stroke and associated complications.
Some stroke survivors recover quickly. But most need some form of long-term stroke rehabilitation. This can last for months or years after the stroke.
Stroke rehabilitation plans change throughout recovery as patients relearn skills and their needs change. With continued practice, patients can continue to make progress over time.
Where to rehabilitate after stroke?
Stroke rehabilitation can begin while still in the hospital. Before discharge, the patient and family will work with medical staff to determine the best rehabilitation environment.
Factors to consider include: the patient's needs, medical condition, and what is most convenient for you and your family.
Stroke rehabilitation involves many professionals from different fields.
Doctors: Primary care physicians, neurologists, and rehabilitation specialists can guide patient care and help prevent complications. Doctors work together to help patients achieve and maintain a healthy lifestyle to avoid future strokes.
Physical therapist: helps patients relearn skills such as walking and balance.
Speech and language therapist: helps improve a patient's language skills, swallowing ability, and develop tools to address memory, thinking, and communication problems.
Psychologists : assess patients' thinking skills and help address patients' mental and emotional health problems.
Factors affecting stroke recovery outcomes
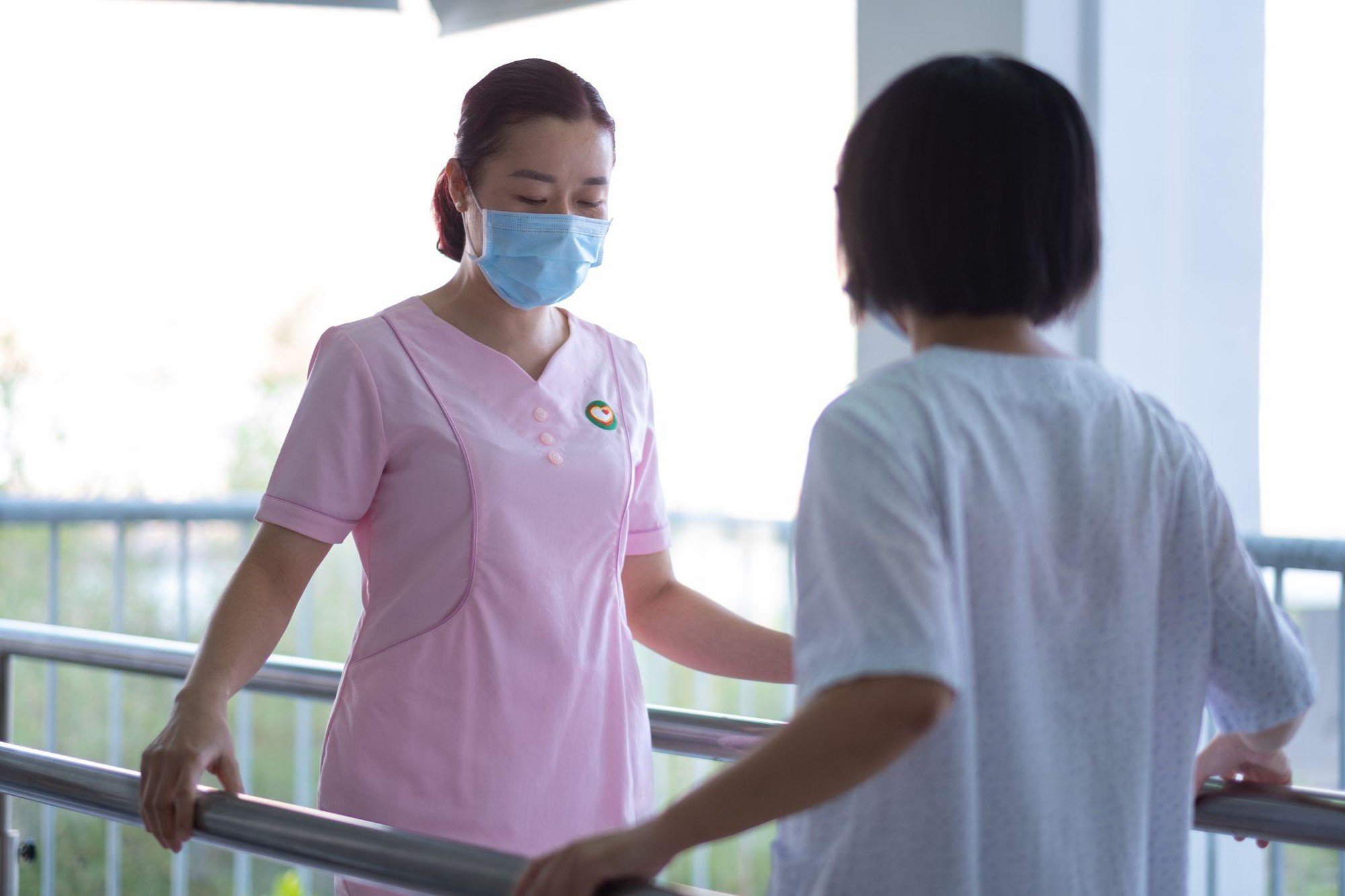

Post-stroke rehabilitation involves many experts from different fields - Photo: T.D.
Stroke recovery varies from patient to patient. It is difficult to predict how much a patient will recover and how long it will take. In general, successful stroke recovery depends on:
The severity of a stroke in terms of both cognitive and physical effects.
Emotional factors: such as motivation, mood, and ability to maintain rehabilitation activities outside of therapy sessions.
Social factors: support from friends and family.
Therapeutic factors, including early initiation of rehabilitation and the skill of the stroke rehabilitation team.
Recovery rates are usually highest in the first weeks and months after a stroke. However, there is evidence that outcomes can improve even 12 to 18 months after a stroke.
Rehabilitation after a stroke is a long-term "battle", requiring close coordination between the patient, family and team of experts. Although it is impossible to predict the exact recovery time, starting early, maintaining motivation and taking advantage of intensive therapies will open up opportunities for the patient to not only survive but also live better, gradually overcoming the "darkness" of the sequelae.
 Why are there strokes in young people?
Why are there strokes in young people?Source: https://tuoitre.vn/phuc-hoi-chuc-nang-sau-dot-quy-dung-cham-tre-20250314152457891.htm




![[Photo] Nhan Dan Newspaper launches “Fatherland in the Heart: The Concert Film”](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/16/1760622132545_thiet-ke-chua-co-ten-36-png.webp)


![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam attends the 18th Hanoi Party Congress, term 2025-2030](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/16/1760581023342_cover-0367-jpg.webp)































![[Video] TripAdvisor honors many famous attractions of Ninh Binh](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/16/1760574721908_vinh-danh-ninh-binh-7368-jpg.webp)



























![[Photo] Nhan Dan Newspaper launches “Fatherland in the Heart: The Concert Film”](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/16/1760622132545_thiet-ke-chua-co-ten-36-png.webp)







































Comment (0)