Intercostal myalgia is a common condition that affects the muscles between two or more ribs. The pain can make it difficult to perform movements that require strength in the rib area, according to the health website Medical News Today (UK).
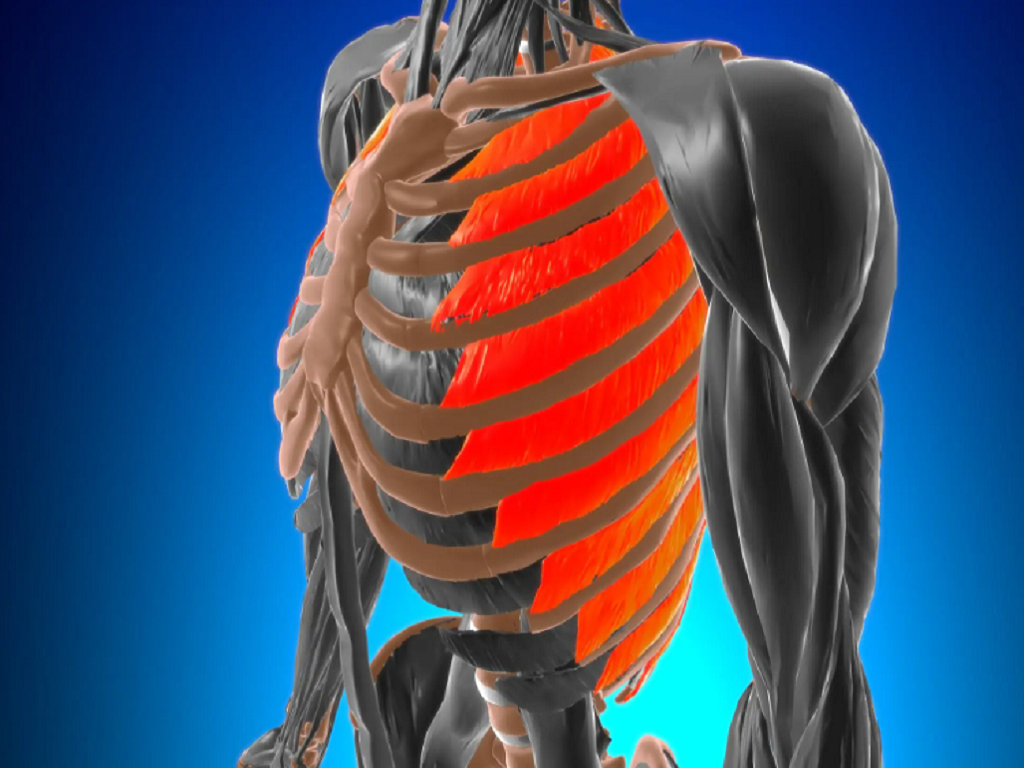
Overexertion can strain or tear the muscles holding the ribs together, leading to intercostal muscle pain.
Common causes of intercostal muscle pain include:
Muscle strain or injury
Many cases of intercostal muscle pain are caused by muscle strains or physical trauma. Muscle strains often occur due to sudden movements, excessive coughing, or overuse of the intercostal muscles during exercise or heavy lifting.
These activities can cause the muscles between the ribs to be stretched or torn. In addition to pain, intercostal muscle strains sometimes cause swelling. Meanwhile, physical injuries are often caused by accidents, falls or collisions while playing sports , especially sports that require strength such as martial arts and football.
Repetitive motion
Performing repetitive movements that impact the rib area can also cause intercostal muscle pain. This is because these movements may not be too strong, but because they are performed repeatedly, they can cause the muscles to be overstretched or torn.
This type of pain is especially evident when performing the same repetitive movements. The sufferer needs to rest and limit movement of the flank area to prevent the risk of further muscle damage.
Poor posture
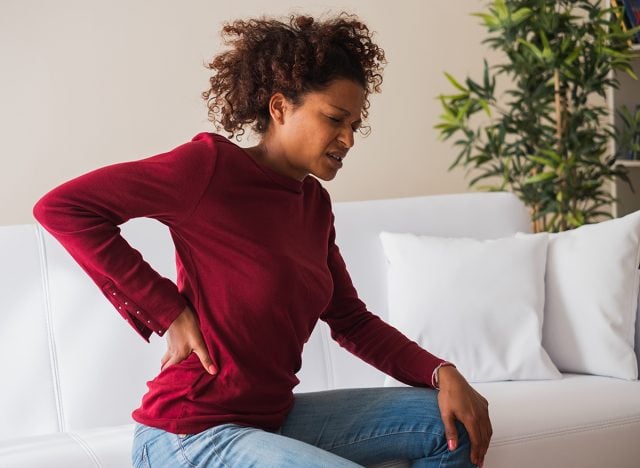

Poor posture, such as sitting slouched, is another cause of intercostal muscle pain.
Poor posture, such as slouching, is another cause of intercostal muscle pain. Holding this position for hours on end can cause muscle imbalances and put pressure on the intercostal muscles. If left untreated and prolonged, this can lead to weakness of the intercostal muscles and increase the risk of back pain and spinal disc damage. It is important to address poor posture habits and seek treatment from a healthcare professional to prevent injury and relieve intercostal muscle pain.
Intercostal pain usually improves with rest, ice packs, and gentle stretching. In severe cases, over-the-counter painkillers, such as paracetamol, may be used.
If the pain persists or worsens, you should see a doctor because it is likely not a physical injury or a simple muscle strain, but a more serious health problem, such as intercostal neuritis, according to Medical News Today.
Source link



![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man receives United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/25/1761390815792_ctqh-jpg.webp)


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh and United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres attend the Press Conference of the Hanoi Convention Signing Ceremony](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/25/1761391413866_conguoctt-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/25/1761390212729_dsc-1484-jpg.webp)























![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam meets with General Secretary and President of Laos Thongloun Sisoulith](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/25/1761380913135_a1-bnd-4751-1374-7632-jpg.webp)












































































Comment (0)