According to the US Federal Reserve (Fed), people with higher incomes will borrow more money than people with lower incomes.
Fed data shows that households with below-average incomes hold about 36% of all home loans, while the richest 1% own more than 4% of all mortgage debt in the country.
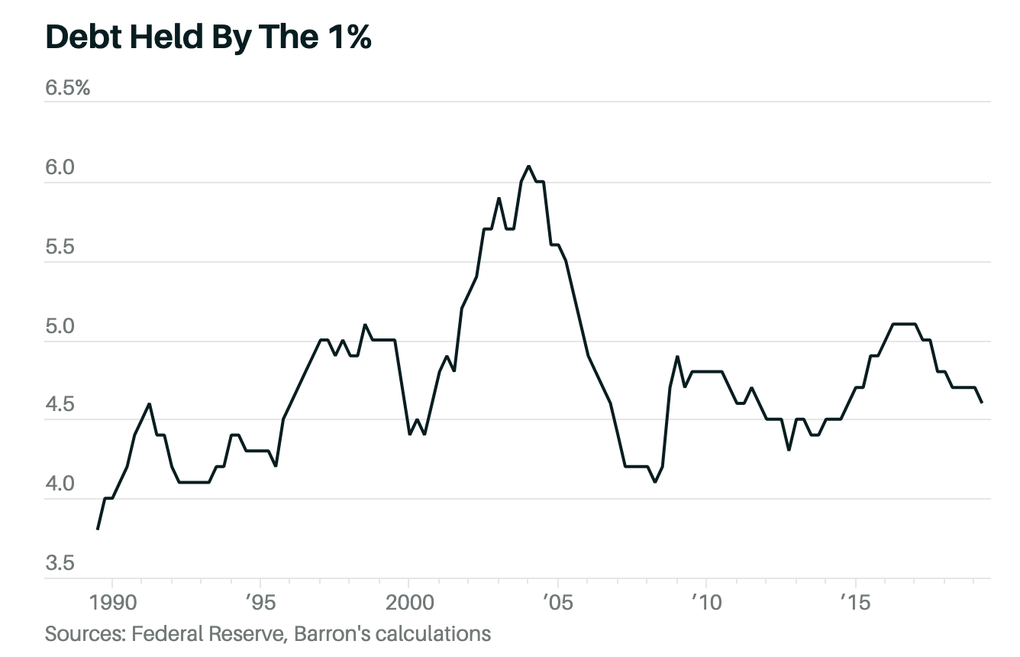
The 2019 figures show that the richest 1% had about $700 billion in debt. The top 1% had a combined net worth of about $25 trillion. Debt is only a small part of their total wealth.
The top 1% of Americans hold about 4-5% of all real estate loans (Photo: Barron).
So why do rich people, even though they have money, still borrow? And they often borrow to invest in large assets such as real estate?
Rich people don't keep a lot of cash.
Contrary to depictions in popular Hollywood movies, millionaires and billionaires don't actually have a lot of money in their homes or in their bank accounts.
In fact, billionaires' money is distributed across different asset classes such as real estate, stocks, bonds, and other valuable assets. Cash is the safest asset but has the lowest return.
In other words, billionaires rarely have cash on hand.
So when they need money to invest in new opportunities, the rich leverage their assets to borrow money. This money is then put into assets that generate more income. Leveraging borrowed money is how billionaires grow their wealth quickly.
The cost of cheap loans
Typically, people with high incomes will receive lower loan terms and interest rates than those with average incomes.
Why is this?
First, they already have assets and high incomes, so they are considered less risky borrowers. Wealthy people are less likely to default. And even if they do default, banks have many different options for recovering their debts. So banks tend to lend to wealthy people at lower interest rates.
In addition, rich people will have large collateral when borrowing. This also reduces interest rates.

Rich people often get loans at low interest rates because they are considered less risky (Photo: Tran Khang).
The Power of Financial Leverage
For example, with a down payment of $10,000, a real estate investor could own a home worth $200,000 with monthly payments of $2,000.
If the property appreciates 20% from $200,000 to $240,000, a $10,000 down payment would generate a 300% return on investment of $40,000. That’s the power of financial leverage.
In addition, the rich also use debt to buy real estate to rent monthly. This real estate creates monthly cash flow. This source of income also creates profits for them greater than the initial cost of borrowing.
Banks help inspect, evaluate and hold assets
When lending, the bank will check the legal factors related to this real estate. From there, the rich will know whether this real estate is clean or not. In addition, the bank will also evaluate this property. The rich will know how valuable this property is.
In addition, the rich are smart to use banks as a custodian of valuable assets. They borrow money and give the bank documents and land certificates instead of leaving them at home where they could be stolen.
Solid legal support
When borrowing, it means that the property is jointly owned with the bank. In case of a dispute related to this real estate, the bank will side with the borrower and share this risk with them.
Source



































































































Comment (0)