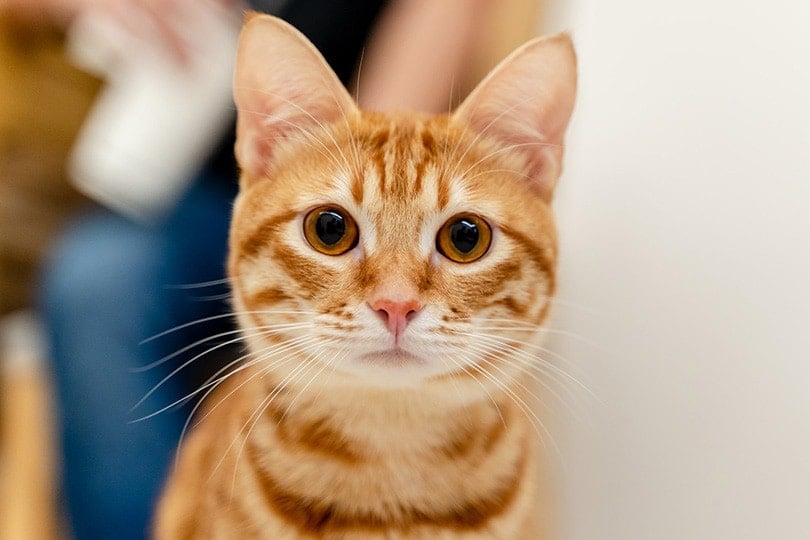

Researchers found a link between cat ownership and increased rates of schizophrenia-related disorders - Photo: Hepper
Australian researchers found a link between cat ownership and schizophrenia after analyzing 17 studies published over the past 44 years, from 11 countries, including the US and UK.
More findings on the link between cats and schizophrenia
"We found an association between cat ownership and increased rates of schizophrenia-related disorders," explain psychiatrist John McGrath and colleagues, all from the Queensland Mental Health Research Centre.
The idea that cat ownership may be linked to an increased risk of schizophrenia was suggested in a 1995 study, with exposure to a parasite called Toxoplasma gondii thought to be the cause.
But so far, research has come to mixed conclusions.
Studies have found that being around cats during childhood may make a person more likely to develop schizophrenia. However, not all studies have found this link.
Some people have also linked exposure to cats to higher scores on scales measuring schizophrenia-related traits, which affect thinking, emotions, and behavior, and psychotic-like experiences. Conversely, again, other studies have shown no link.
To get a clearer picture, McGrath and his team say it’s important to carefully review and analyze all the research on these topics. Toxoplasma gondii is a largely harmless parasite that can be transmitted through undercooked meat or contaminated water.
The bite of an infected cat or infected cat feces can also transmit Toxoplasma gondii .
An estimated 40 million people in the US may be infected, often without any symptoms. Meanwhile, researchers continue to find more bizarre effects the infection can have.
Once in the human body, Toxoplasma gondii can invade the central nervous system and affect neurotransmitters. This parasite has been linked to personality changes, the appearance of psychotic symptoms, and a number of neurological disorders, including schizophrenia.
More research is needed to conclude
"After adjusting for covariates, we found that people exposed to cats had approximately double the risk of developing schizophrenia," the researchers said.
There are a few important things to note here, such as the fact that 15 of the 17 studies were case-control studies. These types of studies cannot prove cause and effect, and often do not consider factors that may influence both exposure and outcome. Some of the studies reviewed were of low quality, which the authors also highlighted.
A US study of 354 psychology students found no link between cat ownership and schizophrenia scores. However, those who had been bitten by a cat scored higher than those who had not.
Another study, which included people with and without psychiatric disorders, found a link between cat bites and higher scores on tests measuring specific psychological experiences. But they suggested that other pathogens such as Pasteurella multocida could be the cause instead.
Researchers agree that better and more extensive research is needed before any firm explanations can be made.
"In summary, our review provides evidence supporting an association between cat ownership and schizophrenia-related disorders. More high-quality studies, based on large representative samples, are needed to better understand cat ownership as a factor that may modify the risk of psychosis," the authors write.
Source



![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam holds a brief meeting with Russian President Vladimir Putin](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/10/bfaa3ffbc920467893367c80b68984c6)


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs a meeting of the Steering Committee for key projects in the transport sector.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/10/0f4a774f29ce4699b015316413a1d09e)























































































Comment (0)