Saliva is secreted from salivary glands in the mouth. The main salivary glands are the parotid gland, the sublingual gland, and the submandibular gland. Saliva not only keeps the mouth moist but also aids digestion, controls oral bacteria, and performs several other functions, according to the health website Healthline (USA).
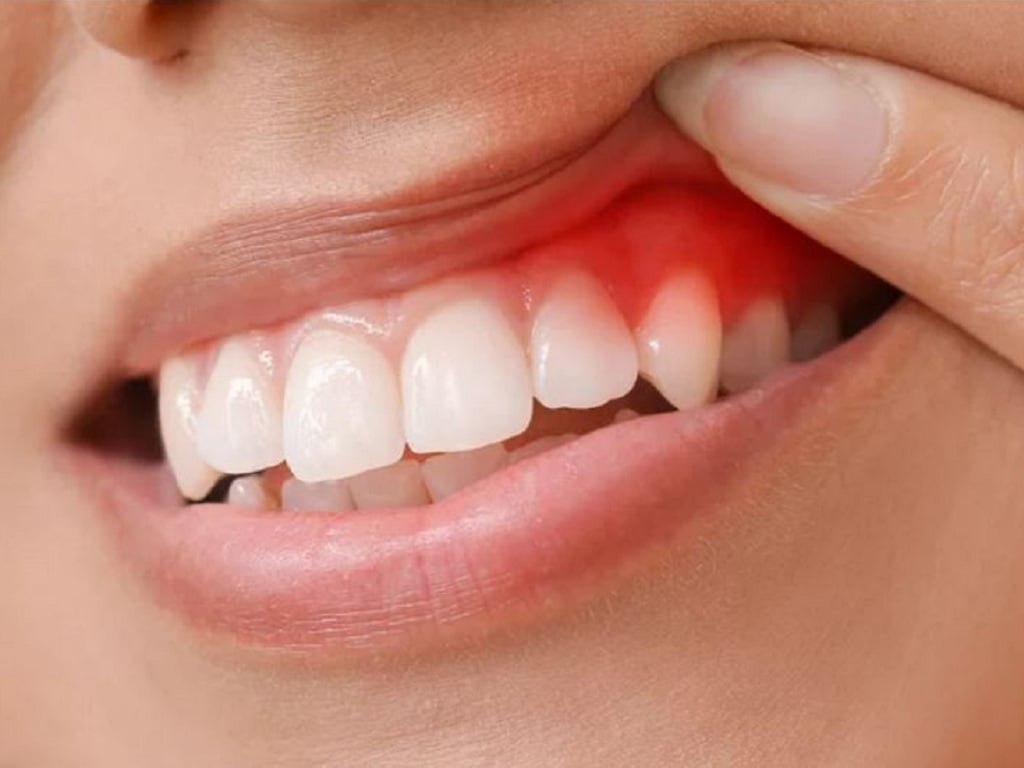
Gum inflammation can cause blood to appear in saliva.
Changes in the color and texture of saliva can be a sign of an abnormality. If you see blood in your saliva, especially after brushing your teeth, it could be a warning sign of gingivitis or periodontitis.
Inflamed or bleeding gums can also mean bacteria are entering the bloodstream. Yellow saliva, in the case of phlegm, may be a sign of a bacterial or viral infection in the respiratory tract.
If your saliva is thick, white, and you have white patches in your mouth, it's a sign of a yeast infection, also known as oral thrush. Oral thrush is caused by an overgrowth of Candida albicans yeast in the mouth.
If your saliva is normal in color and consistency (clear and watery) but you frequently experience a sour taste in your mouth, especially after thorough oral hygiene, it could be a sign of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). If this condition persists, you should see a doctor for prompt examination and treatment, according to Healthline .
Source link
































































































![[Photo] Coc Ly market bustling on the eve of Tet](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2026/02/14/1771062261424_baolaocai-br_img-6457-jpg.webp)







Comment (0)