A proper diet is the key to managing and preventing gout. Patients need to maintain a balanced, nutritious diet, limit foods rich in purines and combine a healthy lifestyle to effectively control the disease.
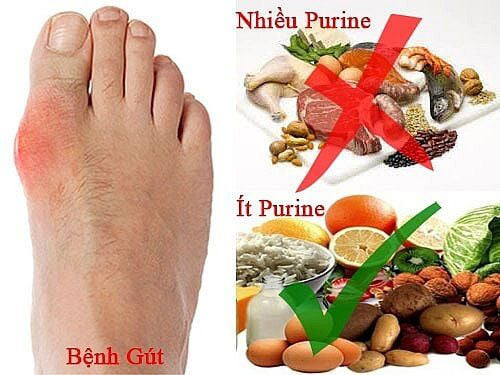
Good and bad foods for people with gout
Common mistakes
According to MSc. Bui Thi Thuy - Department of Pediatric Nutrition Consultation, National Institute of Nutrition, gout is a metabolic disorder, characterized by increased uric acid in the blood, leading to the deposition of urate crystals in joints and soft tissues, causing inflammation and pain.
"This is a common disease in Vietnam, especially among adults. Gout is one of the most common inflammatory joint diseases in middle-aged men in Vietnam. There is an increasing trend of younger people getting the disease, with many cases recorded in the 20-30 age group," said Dr. Thuy.
Although the disease is more common in men, women are also at risk, especially after menopause, the risk increases due to the decline in estrogen, the hormone that helps eliminate uric acid through the kidneys.
A proper diet is the key to managing and preventing gout. Patients need to maintain a balanced, nutritious diet, limit foods rich in purines and combine a healthy lifestyle to effectively control the disease.
However, completely abstaining from protein in the diet of gout patients is a serious mistake.
Below are common mistakes related to protein abstinence in gout patients and how to adjust accordingly:
Completely abstain from protein-rich foods
According to Dr. Thuy, protein is an essential nutrient for the body, helping to maintain muscles, regenerate tissues and produce enzymes. Completely abstaining from protein can cause malnutrition, reduce resistance and weaken the body.
Patients need to reduce foods rich in purines (a component of protein), not abstain from protein completely.
No distinction between protein sources
Dr. Thuy also said that not all types of protein have a negative impact on gout. Animal foods contain more purines than plant foods, so it is important to choose the right type.
For example, mackerel and animal organs contain higher amounts of purines than milk or eggs.
Therefore, people with gout should eat: Eggs, low-fat milk, cheese, tofu, lentils (low purine content).
Limit red meat (beef, lamb), seafood (shrimp, crab, sardines), and animal organs.
Eat a lot of plant protein without control
In fact, some plant foods such as mushrooms, asparagus, or soybeans also contain purines, which, if consumed in excess, will increase uric acid.
So, eat plant-based protein in moderation, combining it with a variety of other foods to ensure balance.
Eating too much protein substitute in one meal
Even if you choose healthy protein sources, eating too much protein in one meal can still increase uric acid, making gout worse.
Therefore, you should divide the amount of protein needed throughout the day (about 0.8-1g protein/kg body weight per day, depending on the condition). Combine protein with vegetables to reduce purine absorption.
Believe that protein-rich foods increase uric acid
Some foods, such as low-fat milk and dairy products, actually help lower uric acid levels and protect joints. Avoiding them will negate the nutritional benefits.
Patients should add low-fat milk, yogurt or whey protein to their diet.
Focusing only on protein and forgetting to control other factors
In addition to protein, other factors such as alcohol, sugary drinks (soft drinks, bottled fruit juices) also increase uric acid. If you only focus on avoiding protein without limiting these factors, the disease will not improve.
Therefore, patients should avoid alcohol (especially beer), sugary soft drinks. Drink enough water (2-3 liters/day) to help eliminate uric acid.
General dietary advice for gout sufferers
Improper protein restriction not only causes nutritional imbalance but can also aggravate the disease. Eating properly, balanced and well-controlled food sources are the key to effective gout control.
- Foods rich in purines (should be avoided or limited as much as possible)
These foods contain 150-1,000mg of purine/100g of food such as animal organs (liver, kidney, heart, lungs, stomach, spleen, pancreas); seafood (sardines, anchovies, herring, mackerel, tuna, salmon, shrimp, crab, clams, oysters); red meat (beef, goat meat, lamb, fatty pork, fatty chicken);
Processed foods (sausages, sausages, bacon, canned meats, liver pâté); some plant foods (mushrooms, asparagus, cauliflower, peas, lentils, dried beans).
Alcoholic beverages: Beer (very rich in purines), spirits, red wine.
- Low purine foods (should be prioritized)
These foods contain
Green vegetables and fruits (green leafy vegetables, cabbage, bok choy, cucumber, pumpkin, carrots, sweet potatoes, potatoes); Fruits (apples, pears, oranges, watermelon, strawberries, blueberries, cherries, bananas, papaya, kiwi); grains and seeds (brown rice, oats, corn, walnuts, almonds, flaxseeds).
Healthy drinks: filtered water, alkaline mineral water, green tea, unsweetened herbal tea, pure fruit juice (cherry, lemon, orange).
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/mac-benh-gout-co-can-kieng-hoan-toan-dam-202502142022572.htm





![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs the second meeting of the Steering Committee on private economic development.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/01/1762006716873_dsc-9145-jpg.webp)




































































































Comment (0)