(NLDO) - A nearly 0.5m long skull and some other fossilized bones of a unique dinosaur were excavated in Jiangxi province, China.
According to Sci-News, the new tyrannosaurus rex species, named Asiatyrannus xui, lived in the southeastern region of China about 69 million years ago, at the end of the Cretaceous period.
The new species is a member of Tyrannosaurinae, one of two extinct subfamilies of Tyrannosauridae, the earliest derived group within the superfamily Tyrannosauroidea.
The most famous representative of the subfamily Tyrannosaurinae to which the new species belongs is the tyrannosaurus rex (T-rex).

The monster recently excavated in China is a relative of the T-rex - Photo AI: Anh Thu
A new sibling species of T-rex was excavated from the Nanxiong Formation in Shahe Town, Ganzhou City, Jiangxi Province, China.
Its discovery was completely unexpected, occurring when a construction project in the area exposed fossilized parts.
The fossil found included a nearly complete skull, measuring 47.5 centimeters long, and several other bones, enough for scientists to identify the lineage and reconstruct the monster's terrifying appearance.
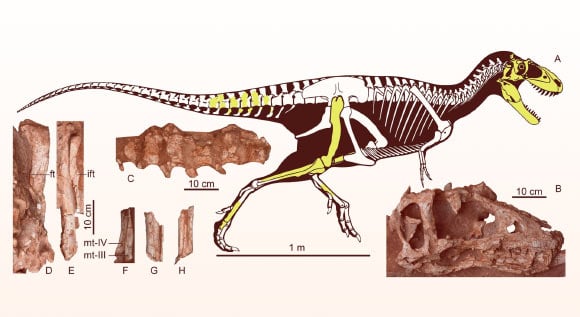
Some bones found - Photo: SCIENCTIFIC REPORTS
Publishing their findings in the scientific journal Scientific Reports, the research team led by Dr. Wenjie Zheng from the Zhejiang Provincial Museum of Natural History (China) said that this dinosaur, when alive, must have had a body length of up to 3.5-4m.
Despite its size, it was still only about half the size of its Qianzhousaurus relative previously found in China and many other tyrannosaurs from the same period.
Even Qianzhousaurus was only a medium-large tyrannosaur, so Asiatyrannus, at up to 4 m long, is still considered a medium-small in this lineage.
However, the animal's size is good news for researchers, because it is the "missing" beast in the fossil record that they have been looking for.
"Asiatyrannus and Qianzhousaurus have different skull proportions and body sizes, suggesting they may have occupied different ecological niches," Dr. Zheng explained.
In the Campano-Maastrichtian of East/Central Asia and Laramidia, large carnivore groups were dominated by tyrannosaurs, while medium-sized adult predators were rare or absent.
The new species may therefore be a good representative of this missing group of mid-sized carnivores, occupying a key ecological niche between giant dinosaurs and small, agile species. It helps complete the picture of the ecosystem in the Late Cretaceous region.
Source: https://nld.com.vn/lo-dien-loai-khung-long-bao-chua-hoan-toan-moi-o-trung-quoc-196240801102941311.htm



![[Photo] President Luong Cuong attends the inauguration of the international container port in Hai Phong](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/13/9544c01a03e241fdadb6f9708e1c0b65)
![[Photo] Many people in Hanoi welcome Buddha's relics to Quan Su Pagoda](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/13/3e93a7303e1d4d98b6a65e64be57e870)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives Ambassador of the French Republic to Vietnam Olivier Brochet](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/13/f5441496fa4a456abf47c8c747d2fe92)
![[Photo] President Luong Cuong awarded the title "Heroic City" to Hai Phong city](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/13/d1921aa358994c0f97435a490b3d5065)



![[Photo] Explore the Great Wall of Water in the Suburbs of Beijing, China](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/5/c2e706533d824a329167c84669e581a0)























































































Comment (0)