"China is not currently leading in innovation in the field of robotics, but it is only a matter of time before Chinese robotics companies gradually catch up with the leading countries," according to the Washington-based Information Technology and Innovation Foundation (ITIF).
Replacing humans with robots is often to save on labor costs. Accordingly, developed countries with high wages will have a higher robot penetration rate than countries with lower wages.
However, ITIF found that China is using more automation than would be expected based on worker wages in manufacturing, with 12.5 times more robots being used than expected. In contrast, the US is only using 70% of the robots it should be using.
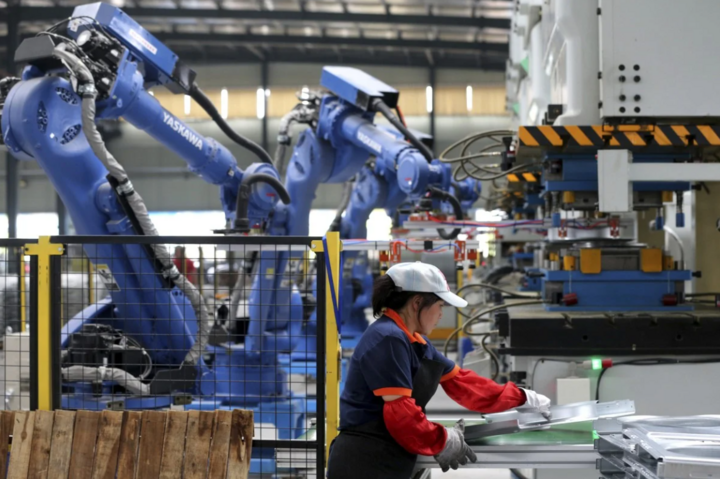

China's rate of robot production and deployment in manufacturing is growing faster than other countries. (Photo: SCMP)
ITIF's analysis of China's robotics industry is based on research of major companies and consultation with global experts.
Research shows that the pace of robot production and deployment in China is accelerating faster than any other country. The Chinese government has made the development of the robotics industry a priority, suggesting that the country’s robotics companies are likely to soon become leading innovators.
"China is now the world's largest industrial robot market. By 2022, 52% of the world's total industrial robots will be installed in China, up from 14% a decade earlier," said ITIF President Robert D. Atkinson, author of the report.
China's booming robot market can be attributed to strong domestic demand and strong policy support. The world's second-largest economy has a good manufacturing base and a complete industrial chain. The country is capable of providing technical support for robot development and has a wide range of applications.
Robots are now used in a wide range of sectors of the Chinese economy, including manufacturing, logistics, hospitality, healthcare and construction. “China’s automotive industry is the largest in the world, which is also a benefit that drives China’s adoption of robots, as the automotive industry is a major customer of industrial robots,” said Mr. Atkinson.
Despite being a pioneer in the field of robotics, the US lags behind the world in robot exports due to lack of long-term investment. The leading companies today come from Germany, Japan and Switzerland. China dominates the production and use of robots.
“China has been the world's largest industrial robot market for eight consecutive years,” said Mr. Atkinson.
According to ITIF, China's booming robot market has been supported by large subsidies from various levels of government, which have encouraged the adoption of robots and other automation technology.
The huge and rapidly growing demand for industrial automation has spawned a plethora of robotics startups, many of which are based in Dongguan city (Guangdong province, southern China), an area known for its large-scale robotics industry.
The rise of these startups signals significant advantages and cost efficiencies.
“Companies in Dongguan can develop a new technology product five to 10 times faster than in Silicon Valley or Europe, at only one-fifth or one-quarter of the cost,” said Professor Li Zexiang at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology.
The ITIF report also pointed out that China's robot industry is still heavily dependent on foreign technology, with many components imported mainly from companies in Japan, Germany and Switzerland.
Despite the positive growth, the report notes two areas where China still lags. First, software, which accounts for about 80% of a robot’s value and is key to its quality and flexibility, remains a weak point for Chinese companies.
Compounding the software shortcomings is a lack of innovation. Many Chinese automation products look similar to those from Fanuc in Japan or Boston Robotics in the US, suggesting a tendency toward copying rather than original innovation.
Source










































































































Comment (0)