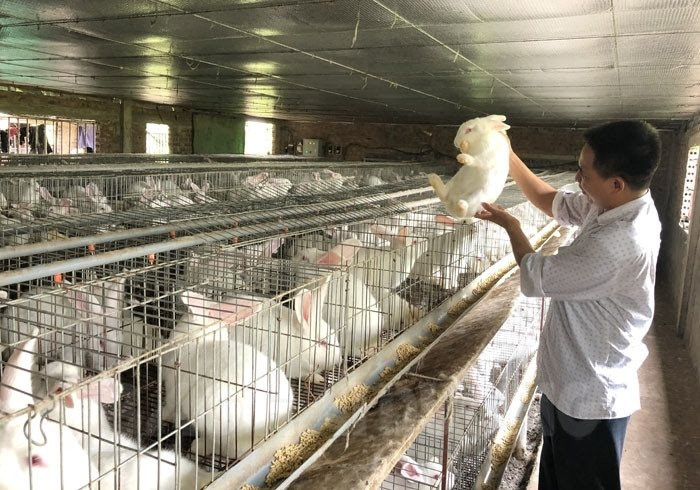

1. Cage
The cage must be airy, clean, and protected from rain and wind. Large-scale rabbit farming requires a cooling system and ventilation fan.
If raising rabbits on a family scale, you can place the cage under a shady tree in the garden or at the front of the house; do not let the rabbits be in the same cage as other pets.
2. Food and drink
Rabbits have a stomach that expands well but contracts weakly, a large caecum, and the ability to digest fiber thanks to microorganisms. Therefore, people pay attention to feeding rabbits a lot of green roughage to meet nutritional needs, prevent heat, and ensure good digestion.
Rabbits must be fed clean food, and rabbit food should not be stored for many days. If using leafy vegetables with a high water content, people should dry them to reduce the water before feeding them to rabbits or not feed rabbits crushed vegetables.
It should be noted that lack of water is more dangerous for rabbits than lack of food. Especially for rabbits giving birth, not providing enough water for them will lead to lack of milk, and the mother rabbit may even eat her babies. Therefore, during this period, people should give the mother rabbit more sugar water and vitamins to help the rabbit recover quickly and produce more milk to feed her babies.
For rabbits raised for meat in hot weather, the density should be 5-6 rabbits/cage. Do not transport rabbits when the temperature is high.
3. Disease prevention and treatment
Rabbits often suffer from diseases such as septicemia, mange, and coccidiosis.
a. Coccidiosis
Symptoms of coccidia infection in rabbits are often ruffled fur, poor appetite, sometimes diarrhea, green loose stools, higher than normal body temperature, runny nose, and drooling.
When rabbits have this disease, use anti-coccidial drugs such as: Anticoc, HanE3: 0.1-0.2 g/kg body weight. For disease prevention, use Anticoc, HanE3 at half the treatment dose.
b. Rabbit septicemia
This is an acute infectious disease caused by a virus. When exposed to an environment with poor hygiene and nutrition conditions, the disease breaks out very quickly and causes mass deaths. The disease mainly occurs in rabbits aged 1.5 months and older.
Rabbits with this disease sometimes become lethargic, stop eating for a short time and then die. Because the disease is caused by a virus, people need to proactively vaccinate with a dose of 1ml/rabbit when the rabbit reaches 2 months of age. For breeding rabbits, vaccinate periodically every 6-8 months.
c. Scabies
This is a very common parasitic skin disease, causing great harm in rabbit farming. If there are rabbits infected with the disease, they must be isolated and the cages and farming equipment must be periodically disinfected. When rabbits are infected, use Ivermectin injection 0.25 ml/1 kg of body weight.
NGUYEN MINH DUC, Deputy Head of the Department of Livestock and Veterinary Medicine of Hai Duong provinceSource: https://baohaiduong.vn/ky-thuat-nuoi-tho-mua-nang-nong-386414.html






![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs a meeting on the implementation of the Lao Cai-Hanoi-Hai Phong railway project.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/20/0fa4c9864f63456ebc0eb504c09c7e26)

















































































Comment (0)