Faced with attacks from powerful prey, many of the world's most foul-smelling animals have had to rely on their unique strength—their scent—to defend themselves. Thanks to this, many species have narrowly escaped death.
Bombardier beetle
The Bombardier beetle's body contains two chemicals called hydroquinone and hydrogen peroxide, which are used in the hair dye and beauty industries. When attacked or hunted, the Bombardier beetle mixes these two chemicals together, creating a sticky, slimy substance with an extremely unpleasant odor.
Although this animal's strength isn't enough to kill or threaten prey, it's its body scent that frightens enemies whenever they approach.
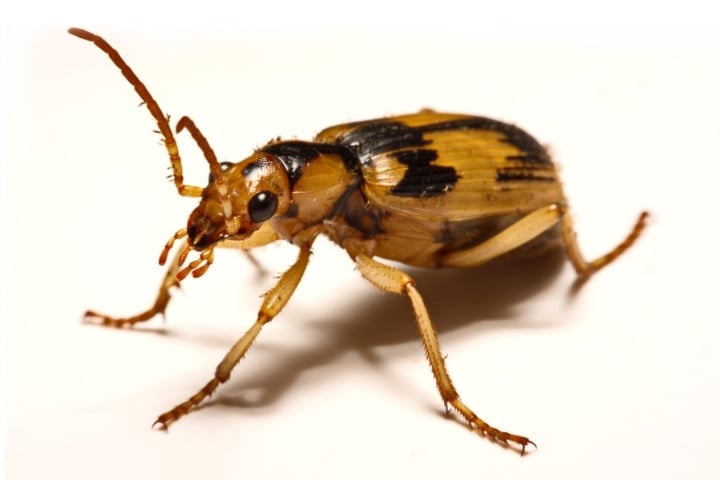

Although beetles are small, they have a scent that frightens many prey animals.
Wild-footed chicken
The wild Stinkbird, or Stinkbird, is found in the Amazon rainforest. One thing that helps this animal avoid humans is its meat, which has a terrible smell. Therefore, those who can eat the meat of the wild Stinkbird must be people who are not afraid of the foul odor.
This species of chicken measures approximately 65 cm in body length, has a long neck and a small head, a blue face, and red eyes. Additionally, it possesses an unusual digestive system and is also known by another name based on the foul odor emanating from its body: the weasel-like bird.
Tamandua tetradacty
Tamandua tetradacty is a mammal belonging to the anteater family, found in several South American countries such as Argentina, Brazil, and Uruguay. This animal is frequently preyed upon by jaguars when hungry.
When attacked, Tamandua tetradactyla emits a terrible stench from its anal glands under its tail, causing prey to stay away. We can easily smell them from about 50 meters away.
Gulo
The wolverine is also known as the skunk or skunk. This is because the animal resembles a carnivorous bear in appearance and has an unpleasant odor. The wolverine's habitat is the northern taiga (coniferous forest), sub-Arctic forests, and high-altitude tundra in the Northern Hemisphere.
Tasmanian Devil Rat
To protect themselves from other animals, the Tasmanian devil rat releases a highly foul-smelling substance accompanied by loud squeals. At the same time, this species of devil rat can eat almost any type of carcass, including bones, due to its sharp teeth and strong jaws.
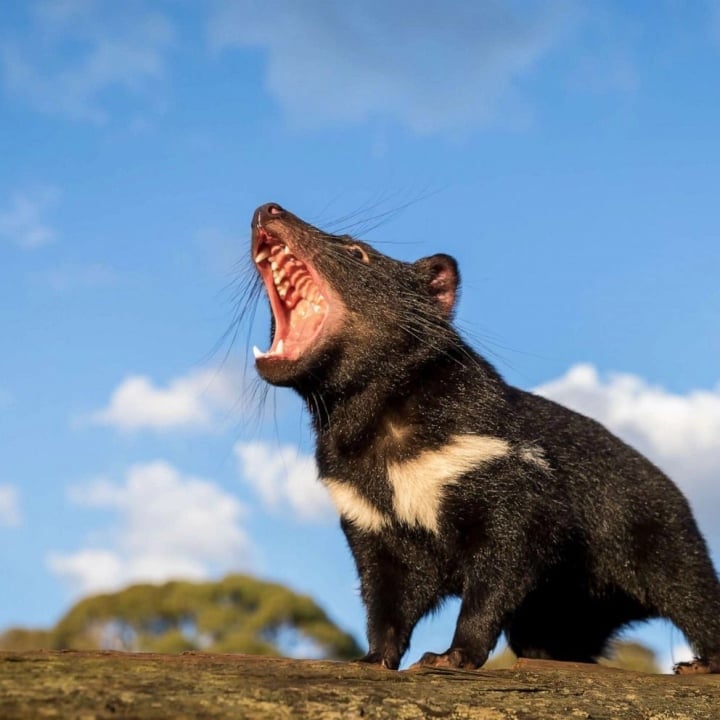

The Tasmanian devil rat is known as a devil.
Tasmani rats typically gather together to hunt prey, making loud growls and screams! Their main habitat is in canyons. Notably, Tasmani rats often feed on carrion, helping to reduce pollution and minimize waste in the human environment.
Musk cow
Musk oxen, native to the Arctic, possess a "foul odor" that causes immediate nausea in potential mates. During mating season, the male ox releases a foul-smelling fluid from special glands near its eyes. This fluid then clings to its fur, creating a stench to attract female oxen.
In the summer, musk oxen typically live in humid areas, such as river valleys. Their diet includes Arctic willow grass, lichens, and mosses found beneath the snow. When food is abundant, these oxen will eat more succulent and nutritious grasses.
Sea rabbit
Sea hares use a purple fluid secreted from glands in their bodies to spread their scent into the surrounding environment and paralyze the olfactory nerves of their prey. When encountering an enemy, they secrete this purple fluid to escape. Another venom gland, located in front of the outer membrane, secretes a milky white, acidic, foul-smelling fluid.
Tuyet Anh (Source: Compilation)
Beneficial
Emotion
Creative
Unique
Wrath
Source


![[Photo] Two flights successfully landed and took off at Long Thanh Airport.](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F15%2F1765808718882_ndo_br_img-8897-resize-5807-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)








































































































Comment (0)