(NB&CL) An alarming trend shows that readers and publishers alike no longer value preserving news online, in a world where readers are focused only on quick news, short videos that are read and then forgotten and never returned to. It is alarming that human knowledge is being lost.
38% of websites disappear after a decade.
The internet is an enormous repository of modern life, with hundreds of billions of web pages indexed. But even as users worldwide rely on the web to access books, images, news articles, and other resources, this content sometimes disappears.
A new analysis by the Pew Research Center reveals just how ephemeral online content truly is: As of October 2023, up to a quarter of websites that existed between 2013 and 2023 are no longer accessible. Specifically, 38% of websites that appeared in 2013 alone are inaccessible after a decade. Note that this lost number includes independent websites or specialized websites of an organization.

Online information and knowledge are disappearing as readers become engrossed in social media or AI chatbots. (Illustration: The Conversation)
This serves as a warning that, despite the ongoing hype surrounding the digital age, many high-quality news sources (including journalistic information) are failing to survive, let alone thrive. It's easy to see that this is partly because advertising revenue has shifted to the social media platforms of tech giants, leaving website owners and organizations less interested in maintaining or developing their own sites.
This implies that users worldwide, including former newspaper readers, are flocking to social media or sharing platforms to enjoy moments of instant information gratification (often sensational or entertaining), instead of seeking in-depth and valuable information sources as before. As a result, these types of knowledge or news websites are no longer valued, leading to their decline and eventual disappearance (note that monthly or annual fees are required to maintain such websites).
Alarming signs of a “digital decline”
This is known as the “digital decline,” and it’s happening in many different online spaces. Pew research examined content links on government and news websites, as well as in the “References” sections of Wikipedia pages as of October 2023. They found that 23% of news websites had at least one broken link, a figure that rose to 21% on even government websites, which are generally more heavily invested in and have more stable funding.
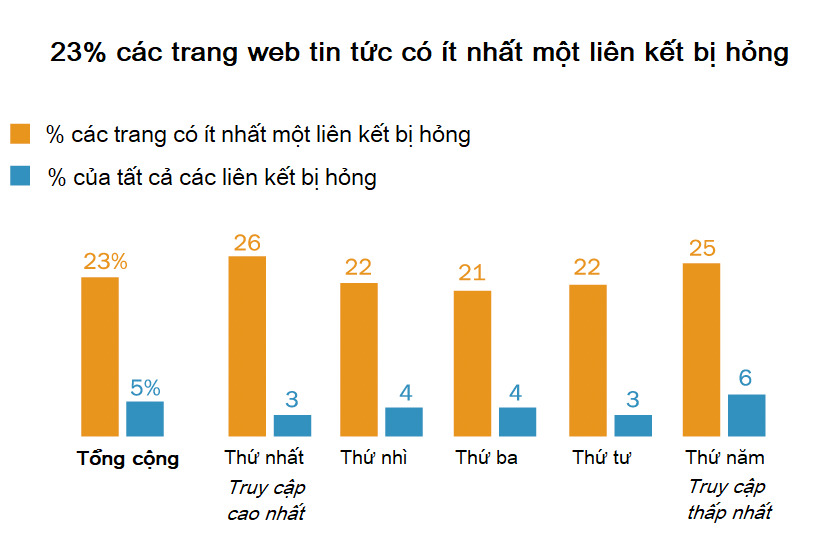
Broken links on news websites, according to website traffic ranking. Graphic source: Pew Research Center
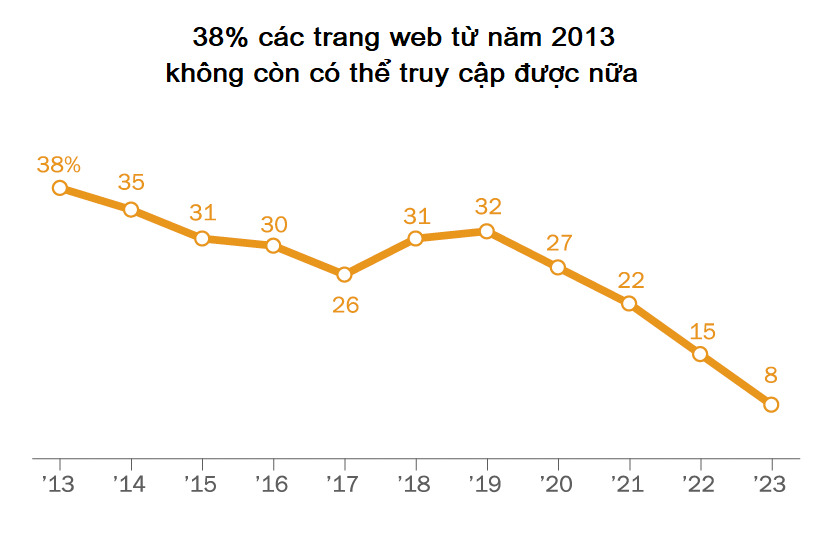
Percentage of inaccessible online links (links) by year (as of October 2023). Graphic source: Pew Research Center
Even high-traffic news websites and those with low views are equally likely to contain broken links. Local government websites are particularly susceptible to broken links. Furthermore, 54% of Wikipedia pages—the world's open encyclopedia—have at least one inaccessible link in the "References" section (i.e., the links at the bottom of the page that cite information from above).
Not only are websites or information pages increasingly at risk of breaking or being deleted, but the “digital decline” is also occurring on today’s trendy social networks. For example, Pew research found that nearly one-fifth of “tweets” are no longer publicly visible on social network X (formerly Twitter) just months after being posted. In 60% of these cases, the account that originally tweeted had been moved to private, suspended, or deleted entirely. In the remaining 40%, the account owner proactively deleted the tweet.
Therefore, searching for or retrieving information or knowledge on X, as well as on many other social networks, is unreliable. Consequently, it would be worrying to believe that social networks or other sharing platforms can replace traditional online news sources or other forms of physical knowledge storage.
Most tweets are deleted after being posted. According to Pew statistics, most tweets deleted from the site tend to disappear shortly after being posted. Specifically, half of the tweets that are subsequently deleted from the platform become unavailable within the first 6 days of posting. 1% of tweets are deleted within an hour; 3% within a day; 10% within a week; and 15% within a month. |
Huy Hoang
Source: https://www.congluan.vn/khi-thong-tin-bien-mat-post328132.html


















































































































Comment (0)