Dementia with many different forms gradually causes disability, placing a great burden on patients, families and social security.
Health consequences and economic pressure
Dementia in the elderly, if not treated to prevent the disease from progressing, can lead to dangerous complications or consequences, even potentially causing death. Specifically, many dementia patients fall into a state of anorexia/refusal to eat due to loss of chewing and swallowing reflexes.
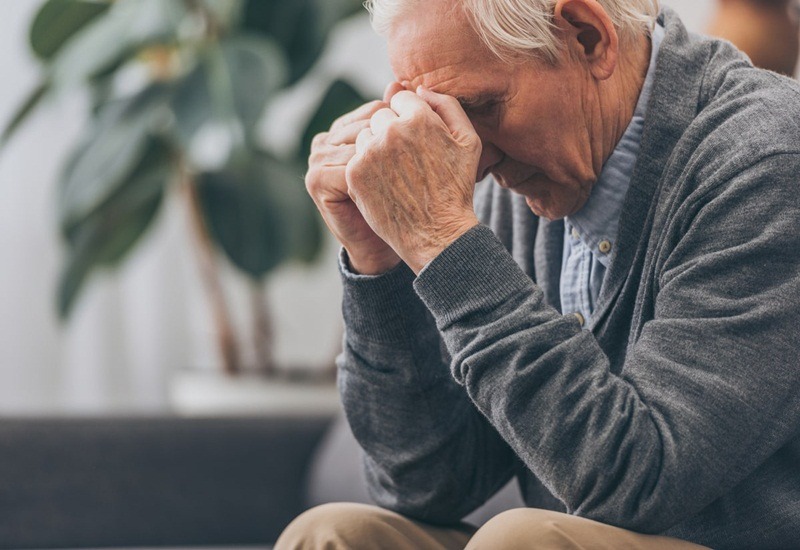 |
| Dementia with many different forms gradually causes disability, placing a great burden on patients, families and social security. |
This condition causes malnutrition/nutrient deficiency, further worsening dementia and reducing the patient's life expectancy.
Dysphagia due to dementia increases the risk of choking or aspirating food into the lungs, which can lead to respiratory failure and pneumonia.
If dementia in the elderly progresses, the patient cannot function normally; cannot take medication as prescribed by a doctor without the support of relatives.
Older adults with dementia may encounter unsafe situations when cooking, driving, walking alone, etc.
Late-stage dementia in the elderly can lead to infections, causing coma and even death.
There is currently no specific method to accurately diagnose dementia. Doctors will diagnose based on medical history, physical examination, results of diagnostic imaging tests, changes in thinking, behavior, etc. Through that, doctors can diagnose the level of dementia a person has.
However, it is more difficult to determine exactly what type of dementia a patient has. This depends on the symptoms, the brain changes of each type of dementia, and whether there is overlap between the diseases.
In some cases, a doctor may diagnose dementia in general or dementia in the elderly in particular but not specify the type of dementia.
Associate Professor, Dr. Nguyen Trung Anh, Director of the Central Geriatric Hospital, said that most of the community considers dementia (commonly Alzheimer's disease) as natural aging, but in fact, this is a serious disease that requires special attention from the family, because the disease has particularly serious developments in the final stage. The disease is posing many urgent challenges to global public health.
The disease has many symptoms, with many different forms that gradually cause disability, causing a great burden for the patient, the family, and social security. Currently, we only have drugs to treat the symptoms, and drugs to change the disease but are not effective.
In Vietnam, with the rapid aging of the population, dementia is posing many great challenges. About 5% of the elderly in Vietnam suffer from dementia, but only about 1% of them are managed, examined and treated.
The Central Geriatric Hospital is currently managing about 400-500 dementia patients covered by health insurance. In addition, the number of patients coming for examination without insurance is also increasing.
According to Associate Professor, Dr. Nguyen Thanh Binh, Director of the Memory and Dementia Research Center, Central Geriatric Hospital, most elderly people come for examination at a relatively late stage, usually after 1-2 years of symptoms, until there are signs of severe cognitive disorders, greatly affecting their self-awareness, then they come for examination. The number of people who are examined early and detected early is very limited.
The Central Geriatric Hospital has now established a Dementia Research Center. This is where suspected patients will be oriented to effective long-term treatment strategies and have effective treatment measures. At the same time, the Center also advises the hospital's Board of Directors to build an effective Alzheimer's disease action program.
In the past 5 years, the number of patients coming for examination under the hospital's official management program has increased 2-3 times.
According to the Director of the Central Geriatric Hospital, to provide good and effective care for Alzheimer's patients, families need to show great love because the care process is arduous, long-lasting, and can cause the caregiver to become depressed and under great pressure. Therefore, caregivers also need support.
With the current pressure and many mental traumas, Alzheimer's disease tends to be younger. Recent studies show that the disease has a large family factor, so early diagnosis is needed in high-risk subjects. Currently, with the rejuvenation, the disease will face a long time living with the disease, so early diagnosis and intervention are very important.
According to Associate Professor Dr. Nguyen Trung Anh, in the future, we can access advanced measures such as scientists are currently researching blood tests to diagnose diseases early; some effective treatments are still being researched.
However, at present, the disease basically requires intensive, comprehensive, and detailed care. Accordingly, the community in general, patients and their families need to be aware early and go to the doctor for early diagnosis.
Mr. Trung Anh also hopes that community activities will raise awareness, promote preventive measures, care and support for the elderly in protecting their memory, and encourage the elderly to go for medical examinations and early diagnosis of dementia.
How to prevent?
Dementia in the elderly is a disease that currently has no cure or can reverse its progression.
However, if detected early, doctors can accurately diagnose the cause of the disease and manage it better by treating the symptoms, helping relatives be more proactive in caring for and controlling the disease.
To help improve dementia symptoms, doctors may prescribe related medications (such as cholinesterase inhibitors, memantine, etc.) and apply therapies (such as occupational therapy, changing the environment, performing simpler tasks, etc.).
Patients should also increase communication, exercise, participate in favorite activities, establish scientific sleeping habits, apply a balanced diet, stop smoking, drinking alcohol, take notes of things to remember during the day, listen to soothing music... to help improve dementia symptoms.
Brain training: Doing mentally stimulating activities, such as solving puzzles, reading books… can delay the onset of dementia.
Physical activity and social interaction: Patients should exercise at least 150 minutes/week and limit sitting for long periods to delay the onset of the disease.
Do not use stimulants/tobacco: Drinking alcohol and smoking increase the risk of dementia and cardiovascular disease.
Vitamin supplements: Low levels of vitamin D in the blood increase the risk of Alzheimer's disease as well as other forms of dementia. Each person should proactively supplement vitamin D through foods such as seafood, milk, eggs... or supplements (as directed by a doctor). Vitamins B and C are also useful in preventing dementia.
Managing cardiovascular risk factors: Uncontrolled diabetes and high blood pressure can potentially lead to stroke - one of the factors leading to vascular dementia. People should proactively treat and manage high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol early (if they have them).
Maintain a scientific diet: A diet rich in green vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce the risk of dementia.
Ensure quality sleep: Sleeping well and getting 8 hours of sleep every night helps keep the brain and nervous system healthy, reducing the risk of dementia.
Source: https://baodautu.vn/gia-hoa-dan-so-va-can-benh-sa-sut-tri-tue-o-nguoi-cao-tuoi-d224941.html














































































































Comment (0)