Accordingly, the planning subjects are higher education institutions as prescribed by the Law amending and supplementing a number of articles of the Law on Higher Education (Law No. 34/2018/QH14) and pedagogical colleges, excluding higher education institutions under the Ministry of Public Security and the Ministry of National Defense, with the planning scope covering the entire national territory.
The plan sets out the development goals by 2030, developing a synchronous and modern network of higher education and pedagogical institutions with reasonable scale, structure and distribution; establishing an open, fair, equal, high-quality and effective higher education system; increasingly better meeting the people's learning needs and the requirements for the country's breakthrough and strong development in the new era based on high-quality human resources, science, technology and innovation.
Specifically, the scale of over 3 million learners, reaching 260 students and 23 postgraduate students per 10,000 people; the rate of university education over the number of people aged 18 - 22 reached 33%, of which no province had a rate lower than 15%. The structure of training levels is suitable for the requirements of knowledge-based economic development and modern industry; the proportion of master's training scale (and equivalent level) reached 7.2%, doctoral training reached 0.8%, pedagogical college training reached 1%; the proportion of training scale in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) reached 35%.
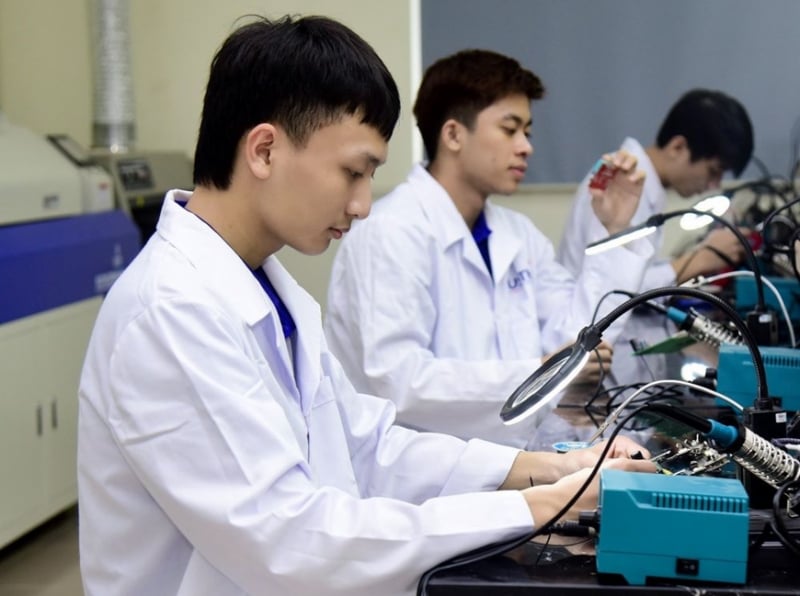

Expanding development space and enhancing capacity for higher education institutions, ensuring that 100% of higher education institutions meet standards; upgrading and developing a number of higher education institutions to meet regional and world quality standards, meeting the requirements of implementing the goals of the Education Development Strategy to 2030.
Establish large higher education centers, high-quality training, high level associated with scientific research, technology development and innovation in 4 urban areas including Hanoi, Da Nang, Ho Chi Minh City and Can Tho, creating momentum for the development of key economic regions and the whole country. Increase the contribution index of higher education in the United Nations sustainable development goals (SDG 4.3) and the global innovation index (GII), striving to be in the top 10 Asian countries.
Vision to 2050, develop a synchronous and modern network of higher education institutions according to regional and international standards, capable of meeting the people's demand for high-quality university education, providing highly qualified human resources and leading the development of science, technology and innovation in developed, high-income countries. The ratio of university students to the number of people aged 18-22 is from 45% to 50%, the proportion of master's and doctoral training scale is equivalent to the average of countries with the same level of development. Vietnam's higher education system has reached an advanced level in the world, becoming the core competitive advantage of the country, the key driving force for national development.
According to the plan, the national network of higher education and pedagogical institutions will be upgraded and developed with specific structural orientations: Public higher education institutions account for about 70% of the total national training scale, playing a key role in providing highly qualified human resources for national development and ensuring favorable and fair access to higher education for the people.
Private and non-profit private higher education institutions account for about 30% of the total national training scale, playing an important role in diversifying higher education services, flexibly meeting the needs of learners and the labor market. From 50 to 60 higher education institutions train to doctoral level, of which about 50% develop in a research-oriented manner, playing a core role in the network of training and nurturing talents associated with scientific research, technology development and innovation. Focus on investing in upgrading and developing national and regional universities to achieve quality and prestige on par with the region and the world, with the capacity to carry out national strategic tasks, regional development tasks, playing a core role in the network of higher education institutions nationwide and in socio-economic regions.
Develop a network of higher education institutions training teachers with a scale of 180,000 to 200,000 students, of which about 85% are at university level and 15% are at college level, with an expected number of 48 to 50 higher education institutions. Develop a network of higher education institutions training in STEM fields with a scale of more than 1 million students, of which about 7% are at master's level (and equivalent level) and 1% are doctoral. Prioritize investment in developing higher education institutions with strengths in research and training in STEM fields and sectors associated with the development orientation of key economic and social sectors of the regions.
Developing a digital university education network based on digital transformation, applying technology in the organization and operation of each institution and the entire university education system. Developing a team of lecturers with sufficient quantity, standardized qualifications, professional and technical capacity, including foreign language capacity, digital capacity and application of educational technology, to meet the development requirements of the university education system. Increasing the number of full-time lecturers by an average of about 5% per year and the number of lecturers with doctoral degrees by 8% so that by 2030 the entire system will have 110,000 full-time lecturers, of which at least 40% will have doctoral degrees...
Source: https://cand.com.vn/giao-duc/den-nam-2050-mang-luoi-co-so-giao-duc-dai-hoc-phat-trien-dat-trinh-do-tien-tien-cua-the-gioi-i760576/







![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man receives First Vice Chairman of the Federation Council of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F02%2F1764648408509_ndo_br_bnd-8452-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)






























































![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam and his wife attend the 50th Anniversary of Laos National Day](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/02/1764644139308_1.jpeg)
































Comment (0)