On November 20, answering questions at the 6th Session of the 15th National Assembly , Minister of Education and Training Nguyen Kim Son agreed with the proposal to include extra teaching and learning in the conditional business sector to have a legal basis to handle violations outside of schools.
In an interview with VOV2, Mr. Nguyen Xuan Thanh, Director of the Department of Secondary Education, Ministry of Education and Training, analyzed why it is necessary to include private tutoring in conditional business sectors.
Lack of regulations - Extra teaching and learning is currently difficult to manage
- Sir, why did the Ministry of Education and Training propose and support the recent proposal of the National Assembly delegate to include private tutoring in the conditional business sector?
Previously, since the establishment and promulgation of Circular 17 regulating extra teaching and learning based on the legal basis, extra teaching and learning organization services were included in the list of conditional business lines in the Investment Law.
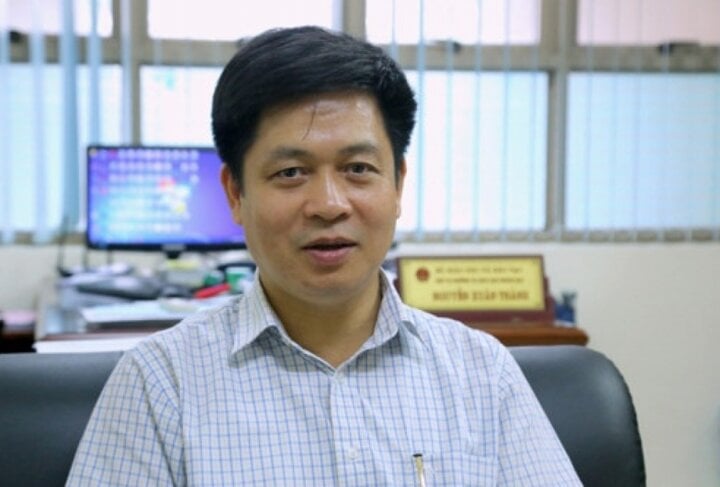

Mr. Nguyen Xuan Thanh, Director of Secondary Education Department - Ministry of Education and Training.
Therefore, Circular 17 has the basis to regulate the conditions for organizing extra teaching and learning. For example, the conditions for organizing extra teaching and learning outside of school, with facilities, organizations and individuals organizing extra teaching and learning outside of school, there must be commitments with the People's Committees at all levels from ward, commune to district to ensure the requirements for organizing extra teaching and learning, publicizing issues about organization, location, fees, and staff.
Circular 17 also has provisions for tutors, for those who organize extra teaching and learning, and conditions on facilities... because this is a very special type of tutoring that affects students.
But later, private tutoring was removed from the list of conditional business lines of the Investment Law and therefore Circular 17 had to abolish the corresponding provisions and regulations as mentioned above.
When abolished, problems arose in the management of extra-curricular teaching and learning, making it difficult to manage extra-curricular teaching and learning activities in localities.
- After announcing the expiration of some provisions in 2019, Circular 17 on extra teaching and learning still has a regulation "prohibiting" extra teaching and learning in schools with two sessions a day and at the primary level. At the same time, there is still a regulation that "teachers are not allowed to give extra teaching outside of school to students that the teacher is teaching in the main course without the permission of the head of the agency or unit of that teacher. So when it is no longer a conditional business, what is the difficult point in management here?
That regulation ensures that when performing school duties, teachers must fully teach all requirements and the full curriculum for their students, avoiding the situation where teachers do not fully teach according to the education plan and then organize extra classes, although it is voluntary, but in the end students must voluntarily do so.
When Circular 17 has to abolish some articles, it means there is no longer a commitment, no longer having to publicize the location, no longer having to publicize the teaching staff, fees and other conditions... Thus, managing the regulation of Circular 17 that "teachers are not allowed to teach their own students outside of school without permission from the Head of the agency" is very difficult to manage because it is such a large social environment.
Of course, when teaching like that, if caught, it can still be handled, but inspection and supervision are difficult, and inspections cannot be organized.
In reality, organizations and individuals registering for business in the locality regardless of any industry, including the organization of extra teaching and learning, must register and be licensed by the competent authority. Specialized inspection channels can also coordinate with local management agencies to inspect and examine that facility, but according to the general regulations of business registration, without any specific characteristics or conditions specific to education.
Teaching and learning extra classes that do not match wishes is a waste for society.
- Public opinion understands that all tutoring activities are currently "banned". Is this understanding correct? If it is currently "banned" but tutoring is still difficult to control, then when it is allowed as a conditional business, will tutoring develop more strongly?
I think it is not correct to say “banned”. Currently, when organizations and individuals register for business, including the business type of organizing extra teaching and learning activities, there is still a legal corridor for those establishments to register and be managed together with other types of business.
However, this management does not have specific regulations for education, so the conditions for ensuring educational quality are not strictly controlled.
- So what does the Ministry of Education and Training expect when putting private tutoring into a conditional business sector?
If the service of organizing extra-curricular teaching and learning activities is included in the conditional business line, the Ministry will develop, amend, supplement or replace Circular 17. In which there will be specific regulations on the conditions for organizing extra-curricular teaching and learning outside of school so that all of these will be managed within a public and transparent legal framework.
The purpose of our not banning extra teaching and learning is because we assess that it is a real need and somewhere we also see that when students have the need to study extra with legitimate reasons, in accordance with their wishes to develop their qualities and abilities according to their needs, then that is a positive thing.
The purpose of regulation is to ensure that cases where extra teaching and learning do not meet the wishes of the students themselves are prevented or prevented.
Teaching and learning extra classes that do not match the wishes not only wastes the energy and money of the students themselves and their parents, but it is also a waste of many resources of society in general without contributing to improving the quality of general education. We must condemn that.
On the other hand, the regulation must promote teacher resources. Good and prestigious teachers who are desired by students and parents are also a place for teachers to continue to dedicate themselves and contribute to the quality of education of our entire country.
Many solutions are needed for the widespread situation of extra teaching and learning.
- However, in reality, public opinion is also very upset with the rampant extra-curricular teaching and learning. When extra-curricular teaching and learning outside of school is more strictly managed, will the rampant extra-curricular teaching and learning situation be reduced? Or what measures are needed to reduce this situation?
The regulation on the organization of extra teaching and learning is to make the organization of activities clear, public and transparent. Students must follow their own wishes and needs, not for the purpose of getting this or that score to serve a few tests.
Reducing extra teaching and learning requires many solutions. Currently, the Ministry of Education and Training has been and is continuing to strongly direct local educational institutions to organize student assessment according to the program's requirements.
The program clearly sets out the requirements to be achieved, the test questions must not be raised too high compared to the program requirements. Raising them too high would inadvertently waste the effort we have put into reducing the program load to focus on developing students' abilities and qualities, making students who want to achieve high scores have to take extra classes.
Secondary school is a universal level, so local regulations require that there must be enough places for students to study. Some schools that are more prestigious, more popular, and have more applicants need to have a competency assessment test as the Circular stipulates, and the Ministry has also directed schools, not advanced knowledge tests that students who want to pass must take extra classes.
As for the transition from junior high school to high school, there are also regulations on the distribution of students. Of course, high school education institutions can only accept a certain percentage of students. In addition, they will have to go to vocational schools. We also hope that society will gradually understand this, not everyone has to go in the same direction to university.
The 2018 program is oriented towards developing learners' capacity. It can be imagined like this, with only basic general knowledge in the program, the tests require students to know how to apply that knowledge to solve problems, at that time, teaching and learning extra lessons like now, just diligently doing knowledge exercises and questions will not achieve the goal.
If the 2018 Program is done well, one is to reduce the number of extra classes just for advanced exercises and if extra teaching and learning are organized, then it will focus on knowledge and skills such as life skills, life values and other skills to contribute to the comprehensive development of students.
Thank you.
Thuc Hien (VOV2)
Source










































































































Comment (0)