The relationship between calcium and vitamin D
Calcium is a mineral found in bones that plays an important role in the entire body. Adequate calcium levels in the blood and intercellular fluid are essential for muscle, heart, and nerve function, according to Verywell Health (USA).
Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, promoting bone, muscle, and immune system health. When blood calcium levels are low, vitamin D and parathyroid hormone (PTH) signal the intestines to absorb more calcium; while bones release calcium, the kidneys reabsorb calcium so it is not lost in urine. Conversely, when blood and fluid calcium levels are too high, hormones signal the bones to absorb more calcium, and the kidneys release calcium in the urine.
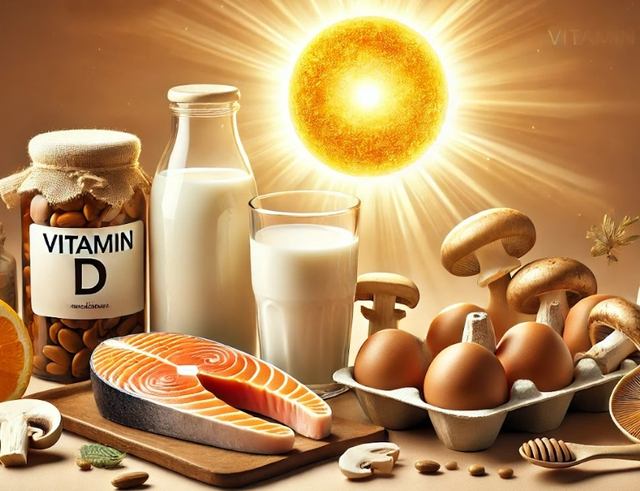

The main sources of vitamin D come from fish, milk, eggs and some nuts.
Photo: AI
Overall, both calcium and vitamin D play an important role in maintaining strong bones. Without vitamin D, children develop rickets. Low calcium levels in adults can lead to weak bones and osteoporosis.
Should I supplement both at the same time?
Calcium is absorbed from the diet, with the help of vitamin D. The body can also absorb vitamin D from sunlight.
When there is enough vitamin D - either through diet or supplements - the body is aided in absorbing calcium. Therefore, the two can be taken together.
Some supplements also combine both nutrients, with calcium levels typically falling between 500-600 mg. However, it is important to learn carefully about the forms of calcium that are suitable for your body and the appropriate dosage before using them to protect your health.
The recommended daily intake of calcium, including from diet and supplements, varies by age and gender.
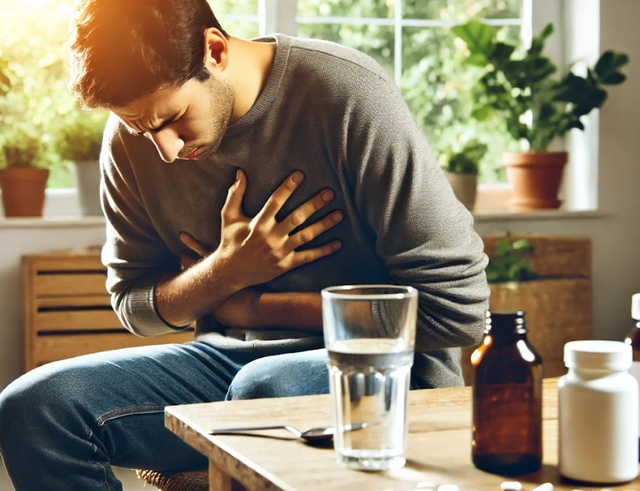

Overuse of vitamin D and calcium can be counterproductive, causing nausea, heart rhythm disturbances, and kidney stones.
PHOTO: AI
Not all good things are worth charging
Taking too much calcium or vitamin D supplements can cause serious health problems by causing too much calcium in the blood. Some people may experience the following symptoms after consuming too much calcium:
- Nausea, constipation.
- Abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia).
- Increased risk of kidney stones.
- Increased risk of heart disease and cancer.
Additionally, taking too much vitamin D can cause a condition known as vitamin D toxicity. This usually occurs when people take very high doses, above 250 mcg per day, causing abnormally high levels of calcium in the blood (hypercalcemia), with symptoms of:
- Constipation.
- Nausea, vomiting and loss of appetite.
- Dehydration and excessive thirst.
- Frequent urination and large amounts of urine.
- Tired, confused.
- Muscle weakness.
Switching to a different supplement or taking it with food may help resolve these conditions. However, it is important to note that taking supplements can also affect the absorption of certain medications, so people should consult their doctor before using them.
Should calcium and vitamin D be supplemented through food or functional products?
According to Dr. Angela Ryan Lee, American College of Cardiology, people should aim to supplement nutrients through food. Foods that are rich in calcium include:
- Milk, cheese and yogurt.
- Sardines and salmon.
- Broccoli, cabbage and kale.
- Cereals and cereal grains.
- Tofu.
- Orange juice.
You can supplement vitamin D through your diet through the following foods:
- Fish, especially fatty fish such as mackerel, salmon and tuna.
- Beef liver.
- Egg yolk.
- Cheese.
- Mushroom.
- Milk, orange juice and some cereals.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/co-nen-bo-sung-canxi-va-vitamin-d-cung-luc-185250301221412233.htm


![[Photo] General Secretary concludes visit to Azerbaijan, departs for visit to Russian Federation](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/8/7a135ad280314b66917ad278ce0e26fa)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh meets with the Policy Advisory Council on Private Economic Development](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/8/387da60b85cc489ab2aed8442fc3b14a)
![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man chairs the meeting of the Subcommittee on Documents of the First National Assembly Party Congress](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/8/72b19a73d94a4affab411fd8c87f4f8d)
![[Photo] President Luong Cuong presents the decision to appoint Deputy Head of the Office of the President](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/8/501f8ee192f3476ab9f7579c57b423ad)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam begins official visit to Russia and attends the 80th Anniversary of Victory over Fascism](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/8/5d2566d7f67d4a1e9b88bc677831ec9d)























































![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh talks on the phone with Singaporean Prime Minister Lawrence Wong](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/8/e2eab082d9bc4fc4a360b28fa0ab94de)































Comment (0)