The Sahara is the world's largest tropical desert, located in North Africa, spanning approximately 12 countries and covering an area of over 9,000,000 square kilometers. Due to a lack of water, it remains arid year-round, and the large temperature differences between day and night make the environment extremely harsh.
The surface of the Sahara Desert is covered with sand dunes, desert grasslands, and desert rocks of varying sizes. In ancient times, this desert was considered an important channel for trade and cultural exchange.
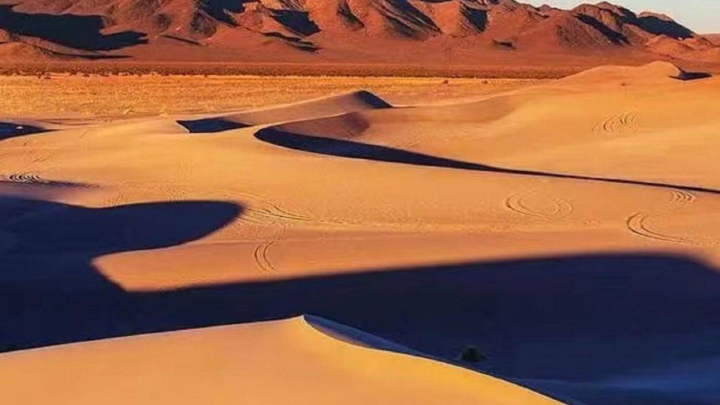

The Sahara Desert covers approximately one-third of Africa's land area. Scientists have used radar technology to measure its depth.
The formation of the Sahara Desert began 2.5 million years ago, linked to climate change. Initially, the area was grassland; as the climate became arid, the grasslands gradually shrank and turned into a desert.
In the western part of the Sahara mountain range, the terrain is relatively high, exceeding 3,000 meters in altitude, and the thickness of the underlying rock layer can reach several thousand meters, while other parts of the desert have much lower terrain and relatively thin rock layers.
Scientists estimate that the average depth of the Sahara Desert is approximately 100-150 meters. The deepest points can even reach 300 meters. If the height of a single floor is 3 meters, then the average depth of this desert is equivalent to 50 floors. These depth calculations are based on a comprehensive consideration of the desert's geological structure, rainfall, water flow, and other factors.
Regarding the depth of the Sahara Desert, there is no fixed answer because the Earth's geological structure is very complex and the depth varies between different areas. Therefore, using radar technology for measurement can easily determine the depth of different locations in the Sahara Desert.
The specific method involves projecting specific electromagnetic waves into the desert ground, then detecting and recording the waveform characteristics of the electromagnetic waves reflected from different interfaces within the ground. Finally, this data is processed using technology to obtain measurement results quickly and accurately.
The bottom of this desert is composed mainly of sandstone and rock, distributed at different depths depending on the area. Research indicates that hidden beneath the Sahara Desert are oil reserves, huge underground reservoirs, and abundant water sources, providing essential living conditions for desert inhabitants.
The Sahara Desert was once home to abundant vegetation.
Previously, the area of a large lake here could reach 108,000 square kilometers, with a depth of 247 meters. These findings suggest that, since ancient times, the Sahara was not a desert, but a lush green paradise with abundant vegetation that nurtured many species of plants and animals.
Numerous dinosaur fossils, some marine creatures such as catfish, whales, sea snakes, and even human artifacts have been found in the depths of the Sahara Desert.
Digging up all the sand in the Sahara Desert to see what lies beneath is impractical; it would not only severely damage the desert ecosystem but also create a host of other environmental problems. Despite its harshness, the Sahara Desert is also one of the most amazing places. Its unique ecosystems and landscapes, as well as its cultural relics, are well worth exploring and protecting.
Ngo Nhung (Source: Sohu)
Beneficial
Emotion
Creative
Unique
Wrath
Source













































































































Comment (0)