A team of scientists, including Tina I. Lam, Christina C. Tam, Larry H. Stanker, and Luisa W. Cheng, published the results of their clinical study in the electronic journal of the National Institutes of Health (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5198571/) on December 16, 2016, along with 62 related reference studies on the topic "Beneficial microorganisms inhibit the intracellularization of Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype A in epithelial cells".
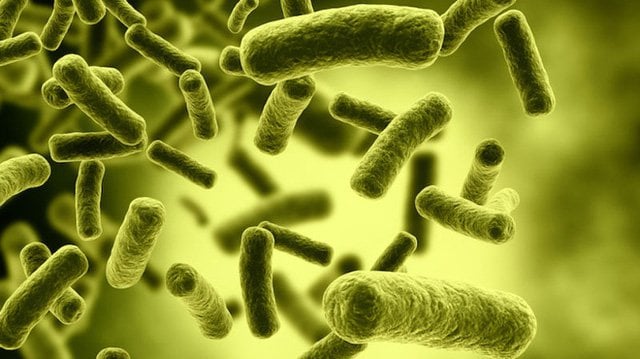
Bacteria C. botulinum
FOOD SAFETY DEPARTMENT, MINISTRY OF HEALTH
The results demonstrated the feasibility of using beneficial microorganisms (probiotics) to inhibit and mitigate the harmful effects of C. botulinum bacteria and the toxins they produce.
Specifically, the solutions presented in the experiment involved using very common probiotics available worldwide and in Vietnam, including bacterial strains such as: Lactobacillus Acidophilus and Lactobacillus Reuteri (found in digestive enzymes and probiotics), Saccharomyces Boulardii (yeast that aids digestion), and Lactobacillus Casei (found in yogurt). These beneficial bacteria and yeast strains are readily available at pharmacies with the advice of pharmacists.
Where does botulinum toxin come from?
Botulinum toxin is produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum (C. botulinum). This is an anaerobic, gram-positive, rod-shaped bacterium with rounded ends, numerous flagella around its body, and is motile. It can multiply rapidly in the host's intestinal tract. In particular, under harsh conditions, it can form spores. Therefore, C. botulinum is widely distributed in nature, found in garden soil, animal feces, pond water, and especially thrives in oxygen-deficient conditions such as in canned goods and vacuum-sealed bags containing meat, fish, and pâté that have been stored for a long time.
During the process of eating and daily activities, the presence of C. botulinum bacteria in the gut can occur at any time, but poisoning rarely happens. This is because of the resistance and ability of beneficial bacteria (probiotics) in the digestive tract to eliminate harmful bacteria, or because the amount of bacteria is not strong enough to overcome the body's natural defenses.
Mechanism of attack by C. botulinum bacteria
Under favorable conditions, the bacterium C. botulinum can proliferate explosively in environments rich in nutrients but lacking oxygen. This is because, in natural conditions, environmental factors and the growth and development of other bacteria can overwhelm the C. botulinum population.
The most common cases of food poisoning caused by C. botulinum bacteria usually result from consuming food that has been stored for a long time in airtight containers, such as canned meat, canned fish, canned pâté, and vacuum-sealed bags. In such environments, the bacteria multiply, grow, and produce botulinum toxin, becoming a source of "double poison," including a large amount of botulinum bacteria and toxins produced by the bacterial population.
When food containing toxins and harmful bacteria enters the intestines through ingestion, the toxins affect the nervous system, and large numbers of Botulinum bacteria proliferate, producing new toxins. Due to the rapid action of the toxins and the high replication rate of Botulinum bacteria, cases of poisoning often have very quick consequences, potentially causing coma or even death.
The human body's defense mechanism against the bacterium C. botulinum.
C. botulinum bacteria are found everywhere, but poisoning is not common because the human body has many "biological barriers" to protect people from harmful bacteria in general and C. botulinum bacteria in particular.
First, there's the intestinal mucosa, where antimicrobial peptides play a role in preventing harmful bacteria from penetrating beneath the mucosal layer. Next is the gut microbiota, which contains many groups of beneficial symbiotic bacteria (probiotics) that overwhelm and compete with harmful bacteria for survival, preventing their explosive growth.
Toxins produced by harmful bacteria are partially processed by beneficial microorganisms, while the rest triggers the body's alarm signals and attempts to eliminate them. In everyday life, we commonly refer to this as vomiting and diarrhea, or colloquially as "vomiting and diarrhea." This is a crucial defense mechanism of the body against the attack of toxins and harmful bacteria.
However, this mechanism will not work effectively if the human digestive system has too few symbiotic microorganisms (probiotics) or if the levels of harmful bacteria and toxins are too high and exceed the tolerable threshold.
Using probiotics to treat botulinum poisoning.
According to research conducted by reputable international research institutions, beneficial bacteria (probiotics), in addition to supporting nutrient absorption from food, also play important roles in treating poisoning caused by harmful bacteria through the following mechanisms: eliminating and inhibiting harmful bacterial populations through competition; processing and breaking down toxins, including natural toxins produced by harmful bacteria; and even preventing the effects of heavy metals.
Applying scientific knowledge to real life.
With the knowledge mentioned above, we can certainly implement solutions to prevent and minimize damage caused by harmful bacteria, such as: limiting the use of canned foods, especially expired canned foods.
Canned foods that have been opened and then stored in the refrigerator can still be a source of dangerous toxins from harmful bacteria; Regularly consume foods rich in beneficial bacteria such as probiotics, yogurt, fermented fruits, and fermented rice wine... because in environments where beneficial bacteria (probiotics) thrive, harmful bacteria will be inhibited and destroyed.
When symptoms such as abdominal pain and vomiting occur, a mixture of digestive enzymes (probiotics) and honey or concentrated sugar water (prebiotics) can be used immediately to temporarily inhibit bacterial growth and the effects of toxins. Alternatively, a larger-than-usual amount of yogurt mixed with honey can be used. This is a scientifically-based first aid solution for food poisoning. Afterwards, the affected person should be taken to a medical facility for further monitoring and treatment.
Associate Professor and Doctor Pham Thi Ly, former senior lecturer at Hai Phong University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Head of the Department of Biochemistry, now a full-time lecturer at Thang Long University in Hanoi, stated: Several recent food poisoning incidents caused by C. Botulism have caused widespread fear and anxiety in the community, such as poisoning from vegetarian pate, mass food poisoning in schools, and street food poisoning... Treating botulism poisoning is very costly and poses a high threat to the patient's life. This article provides readers with an objective and scientific perspective, from self-prevention methods to effective initial first aid using readily available items such as digestive enzymes, yogurt, honey, and fermented fruit juices...
The information presented by the author is very objective and scientific, with numerous references to clinical research results from many reputable scientists. Many thanks to the author for this timely and relevant information.
Source link


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives Lao Minister of Education and Sports Thongsalith Mangnormek](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F16%2F1765876834721_dsc-7519-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)
![[Image] Leaked images ahead of the 2025 Community Action Awards gala.](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F16%2F1765882828720_ndo_br_thiet-ke-chua-co-ten-45-png.webp&w=3840&q=75)

![[Live] 2025 Community Action Awards Gala](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F16%2F1765899631650_ndo_tr_z7334013144784-9f9fe10a6d63584c85aff40f2957c250-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)

![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives the Governor of Tochigi Province (Japan)](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F16%2F1765892133176_dsc-8082-6425-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)




































































































Comment (0)