Whether it's a headache or chronic pain from arthritis... painkillers help us get rid of the pain. Although they provide temporary relief, painkillers also carry potential risks and must be used appropriately and correctly.
1. Principles of pain relief and pain classification
The mechanism of action of pain relievers often involves interference with pain signaling pathways. For example, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) reduce inflammation and pain by inhibiting the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX). Opioids bind to opioid receptors in the central nervous system and activate the endogenous pain-relieving system to reduce pain.
The Pain Rating Scale (PRS) is a widely used pain assessment tool in clinical practice that can more accurately evaluate a patient's pain level. The scoring criteria are primarily divided into 0 to 10 points: 0 points for no pain, 1-3 points for mild pain, 4-6 points for moderate pain requiring intervention, and 7-10 points for severe pain requiring urgent intervention.
This scoring method is a simple, effective, and widely applicable pain assessment tool. It not only helps healthcare professionals accurately assess patients' pain levels but also provides valuable insights for patients' treatment and self-management.

Painkillers provide temporary relief from pain.
2. Classification of pain relievers
2.1 Mild to moderate pain relievers
- Paracetamol is a widely used medication for mild to moderate pain relief. It's an over-the-counter pain reliever commonly used for conditions like headaches and muscle aches. The usual dose is 500mg to 1g every 4-6 hours, with a maximum of 4g per day. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen are also a common group of medications used to relieve mild to moderate pain, inflammatory pain, and bone pain not associated with tumor emergencies.
Paracetamol can cause serious liver damage if taken in excessive doses. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) should be taken with or after meals. Patients should carefully read the instructions before use to understand the medication and use it correctly.
- Moderate pain is defined as pain with an NRS score of 4 to 6, such as musculoskeletal pain, menstrual cramps, toothache, pain after dental procedures, etc. Codeine, tramadol, dextropropoxyphene, etc., can be used to relieve moderate pain. In addition, combination drugs containing paracetamol and codeine are also effective in relieving moderate pain.
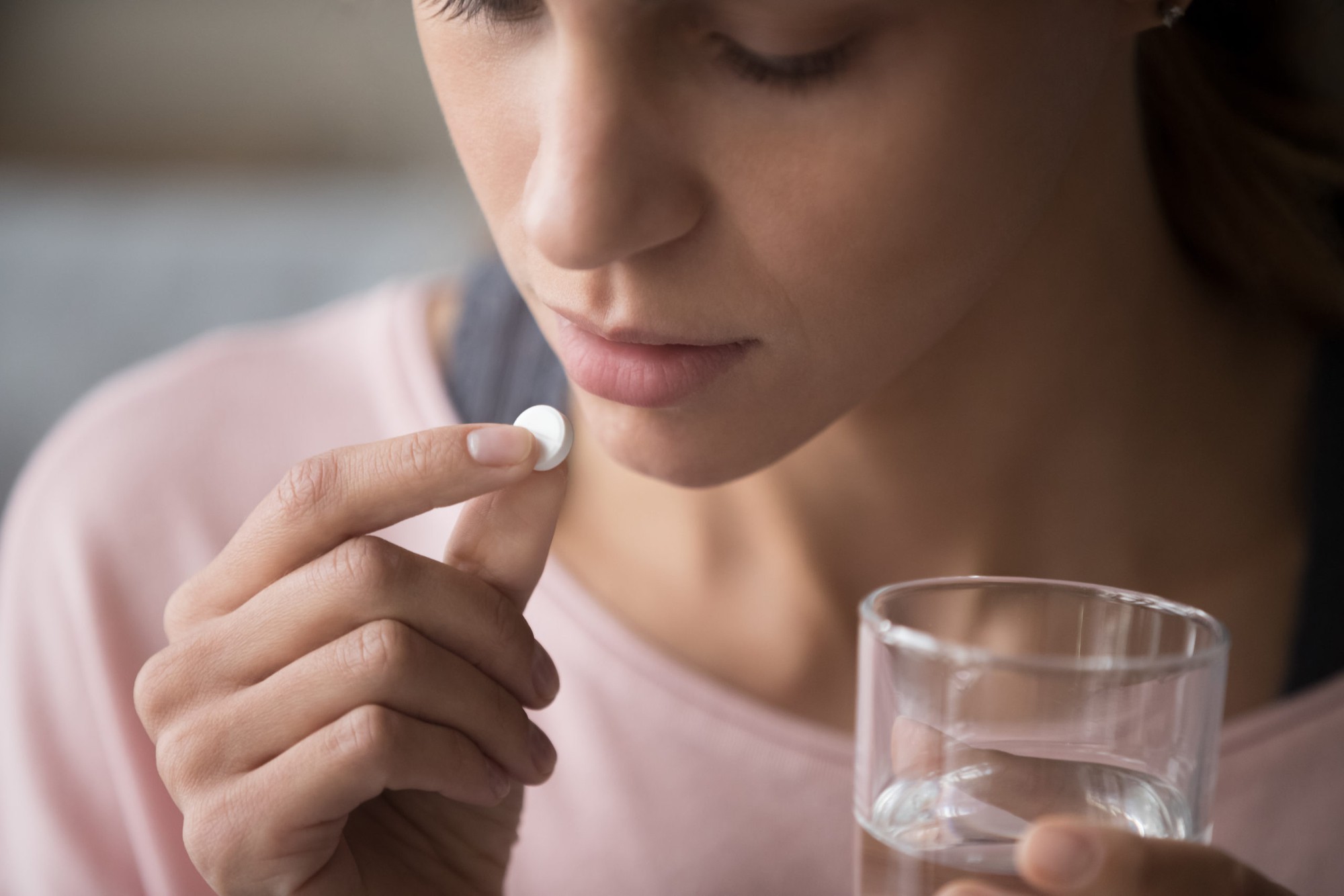
Although it provides temporary pain relief, the medication also carries many risks and must be used appropriately and correctly.
2.2 Strong painkillers ( strong opioids)
Typical medications include fentanyl, sufentanil, morphine, etc., suitable for severe pain (NRS score of 6 or higher), post-surgical pain relief, cancer pain, and maintenance treatment of chronic pain.
Although the drug is very effective in controlling pain, it can cause many adverse reactions and dangerous side effects, especially if used improperly or in excessive doses. For example, fentanyl can suppress respiration, causing shortness of breath, slow breathing, or cessation of breathing. This is a serious side effect that can lead to cardiac arrest if not treated promptly. Therefore, the use of the drug requires close medical supervision and strict adherence to dosage and usage instructions to minimize the risk of serious side effects.
In summary, when using painkillers, it's important to consider their pros and cons. Long-term or excessive use can lead to dependence, increasing the risk of abuse and health problems, and may mask underlying health issues and delay treatment. It's crucial to understand the underlying cause of pain and treat it accordingly, rather than relying solely on painkillers.
Pain relievers are generally safe when used moderately to relieve mild pain, but for prolonged or severe pain, consult a doctor and do not self-medicate.
Dr. Tran Phuong Duy
Source: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/can-luu-y-gi-khi-lua-chon-thuoc-giam-dau-172250219215025959.htm





![[Photo] Da Nang: Mountainous commune adorned with flags and flowers, ready for election day.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2026/03/10/1773113803384_ndo_br_9-jpg.webp)

![[Photo] Meeting of the Standing Committee of the National Assembly Party Committee with the Standing Committee of the Government Party Committee on the First Session of the 16th National Assembly](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2026/03/10/1773107502031_ndo_br_thu-tuong-pham-minh-chinh-va-chu-tich-qh-tran-thanh-man-dong-chu-tri-hoi-nghijpg-jpg.webp)



















![[Image] 20 islands in the Spratly Islands special administrative region hold early elections.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2026/03/08/1772949669607_img-20260308-112026-90-jpg.webp)
















































































Comment (0)