For people with diabetes, drinking one or two cups of brewed coffee or three or four cups of black tea, equivalent to 200 mg of caffeine, can increase blood sugar levels.
For healthy individuals, consuming coffee, tea, soda, chocolate, and other caffeinated beverages generally does not affect their health. However, for people with diabetes, consuming foods high in caffeine can affect their blood sugar levels.
One study examined people with type 2 diabetes who took a 250mg caffeine pill at breakfast and another at lunchtime. This is equivalent to drinking two cups of coffee with each meal. The results showed that their blood sugar levels were 8% higher than on days they didn't consume caffeine. Researchers explained this by saying that caffeine can affect how the body responds to insulin – the hormone that allows sugar to enter cells and be converted into energy.
Caffeine can reduce insulin sensitivity. In people with type 2 diabetes, the body doesn't use insulin as effectively. After meals, blood sugar levels rise higher than normal. Excessively high blood sugar over time can increase the risk of diabetes complications such as nerve damage or heart disease.
Scientists are still trying to understand how caffeine affects insulin levels and blood sugar. One explanation is that caffeine increases levels of certain stress hormones such as epinephrine (also known as adrenaline). Epinephrine may prevent cells from processing sugar, preventing the body from producing more insulin.
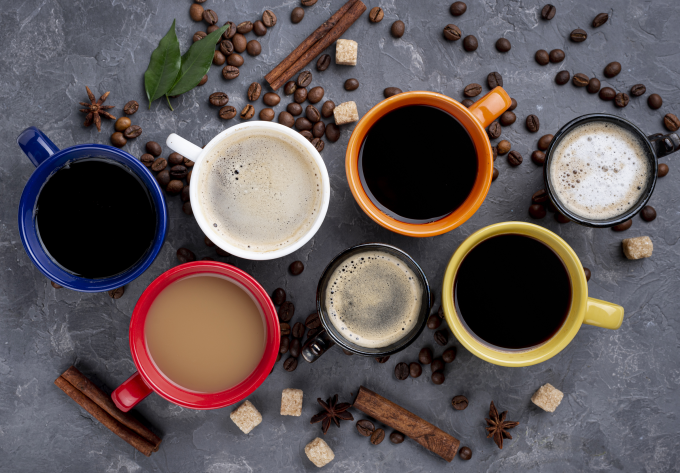

Drinking too much coffee can increase blood sugar levels. Photo: Freepik
Caffeine works by blocking the effects of adenosine. Adenosine plays a crucial role in the body's production of insulin. Caffeine also controls how cells respond to it. Drinking too much caffeine can keep you awake. Lack of sleep can also reduce insulin sensitivity.
Approximately 200 mg of caffeine (about 1-2 cups of brewed coffee or 3-4 cups of black tea) can affect blood sugar levels. However, each person's body may react differently to caffeine depending on age and weight.
People with diabetes who regularly drink coffee don't have higher blood sugar levels than those who don't. Some experts suggest the body adjusts to caffeine over time. But other research shows that caffeine can still cause blood sugar spikes, even if a person typically starts their day with a cup of coffee.
To determine if caffeine raises blood sugar levels, people with diabetes should consult a doctor. Blood sugar levels can be checked throughout the morning after drinking a cup of coffee or tea as usual. Then, check again after skipping a few days. Comparing these results will help determine if caffeine affects blood sugar.
Studies suggest that coffee may reduce the incidence of type 2 diabetes. Experts attribute this to the beverage's high antioxidant content. However, this may not be true for someone who already has type 2 diabetes. Drinking caffeinated coffee can make it more difficult for patients to control their blood sugar levels.
Kim Uyen (According to Web MD )
Source link










































































































Comment (0)