Children aged 5-15 years are more likely to get strep throat than adults, close contact, smoking, poor hygiene… also increase the risk of getting the disease.
Strep throat is caused by the bacterium Streptococcus pyogenes (S. pyogenes). Untreated disease can lead to recurrent episodes or serious complications such as rheumatic fever, but rarely, post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. In addition, this bacterium also causes common infections such as cellulitis, ear infections, impetigo, and scarlet fever. Factors that increase the likelihood of getting strep throat.
Age
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), strep throat is most common in children ages 5-15. Younger children can also get the infection, but it is less common and often has atypical symptoms. Adults can also get the infection, but at a much lower rate of 5-10%. Strep throat is usually treated with antibiotics.
Close contact
Streptococcus bacteria are most commonly spread from person to person through secretions such as saliva, nasal mucus when coughing, sneezing or hands directly contacting secretions containing bacteria and then touching the eyes, nose, mouth... Bacteria are rarely transmitted through food or water sources. People are not susceptible to streptococcal infection from animals, so there is no need to worry about family pets.
Close contact increases the risk of infection, especially in schools and daycare centers. People who live with someone who has strep throat are also at increased risk.
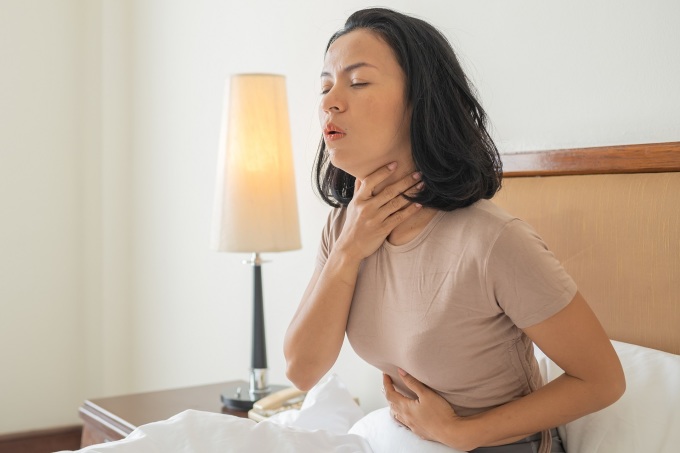

Strep throat is more common in children than adults. Photo: Freepik
Poor hygiene
Poor personal hygiene is also a common cause of the spread of streptococcal infections. Infected children may cough into their hands or rub their eyes and nose without using a tissue and then pass the infection to others through contact. This is because S. pyogenes bacteria can live on hands for up to 3 hours.
Washing your hands frequently can help reduce the spread of streptococcus. When soap and water are not available, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer (hand rub). Also, avoid sharing food, drinks, or utensils and close contact while you are sick.
Pollution or exposure to cigarette smoke
Smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke can irritate the throat and airways with particulate matter. This makes the throat more susceptible to streptococcal and viral infections. Air pollution can also irritate the throat, increasing the likelihood of contracting the strep throat virus.
Time of year
Strep throat can occur year-round but is more common in late winter and early spring, when the climate is more favorable for the growth of S.pyogenes bacteria.
According to the CDC, the typical incubation period for strep throat is 2-5 days. On average, it takes three days from exposure to the bacteria for symptoms to develop. Sore throats usually last 3-7 days with or without treatment. If treated with antibiotics, symptoms improve within 1-2 days, and the person is no longer contagious for 24 hours after the first dose. However, if left untreated, you can infect others from the time you are exposed to the bacteria until your symptoms go away. Some people may be contagious for more than a week afterward.
Some people live with streptococcus bacteria in their throats and noses without developing symptoms because the strains tend to be less virulent. These people are called carriers and are very unlikely to infect others. However, if a carrier is in frequent close contact with someone who has a weakened immune system (for example, someone undergoing chemotherapy), they will still need antibiotic treatment to avoid infecting them and other family members.
Mai Cat (According to Very Well Health )
Source link







![[Photo] Cat Ba - Green island paradise](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F04%2F1764821844074_ndo_br_1-dcbthienduongxanh638-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)























































![[VIMC 40 days of lightning speed] Da Nang Port: Unity - Lightning speed - Breakthrough to the finish line](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/04/1764833540882_cdn_4-12-25.jpeg)
















































Comment (0)