Luxury food popular in China
Considered a delicious and nutritious dish, in China, fish bladders are sold for between 450-1,000 USD/kg. In Hong Kong (China) alone, the price can reach up to 7,700 USD/kg.
Fish maw is often seen as a symbol of wealth and prosperity, given as gifts at important events and held as a speculative investment. Fish maw is one of the “four treasures” of Cantonese cuisine, along with abalone, sea cucumber and shark fin.
The main reason why fish maw is so popular is because of its medicinal value. Due to its high collagen and fiber content, fish maw is said to help maintain healthy skin, boost the immune system, and aid digestion. Fish maw is also often recommended in China for postpartum recovery and post-operative pain relief, and has even been used to enhance male fertility.
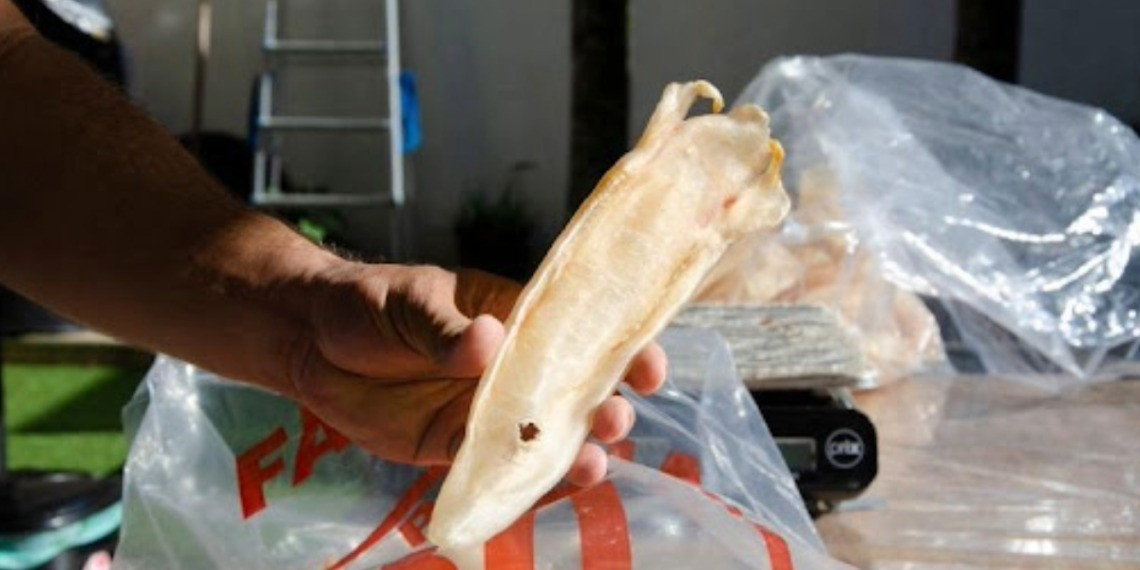

Due to overfishing in East Asia and elsewhere, China now imports most of its fish maw from Africa. In Uganda in particular, a multimillion-dollar fish maw industry is rapidly developing to meet the demand for high-end cuisine in China.
Uganda currently produces at least 520 tonnes of maw annually and exported 51% of its total catch to Hong Kong between 2012 and 2019. In 2018 alone, Uganda recorded maw trade with the Chinese market worth $52.1 million.
Ecological impact and the creation of a million dollar industry
The Chinese market used to favor Mexican swim bladders, but due to the threat of extinction of some endemic fish species, the trade is tightly regulated by local authorities. As a result, the Chinese market has shifted its attention to fish from Lake Victoria (Africa).
In recent years, growing demand from China has driven the depletion of many fish species in Lake Victoria, causing ecological consequences and affecting the lives of indigenous people.
The rapid increase in demand has led to illegal exploitation of both juvenile and juvenile fish, causing the fish population in Lake Victoria to decline rapidly and rob people of their livelihoods. As fish stocks become increasingly scarce, fishermen are increasingly turning to illegal fishing, harvesting fish weighing 1kg or less. The capture of juvenile fish threatens the sustainability of Lake Victoria’s fish species.
The demand for fish swim bladders has led to a focus on harvesting the organs. After the swim bladders are removed, tons of dead fish are dumped indiscriminately into lakes, causing serious environmental pollution and destroying the habitat of other species.
Notably, although the profits from the fish maw trade are considerable, most of the money does not go to the local people. A 2020 study of the fish maw trade found that locals mainly harvest and sell the raw product to foreign middlemen (mostly from China and India). After being sold to the middlemen, the fish maws are supplied to processing plants owned by Chinese traders.
So in 2020, Uganda signed a formal memorandum of understanding with China in this area, creating a tightly controlled fish maw industry that will benefit Ugandans. Ugandan officials warn that the agreement means fish maw processors will have to meet stricter standards, especially in terms of fishery conservation and environmental protection.
(According to Fishsite)
Source







![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs conference on anti-smuggling, trade fraud, and counterfeit goods](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/14/6cd67667e99e4248b7d4f587fd21e37c)



























































































Comment (0)