Vaccines and specific treatments for diphtheria are available. However, since the disease has not yet been eradicated in Vietnam, vaccination remains the most important and effective preventive measure.
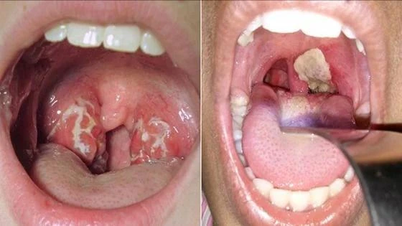
Diphtheria is an acute infectious and toxic disease caused by the diphtheria bacterium. It commonly affects young children, but adults can also contract it if they lack immunity. The diphtheria bacteria produce toxins that damage the upper respiratory tract and can spread throughout the body, leading to serious complications.
 |
| Illustrative image. |
Currently, vaccines and specific treatments for diphtheria are available. However, since the disease has not yet been eradicated in Vietnam, vaccination remains the most important and effective preventive measure.
Diphtheria vaccination has been included in the Expanded Immunization Program since 1985. Currently, the diphtheria-containing vaccine is administered in the program in three doses to provide basic immunity for children under 1 year old and one booster dose when children are 18-24 months old.
To date, based on the recommendations of the World Health Organization and international trends, the Ministry of Health has issued Circular No. 10/2024/TT-BYT, which adds an extra dose of diphtheria-containing vaccine for 7-year-old children.
Currently, Vietnam administers a 5-dose diphtheria-containing vaccine to children from 2 months of age. This vaccination schedule is entirely consistent with WHO recommendations for long-lasting immunity, as well as national vaccination schedules worldwide , ensuring the necessary basic level of immunity for children in Vietnam at important ages.
According to the WHO, supplemental vaccine doses should be based on the specific epidemiological situation of each country and an assessment of the risk of contracting the disease. In Vietnam, the incidence of diphtheria is currently low, and the healthcare system is able to control cases.
To proactively prevent diphtheria, the Department of Preventive Medicine recommends that people take their children for vaccination according to the schedule of vaccines containing diphtheria components (DPT-VGB-Hib, DPT, etc.) to ensure immunity against the disease for children in the eligible age group. In case of postponement, take children for vaccination as soon as possible.
People in areas with outbreaks must strictly adhere to taking preventive medication and receiving vaccinations as directed and recommended by health authorities. In case of close contact, they should monitor their health and immediately notify health officials if they experience any suspected symptoms.
People should not panic, receive false information from unofficial mass media, and should not arbitrarily vaccinate with vaccines containing diphtheria without specific instructions and recommendations from health authorities in epidemic areas and according to the instructions of each type of vaccine containing diphtheria.
If necessary, contact the nearest health facilities for advice on preventive measures, ensuring that vaccinations are administered to the correct individuals, at the correct doses, and at the correct times, as well as safely and effectively preventing disease.
Source: https://baodautu.vn/bo-y-te-thong-tin-ve-tiem-chung-vac-xin-phong-benh-bach-hau-d219774.html
















































































































Comment (0)