Untreated strep throat can cause complications such as tonsil abscess, rheumatic fever, autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders...
Strep throat is caused by the bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes. Doctors usually prescribe antibiotics to treat it. In some cases, the disease can cause the following complications:
Tonsillar abscess
A tonsil abscess is an infection (pus, mucus, or fluid) that forms in the area around the tonsils. This condition is more common in children and teenagers than in older adults.
Glomerulonephritis
A form of kidney disease that can develop one to two weeks after an untreated throat infection occurs when small blood vessels in the kidneys become inflamed and is most common in children aged 6 to 10 years.
Erythema
This is not a complication of strep throat, but a form of streptococcal infection that can develop along with throat symptoms. It is characterized by fever and a red rash that first appears on the neck and chest and then spreads to the rest of the body. The rash has a rough, sandpaper-like texture.
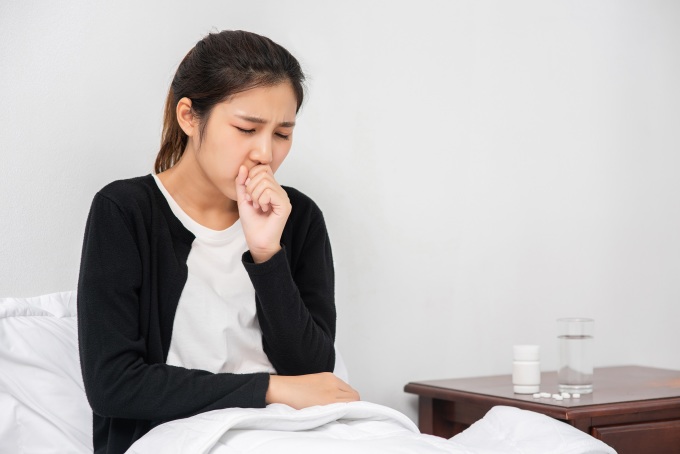

Strep throat is usually treated with antibiotics. Photo: Freepik
Rheumatic fever
This complication can develop 14-28 days after a throat infection. If strep throat is treated within the first 9 days of symptoms, the risk of rheumatic fever is low. Rheumatic fever can cause fever, nosebleeds, abdominal pain, and heart problems. This complication can also cause painful swelling in the knees, ankles, elbows, or wrists, sometimes leading to abnormal body movements.
Autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders
Childhood autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcal infection. These include obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) or tic disorders (uncontrollable, repetitive muscle movements) that first appear or suddenly worsen soon after a streptococcal infection.
Sinus and ear infections
Strep throat viruses can cause sinus and ear infections.
To prevent streptococcal infections, people need to wash their hands frequently, throw away tissues after use, not share items (towels, drinking cups, toothbrushes, etc.), and cover their mouths when coughing or sneezing.
Avoid direct contact with people who have strep throat. Patients should take the full dose of antibiotics as prescribed by their doctor to avoid relapse and to avoid infecting others during treatment.
Mai Cat (According to Everyday Health )
Source link


![[Photo] Urgently help people soon have a place to live and stabilize their lives](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F09%2F1765248230297_c-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)








































































![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam works with the Standing Committees of the 14th Party Congress Subcommittees](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/09/1765265023554_image.jpeg)


































Comment (0)